|
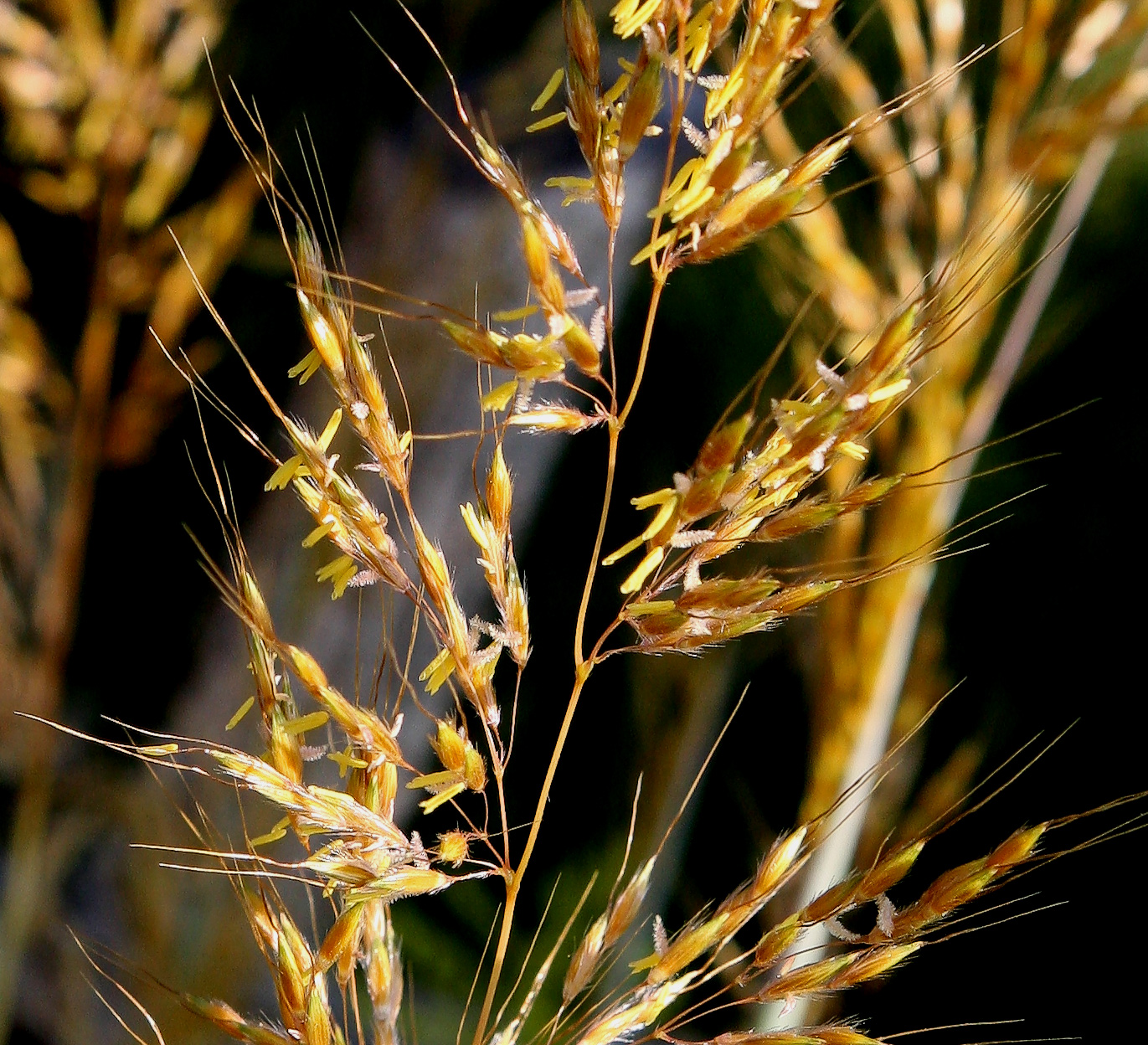
Muttongrass
''Poa fendleriana'' is a species of grass known by the common name muttongrass. It is native to western North America, where its distribution extends from western Canada to northern Mexico.''Poa fendleriana''. Grass Manual Treatment.Howard, Janet L. 1997 In: Fire Effects Information System, nline U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory. Description This species is a perennial grass with small |
Temperate Coniferous Forest
Temperate coniferous forest is a terrestrial biome defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature. Temperate coniferous forests are found predominantly in areas with warm summers and cool winters, and vary in their kinds of plant life. In some, needleleaf trees dominate, while others are home primarily to broadleaf evergreen trees or a mix of both tree types. A separate habitat type, the tropical coniferous forests, occurs in more tropical climates. Temperate coniferous forests are common in the coastal areas of regions that have mild winters and heavy rainfall, or inland in drier climates or montane areas. Many species of trees inhabit these forests including pine, cedar, fir, and redwood. The understory also contains a wide variety of herbaceous and shrub species. Temperate coniferous forests sustain the highest levels of biomass in any terrestrial ecosystem and are notable for trees of massive proportions in temperate rainforest regions. Structurally, these forests are rather si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grasses Of Mexico
Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns and pasture. The latter are commonly referred to collectively as grass. With around 780 genera and around 12,000 species, the Poaceae is the fifth-largest plant family, following the Asteraceae, Orchidaceae, Fabaceae and Rubiaceae. The Poaceae are the most economically important plant family, providing staple foods from domesticated cereal crops such as maize, wheat, rice, barley, and millet as well as feed for meat-producing animals. They provide, through direct human consumption, just over one-half (51%) of all dietary energy; rice provides 20%, wheat supplies 20%, maize (corn) 5.5%, and other grains 6%. Some members of the Poaceae are used as building materials (bamboo, thatch, and straw); others can provide a source of biofuel, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grasses Of Canada
Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns and pasture. The latter are commonly referred to collectively as grass. With around 780 genera and around 12,000 species, the Poaceae is the fifth-largest plant family, following the Asteraceae, Orchidaceae, Fabaceae and Rubiaceae. The Poaceae are the most economically important plant family, providing staple foods from domesticated cereal crops such as maize, wheat, rice, barley, and millet as well as feed for meat-producing animals. They provide, through direct human consumption, just over one-half (51%) of all dietary energy; rice provides 20%, wheat supplies 20%, maize (corn) 5.5%, and other grains 6%. Some members of the Poaceae are used as building materials (bamboo, thatch, and straw); others can provide a source of biofuel, primar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grasses Of The United States
Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns and pasture. The latter are commonly referred to collectively as grass. With around 780 genera and around 12,000 species, the Poaceae is the fifth-largest plant family, following the Asteraceae, Orchidaceae, Fabaceae and Rubiaceae. The Poaceae are the most economically important plant family, providing staple foods from domesticated cereal crops such as maize, wheat, rice, barley, and millet as well as feed for meat-producing animals. They provide, through direct human consumption, just over one-half (51%) of all dietary energy; rice provides 20%, wheat supplies 20%, maize (corn) 5.5%, and other grains 6%. Some members of the Poaceae are used as building materials (bamboo, thatch, and straw); others can provide a source of biofuel, primar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distinct from weathering which involves no movement. Removal of rock or soil as clastic sediment is referred to as ''physical'' or ''mechanical'' erosion; this contrasts with ''chemical'' erosion, where soil or rock material is removed from an area by dissolution. Eroded sediment or solutes may be transported just a few millimetres, or for thousands of kilometres. Agents of erosion include rainfall; bedrock wear in rivers; coastal erosion by the sea and waves; glacial plucking, abrasion, and scour; areal flooding; wind abrasion; groundwater processes; and mass movement processes in steep landscapes like landslides and debris flows. The rates at which such processes act control how fast a surface is eroded. Typically, physical erosion procee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
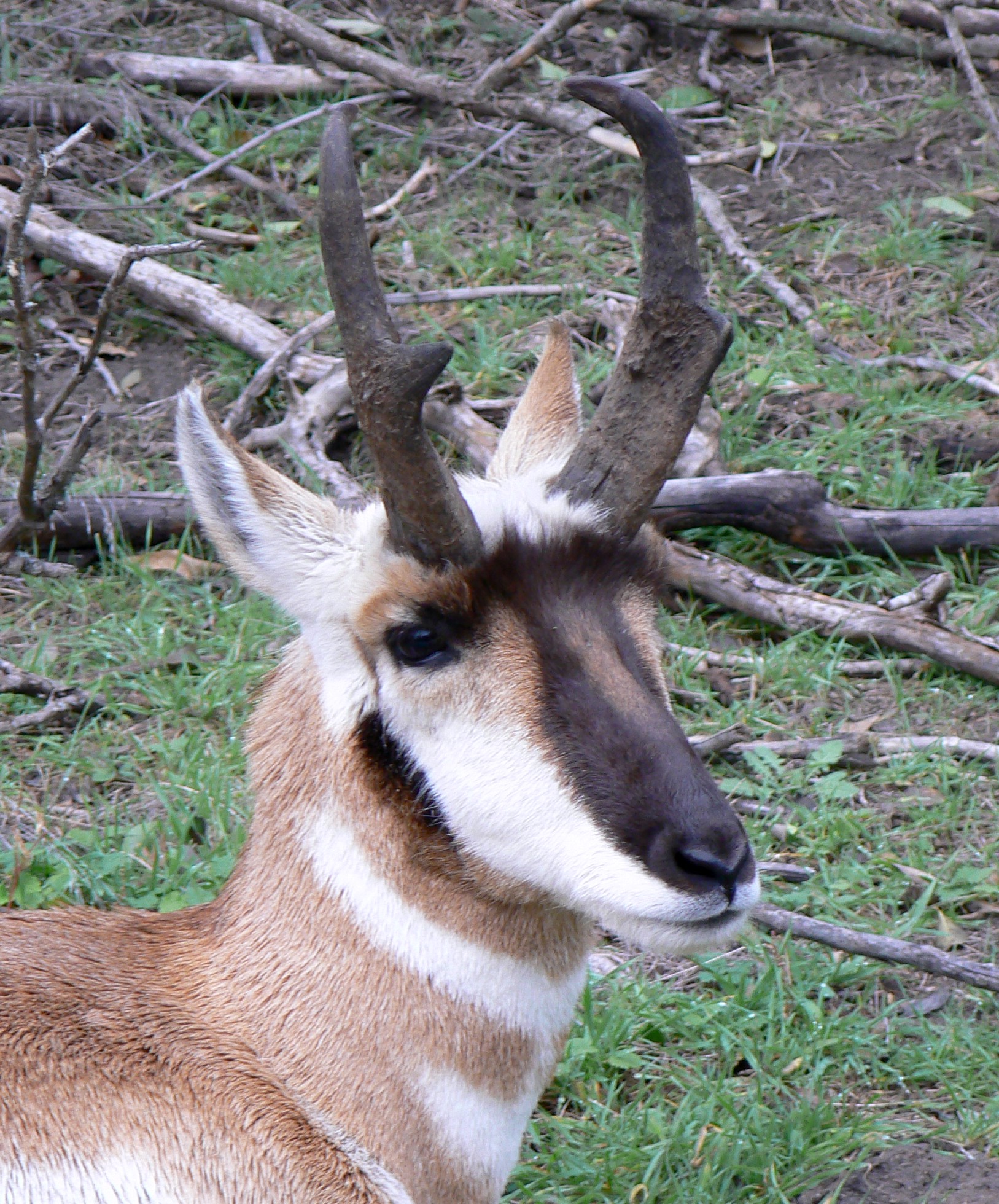
Pronghorn
The pronghorn (, ) (''Antilocapra americana'') is a species of artiodactyl (even-toed, hoofed) mammal indigenous to interior western and central North America. Though not an antelope, it is known colloquially in North America as the American antelope, prong buck, pronghorn antelope and prairie antelope, because it closely resembles the antelopes of the Old World and fills a similar ecological niche due to parallel evolution. It is the only surviving member of the family Antilocapridae. During the Pleistocene epoch, about 11 other antilocaprid species existed in North America.Smithsonian Institution. North American MammalsPronghorn ''Antilocapra americana''/ref> Three other genera (''Capromeryx'', '' Stockoceros'' and ''Tetrameryx'') existed when humans entered North America but are now extinct. As a member of the superfamily Giraffoidea, the pronghorn's closest living relatives are the giraffe and okapi. See Fig. S10 in Supplementary Information. The Giraffoidea are in tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominance (ecology)
Ecological dominance is the degree to which one or several species have a major influence controlling the other species in their ecological community (because of their large size, population, productivity, or related factors) or make up more of the biomass. Most ecological communities are defined by their dominant species. *In many examples of wet woodland in western Europe, the dominant tree is alder ('' Alnus glutinosa''). *In temperate bogs, the dominant vegetation is usually species of ''Sphagnum'' moss. *Tidal swamps in the tropics are usually dominated by species of mangrove (''Rhizophoraceae'') *Some sea floor communities are dominated by brittle stars. *Exposed rocky shorelines are dominated by sessile organisms such as barnacles and limpets. See also * National Vegetation Classification, a system for classifying British British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Vasey (botanist)
George Vasey (February 28, 1822 – March 3, 1893) was an English-born American botanist who collected a lot in Illinois before integrating the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), where he became Chief Botanist and curator of the greatly expanded National Herbarium. Biography George Vasey was born in 1822 near Scarborough, England, the fourth of ten children. His family emigrated to the United States the next year, and they established in Oriskany, New York. He left school at 12 to take a job as a store clerk. He took interest in botany after borrowing and, since he could not afford the volume, manually copying a book on the subject. This interest was later encouraged after a chance encounter with Peter D. Knieskern, another naturalist who allowed Vasey to begin writing to various other botanists. Until 1870 he would maintain an extensive correspondence and collect a great many specimens both in Oneida County and later McHenry County, but did not publish material of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sagebrush
Sagebrush is the common name of several woody and herbaceous species of plants in the genus ''Artemisia''. The best known sagebrush is the shrub ''Artemisia tridentata''. Sagebrushes are native to the North American west. Following is an alphabetical list of common names for various species of the genus ''Artemisia'', along with their corresponding scientific name. Many of these species are known by more than one common name, and some common names represent more than one species. * Alpine sagebrush—' * African sagebrush—''Artemisia afra'' * Basin sagebrush—''Artemisia tridentata'' * Big sagebrush—see Basin sagebrush * Bigelow sagebrush—''Artemisia bigelovii'' * Birdfoot sagebrush—'' Artemisia pedatifida'' * Black sagebrush—''Artemisia nova'' * Blue sagebrush—see Basin sagebrush * Boreal sagebrush—'' Artemisia norvegica'' * Budsage—''Artemisia spinescens'' * California sagebrush—''Artemisia californica'' * Carruth's sagebrush—'' Artemisia carruthii'' * C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elevation
The elevation of a geographic location is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface (see Geodetic datum § Vertical datum). The term ''elevation'' is mainly used when referring to points on the Earth's surface, while ''altitude'' or ''geopotential height'' is used for points above the surface, such as an aircraft in flight or a spacecraft in orbit, and '' depth'' is used for points below the surface. Elevation is not to be confused with the distance from the center of the Earth. Due to the equatorial bulge, the summits of Mount Everest and Chimborazo have, respectively, the largest elevation and the largest geocentric distance. Aviation In aviation the term elevation or aerodrome elevation is defined by the ICAO as the highest point of the landing area. It is often measured in feet and can be found in approach charts of the aerodrome. It is n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |