|
Motor Speech Disorder
Motor speech disorders are a class of speech disorders that disturb the body's natural ability to speak due to neurologic impairments. These neurologic impairments make it difficult for individuals with motor speech disorders to plan, program, control, coordinate, and execute speech productions.Duffy, J. R. (2013). Motor speech disorders (3rd ed.)St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Mosby. Disturbances to the individual's natural ability to speak vary in their etiology based on the integrity and integration of cognitive, neuromuscular, and musculoskeletal activities. Speaking is an act dependent on thought and timed execution of airflow and oral motor / oral placement of the lips, tongue, and jaw that can be disrupted by weakness in oral musculature (dysarthria) or an inability to execute the motor movements needed for specific speech sound production (apraxia of speech or developmental verbal dyspraxia). Such deficits can be related to pathology of the nervous system (central and /or peripher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speech Disorders
Speech disorders or speech impairments are a type of communication disorder in which normal speech is disrupted. This can mean stuttering, lisps, etc. Someone who is unable to speak due to a speech disorder is considered mute. Speech skills are vital to social relationships and learning, and delays or disorders that relate to developing these skills can impact individuals function. For many children and adolescents, this can present as issues with academics. Speech disorders affect roughly 11.5% of the US population, and 5% of the primary school population. Speech is a complex process that requires precise timing, nerve and muscle control, and as a result is susceptible to impairments. A person who has a stroke, an accident or birth defect may have speech and language problems. Classification Classifying speech into normal and disordered is more problematic than it first seems. By strict classification, only 5% to 10% of the population has a completely normal manner of spea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respiration (physiology)
In physiology, respiration is the movement of oxygen from the outside environment to the cells within tissues, and the removal of carbon dioxide in the opposite direction that's to the environment. The physiological definition of respiration differs from the biochemical definition, which refers to a metabolic process by which an organism obtains energy (in the form of ATP and NADPH) by oxidizing nutrients and releasing waste products. Although physiologic respiration is necessary to sustain cellular respiration and thus life in animals, the processes are distinct: cellular respiration takes place in individual cells of the organism, while physiologic respiration concerns the diffusion and transport of metabolites between the organism and the external environment. Gas exchanges in the lung occurs by ventilation and perfusion. Ventilation refers to the in and out movement of air of the lungs and perfusion is the circulation of blood in the pulmonary capillaries. In mammals, physi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurological Disorders
A neurological disorder is any disorder of the nervous system. Structural, biochemical or electrical abnormalities in the brain, spinal cord or other nerves can result in a range of symptoms. Examples of symptoms include paralysis, muscle weakness, poor coordination, loss of sensation, seizures, confusion, pain and altered levels of consciousness. There are many recognized neurological disorders, some relatively common, but many rare. They may be assessed by neurological examination, and studied and treated within the specialities of neurology and clinical neuropsychology. Interventions foneurological disordersinclude preventive measures, lifestyle changes, physiotherapy or other therapy, neurorehabilitation, pain management, medication, operations performed by neurosurgeons or a specific diet. The World Health Organization estimated in 2006 that neurological disorders and their sequelae (direct consequences) affect as many as one billion people worldwide, and identified hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KE Family
The KE family is a medical name designated for a British family, about half of whom exhibit a severe speech disorder called developmental verbal dyspraxia. It is the first family with speech disorder to be investigated using genetic analyses, by which the speech impairment is discovered to be due to genetic mutation, and from which the gene ''FOXP2'', often dubbed the "language gene", was discovered. Their condition is also the first human speech and language disorder known to exhibit strict Mendelian inheritance. Brought to medical attention from their school children in the late 1980s, the case of KE family was taken up at the UCL Institute of Child Health in London in 1990. Initial report suggested that the family was affected by a genetic disorder. Canadian linguist Myrna Gopnik suggested that the disorder was characterized primarily by grammatical deficiency, supporting the controversial notion of a "grammar gene". Geneticists at the University of Oxford determined that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FOXP2
Forkhead box protein P2 (FOXP2) is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''FOXP2'' gene. FOXP2 is a member of the forkhead box family of transcription factors, proteins that regulate gene expression by binding to DNA. It is expressed in the brain, heart, lungs and digestive system. ''FOXP2'' is found in many vertebrates, where it plays an important role in mimicry in birds (such as birdsong) and echolocation in bats. ''FOXP2'' is also required for the proper development of speech and language in humans. In humans, mutations in ''FOXP2'' cause the severe speech and language disorder developmental verbal dyspraxia. Studies of the gene in mice and songbirds indicate that it is necessary for vocal imitation and the related motor learning. Outside the brain, ''FOXP2'' has also been implicated in development of other tissues such as the lung and digestive system. Initially identified in 1998 as the genetic cause of a speech disorder in a British family designated the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosody (linguistics)
In linguistics, prosody () is concerned with elements of speech that are not individual phonetic segment (linguistics), segments (vowels and consonants) but are properties of syllables and larger units of speech, including linguistic functions such as intonation (linguistics), intonation, stress (linguistics), stress, and Rhythm (linguistics), rhythm. Such elements are known as suprasegmentals. Prosody may reflect features of the speaker or the utterance: their emotional state; the form of utterance (statement, question, or command); the presence of irony or sarcasm; emphasis, Contrast (linguistics), contrast, and focus (linguistics), focus. It may reflect elements of language not encoded by grammar or choice of vocabulary. Attributes of prosody In the study of prosodic aspects of speech, it is usual to distinguish between Auditory phonetics, auditory measures (Subjectivity, subjective impressions produced in the mind of the listener) and objective measures (physical properties o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manner Of Articulation
In articulatory phonetics, the manner of articulation is the configuration and interaction of the articulators ( speech organs such as the tongue, lips, and palate) when making a speech sound. One parameter of manner is ''stricture,'' that is, how closely the speech organs approach one another. Others include those involved in the r-like sounds ( taps and trills), and the sibilancy of fricatives. The concept of manner is mainly used in the discussion of consonants, although the movement of the articulators will also greatly alter the resonant properties of the vocal tract, thereby changing the formant structure of speech sounds that is crucial for the identification of vowels. For consonants, the place of articulation and the degree of phonation of voicing are considered separately from manner, as being independent parameters. Homorganic consonants, which have the same place of articulation, may have different manners of articulation. Often nasality and laterality are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resonance
Resonance describes the phenomenon of increased amplitude that occurs when the frequency of an applied periodic force (or a Fourier component of it) is equal or close to a natural frequency of the system on which it acts. When an oscillating force is applied at a resonant frequency of a dynamic system, the system will oscillate at a higher amplitude than when the same force is applied at other, non-resonant frequencies. Frequencies at which the response amplitude is a relative maximum are also known as resonant frequencies or resonance frequencies of the system. Small periodic forces that are near a resonant frequency of the system have the ability to produce large amplitude oscillations in the system due to the storage of vibrational energy. Resonance phenomena occur with all types of vibrations or waves: there is mechanical resonance, orbital resonance, acoustic resonance, electromagnetic resonance, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), electron spin resonance (ESR) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonation
The term phonation has slightly different meanings depending on the subfield of phonetics. Among some phoneticians, ''phonation'' is the process by which the vocal folds produce certain sounds through quasi-periodic vibration. This is the definition used among those who study laryngeal anatomy and physiology and speech production in general. Phoneticians in other subfields, such as linguistic phonetics, call this process '' voicing'', and use the term ''phonation'' to refer to any oscillatory state of any part of the larynx that modifies the airstream, of which voicing is just one example. Voiceless and supra-glottal phonations are included under this definition. Voicing The phonatory process, or voicing, occurs when air is expelled from the lungs through the glottis, creating a pressure drop across the larynx. When this drop becomes sufficiently large, the vocal folds start to oscillate. The minimum pressure drop required to achieve phonation is called the phonation thresh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
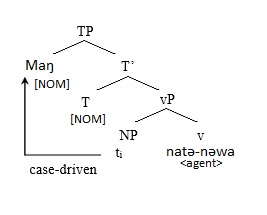
Volition (linguistics)
In linguistics, volition is a concept that distinguishes whether the subject, or agent of a particular sentence intended an action or not. Simply, it is the intentional or unintentional nature of an action.Tournadre, Nicolas. The Rhetorical Use of the Tibetan Ergative. 1991. Web. Volition concerns the idea of control and for the purposes outside of psychology and cognitive science, is considered the same as intention in linguistics. Volition can then be expressed in a given language using a variety of possible methods. These sentence forms usually indicate that a given action has been done intentionally, or willingly. There are various ways of marking volition cross-linguistically. When using verbs of volition in English, like "want" or "prefer", these verbs are not expressly marked.Hogeweg, Lotte, Helen de Hoop, Andrej Malchukov. Cross-linguistic Semantics of Tense, Aspect and Modality. Linguistics Today. 148 (2009). Print. Other languages handle this with affixes, while others ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speech
Speech is a human vocal communication using language. Each language uses phonetic combinations of vowel and consonant sounds that form the sound of its words (that is, all English words sound different from all French words, even if they are the same word, e.g., "role" or "hotel"), and using those words in their semantic character as words in the lexicon of a language according to the syntactic constraints that govern lexical words' function in a sentence. In speaking, speakers perform many different intentional speech acts, e.g., informing, declaring, asking, persuading, directing, and can use enunciation, intonation, degrees of loudness, tempo, and other non-representational or paralinguistic aspects of vocalization to convey meaning. In their speech, speakers also unintentionally communicate many aspects of their social position such as sex, age, place of origin (through accent), physical states (alertness and sleepiness, vigor or weakness, health or illness), psycholo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motor Planning
In psychology and neuroscience Neuroscience is the science, scientific study of the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system), its functions and disorders. It is a Multidisciplinary approach, multidisciplinary science that combines physiology, an ..., motor planning is a set of processes related to the preparation of a movement that occurs during the reaction time (the time between the presentation of a stimulus to a person and that person's initiation of a motor response). Colloquially, the term applies to any process involved in the preparation of a movement during the reaction time, including perception-related and action-related processes. For example, the identification of a task-relevant stimulus is captured by the usual meaning of the term, "motor planning", but this identification process is not strictly motor-related. Wong and colleagues (2015) have proposed a narrower definition to include only movement-related processes: "Specification of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)