|
Myofibroblastoid
A myofibroblast is a cell phenotype that was first described as being in a state between a fibroblast and a smooth muscle cell. Structure Myofibroblasts are contractile web-like fusiform cells that are identifiable by their expression of α-smooth muscle actin within their cytoplasmic stress fibers. In the gastrointestinal and genitourinary tracts, myofibroblasts are found subepithelially in mucosal surfaces. Here they not only act as a regulator of the shape of the crypts and villi, but also act as stem-niche cells in the intestinal crypts and as parts of atypical antigen-presenting cells. They have both support as well as paracrine function in most places. Location Myofibroblasts were first identified in granulation tissue during skin wound healing. Typically, these cells are found in granulation tissue, scar tissue (fibrosis) and the stroma of tumours. They also line the gastrointestinal tract, wherein they regulate the shapes of crypts and villi. Markers Myofibroblasts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The species is now one of the widest-ranging mammals in the world, as well as the most widespread suiform. It has been assessed as least concern on the IUCN Red List due to its wide range, high numbers, and adaptability to a diversity of habitats. It has become an invasive species in part of its introduced range. Wild boars probably originated in Southeast Asia during the Early Pleistocene and outcompeted other suid species as they spread throughout the Old World. , up to 16 subspecies are recognized, which are divided into four regional groupings based on skull height and lacrimal bone length. The species lives in matriarchal societies consisting of interrelated females and their young (both male and female). Fully grown males are usually solitary outsid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scaffold Protein
In biology, scaffold proteins are crucial regulators of many key signalling pathways. Although scaffolds are not strictly defined in function, they are known to interact and/or bind with multiple members of a signalling pathway, tethering them into complexes. In such pathways, they regulate signal transduction and help localize pathway components (organized in complexes) to specific areas of the cell such as the plasma membrane, the cytoplasm, the nucleus, the Golgi, endosomes, and the mitochondria. History The first signaling scaffold protein discovered was the Ste5 protein from the yeast ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae''. Three distinct domains of Ste5 were shown to associate with the protein kinases Ste11, Ste7, and Fus3 to form a multikinase complex. Function Scaffold proteins act in at least four ways: tethering signaling components, localizing these components to specific areas of the cell, regulating signal transduction by coordinating positive and negative feedback s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancreatic Stellate Cells
Pancreatic stellate cells (PaSCs) are classified as myofibroblast-like cells that are located in exocrine regions of the pancreas. PaSCs are mediated by paracrine and autocrine stimuli and share similarities with the hepatic stellate cell. Pancreatic stellate cell activation and expression of matrix molecules constitute the complex process that induces pancreatic fibrosis. Synthesis, deposition, maturation and remodelling of the fibrous connective tissue can be protective, however when persistent it impedes regular pancreatic function. Structure PaSCs are located within the peri-acinar spaces of the pancreas and extrude long cytoplasmic processes that surround the base of the acinus. PaSCs compose 4% of the total cell mass in the gland Stellate cells derive their name from their star shape and are located in other organs such as the kidney and lungs. The cells are located in periductal and perivascular regions of the pancreas and contain vitamin A lipid droplets in their cytoplasm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatic Stellate Cell
Hepatic stellate cells (HSC), also known as perisinusoidal cells or Ito cells (earlier ''lipocytes'' or ''fat-storing cells''), are pericytes found in the perisinusoidal space of the liver, also known as the space of Disse (a small area between the sinusoids and hepatocytes). The stellate cell is the major cell type involved in liver fibrosis, which is the formation of scar tissue in response to liver damage. Structure Hepatic stellate cells can be selectively stained with gold chloride, but their distinguishing feature in routine histological preparations is the presence of multiple lipid droplets in their cytoplasm. Cytoglobin expression has been shown to be a specific marker with which hepatic stellate cells can be distinguished from portal myofibroblasts in the damaged human liver. In murine (rats, mice) liver, reelin expressed by Ito cells has been shown to be a reliable marker in discerning them from other myofibroblasts. The expression of reelin is increased after liver inju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellular Differentiation
Cellular differentiation is the process in which a stem cell alters from one type to a differentiated one. Usually, the cell changes to a more specialized type. Differentiation happens multiple times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Although metabolic composition does get altered quite dramaticall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are often known as muscle fibers. The muscle tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles under the control of the somatic nervous system. The other types of muscle are cardiac muscle which is also striated and smooth muscle which is non-striated; both of these types of muscle tissue are classified as involuntary, or, under the control of the autonomic nervous system. A skeletal muscle contains multiple fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber, and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the fusion of developmental myoblasts in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein
Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) is a protein that is encoded by the ''GFAP'' gene in humans. It is a type III intermediate filament (IF) protein that is expressed by numerous cell types of the central nervous system (CNS), including astrocytes and ependymal cells during development. GFAP has also been found to be expressed in glomeruli and peritubular fibroblasts taken from rat kidneys, Leydig cells of the testis in both hamsters and humans, human keratinocytes, human osteocytes and chondrocytes and stellate cells of the pancreas and liver in rats. GFAP is closely related to the other three non-epithelial type III IF family members, vimentin, desmin and peripherin, which are all involved in the structure and function of the cell’s cytoskeleton. GFAP is thought to help to maintain astrocyte mechanical strength as well as the shape of cells, but its exact function remains poorly understood, despite the number of studies using it as a cell marker. The protein was named and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collagen, Type I, Alpha 2
Collagen alpha-2(I) chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''COL1A2'' gene. This gene encodes one of the chains for type I collagen, the fibrillar collagen found in most connective tissues. Mutations in this gene are associated with osteogenesis imperfecta, Cardiac-valvular, and Arthrochlasia type Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, idiopathic osteoporosis, and atypical Marfan syndrome. Symptoms associated with mutations in this gene, however, tend to be less severe than mutations in the gene for alpha-1 type I collagen since alpha-2 is less abundant. Multiple messages for this gene result from multiple polyadenylation signals, a feature shared by most of the other collagen genes. See also * Type-I collagen Type I collagen is the most abundant collagen of the human body. It forms large, eosinophilic fibers known as collagen fibers. It is present in scar tissue, the end product when tissue heals by repair, as well as tendons, ligaments, the endomys ... * Collagen Reference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collagen, Type I, Alpha 1
Collagen, type I, alpha 1, also known as alpha-1 type I collagen, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the gene. ''COL1A1'' encodes the major component of type I collagen, the fibrillar collagen found in most connective tissues, including cartilage. Function Collagen is a protein that strengthens and supports many tissues in the body, including cartilage, bone, tendon, skin and the white part of the eye (sclera). The gene produces a component of type I collagen, called the pro-alpha1(I) chain. This chain combines with another pro-alpha1(I) chain and also with a pro-alpha2(I) chain (produced by the gene) to make a molecule of type I procollagen. These triple-stranded, rope-like procollagen molecules must be processed by enzymes outside the cell. Once these molecules are processed, they arrange themselves into long, thin fibrils that cross-link to one another in the spaces around cells. The cross-links result in the formation of very strong mature type I collagen fibers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyaluronic Acid
Hyaluronic acid (; abbreviated HA; conjugate base hyaluronate), also called hyaluronan, is an anionic, nonsulfated glycosaminoglycan distributed widely throughout connective, epithelial, and neural tissues. It is unique among glycosaminoglycans as it is non-sulfated, forms in the plasma membrane instead of the Golgi apparatus, and can be very large: human synovial HA averages about 7 million Da per molecule, or about 20,000 disaccharide monomers, while other sources mention 3–4 million Da. The average 70 kg (150 lb) person has roughly 15 grams of hyaluronan in the body, one-third of which is turned over (i.e., degraded and synthesized) per day. As one of the chief components of the extracellular matrix, it contributes significantly to cell proliferation and migration, and is involved in the progression of many malignant tumors. Hyaluronic acid is also a component of the group A streptococcal extracellular capsule, and is believed to play a role in virule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whole-body protein content. Collagen consists of amino acids bound together to form a triple helix of elongated fibril known as a collagen helix. It is mostly found in connective tissue such as cartilage, bones, tendons, ligaments, and skin. Depending upon the degree of mineralization, collagen tissues may be rigid (bone) or compliant (tendon) or have a gradient from rigid to compliant (cartilage). Collagen is also abundant in corneas, blood vessels, the gut, intervertebral discs, and the dentin in teeth. In muscle tissue, it serves as a major component of the endomysium. Collagen constitutes one to two percent of muscle tissue and accounts for 6% of the weight of the skeletal muscle tissue. The fibroblast is the most common cell that crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
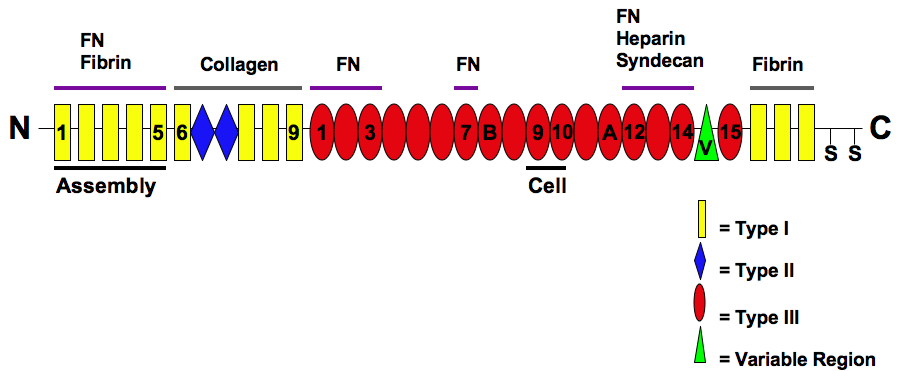
Fibronectin
Fibronectin is a high- molecular weight (~500-~600 kDa) glycoprotein of the extracellular matrix that binds to membrane-spanning receptor proteins called integrins. Fibronectin also binds to other extracellular matrix proteins such as collagen, fibrin, and heparan sulfate proteoglycans (e.g. syndecans). Fibronectin exists as a protein dimer, consisting of two nearly identical monomers linked by a pair of disulfide bonds. The fibronectin protein is produced from a single gene, but alternative splicing of its pre-mRNA leads to the creation of several isoforms. Two types of fibronectin are present in vertebrates: * soluble plasma fibronectin (formerly called "cold-insoluble globulin", or CIg) is a major protein component of blood plasma (300 μg/ml) and is produced in the liver by hepatocytes. * insoluble cellular fibronectin is a major component of the extracellular matrix. It is secreted by various cells, primarily fibroblasts, as a soluble protein dimer and is then ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |