|
Motillas
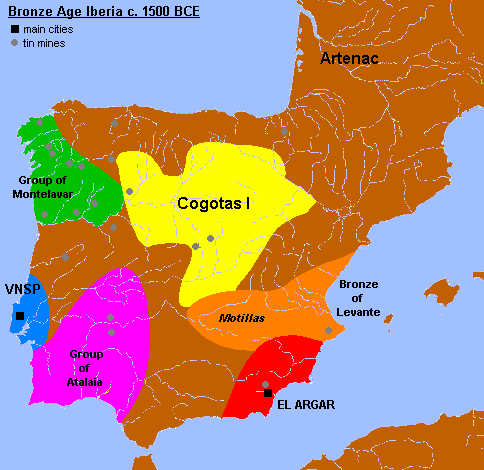
The ''motillas'' were the early settlements of La Mancha (Spain) belonging to the Middle Bronze Age, and connected to the Bronze of Levante culture. These were human-made hills atop of which are placed fortified settlements. Their height is usually between four and five meters and the ''motillas'' are separated from each other by a distance of four to five kilometers. Their construction started BCE and they were used for about 1000 years. History of research The ''motillas'' were first believed to be antique burial mounds. However, this hypothesis was ruled out when an excavation at the Motilla del Azuer that took place in the seventies proved their defensive and management faculties. This way, a wide area could be controlled easily. Some similar sites in the foothills of Sierra Morena mountains are fortified towns of larger size. Construction and use The ''motillas'' were constructed in the period of BCE–1200 BCE. Their use started at the time of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motilla Del Azuer
The Motilla del Azuer is a prehistoric fortification dating from the Bronze Age in the municipality of Daimiel, in the Province of Ciudad Real, Castilla–La Mancha, Spain. Extensive field work has been carried out since 1974 and was ongoing in 2021.T. Nájera, G. Aranda, M. Sánchez, M. Haro"Recent fieldwork at the Bronze Age fortified site of Motilla del Azuer (Daimiel, Spain)" Antiquity (journal), Antiquity 79 (December 2005) On 20 June 2013 the site was declared a "Bien de Interés Cultural" (asset of cultural interest) to archaeology."Acuerdo de aprobación, Motilla del Azuer, localizada en Daimiel (Ciudad Real)" in ''Diario Oficial de Castilla-La Mancha'' (Official Gazette of Castilla-La Mancha), Issue nº 127, 3 July 2013, declaring Motilla del Azuer to be a "Bien de Interés Cultural, con categoría de Zona Arqueológica" Context The artificial mounds known as motillas are the remains of one of the most unusual types of prehistoric settlement on the Iberian Peninsula. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motilla Del Azuer (29425303165)
The Motilla del Azuer is a prehistoric fortification dating from the Bronze Age in the municipality of Daimiel, in the Province of Ciudad Real, Castilla–La Mancha, Spain. Extensive field work has been carried out since 1974 and was ongoing in 2021.T. Nájera, G. Aranda, M. Sánchez, M. Haro"Recent fieldwork at the Bronze Age fortified site of Motilla del Azuer (Daimiel, Spain)" Antiquity 79 (December 2005) On 20 June 2013 the site was declared a " Bien de Interés Cultural" (asset of cultural interest) to archaeology."Acuerdo de aprobación, Motilla del Azuer, localizada en Daimiel (Ciudad Real)" in ''Diario Oficial de Castilla-La Mancha'' (Official Gazette of Castilla-La Mancha), Issue nº 127, 3 July 2013, declaring Motilla del Azuer to be a "Bien de Interés Cultural, con categoría de Zona Arqueológica" Context The artificial mounds known as motillas are the remains of one of the most unusual types of prehistoric settlement on the Iberian Peninsula. They are found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castilla–La Mancha
Castilla–La Mancha (, , ), or Castile La Mancha, is an autonomous community of Spain. Comprising the provinces of Albacete, Ciudad Real, Cuenca, Guadalajara and Toledo, it was created in 1982. The government headquarters are in Toledo, and its largest city is in Albacete. The region largely occupies the southern half of the Iberian Peninsula's Inner Plateau, including large parts of the catchment areas of the Tagus, the Guadiana and the Júcar, while the northeastern relief comprises the Sistema Ibérico mountain massif. It is bordered by Castile and León, Madrid, Aragon, Valencia, Murcia, Andalusia, and Extremadura. It is one of the most sparsely populated of Spain's regions. Albacete, Guadalajara, Toledo, Talavera de la Reina and Ciudad Real concentrate the largest urban areas in the region. Geography Castilla–La Mancha is located in the middle of the Iberian peninsula, occupying the greater part of the Submeseta Sur, the vast plain composing the southern par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iberia Bronze
The Iberian Peninsula (), ** * Aragonese language, Aragonese and Occitan language, Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica'' ** ** * french: Péninsule Ibérique * mwl, Península Eibérica * eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defining the westernmost edge of Eurasia. It is principally divided between Peninsular Spain, Spain and Continental Portugal, Portugal, comprising most of their territory, as well as a small area of Southern France, Andorra, and Gibraltar. With an area of approximately , and a population of roughly 53 million, it is the second largest European peninsula by area, after the Scandinavian Peninsula. Name Greek name The word ''Iberia'' is a noun adapted from the Latin word "Hiberia" originating in the Ancient Greek word Ἰβηρία ('), used by Greek geographers under the rule of the Roman Empire to refer to what is known today in English as the Iberian Peninsula. At that time, the name did not describe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Mancha
La Mancha () is a natural and historical region located in the Spanish provinces of Albacete, Cuenca, Ciudad Real, and Toledo. La Mancha is an arid but fertile plateau (610 m or 2000 ft) that stretches from the mountains of Toledo to the western spurs of the hills of Cuenca, and bordered to the south by the Sierra Morena and to the north by the Alcarria region. La Mancha historical comarca constitutes the southern portion of Castilla-La Mancha autonomous community and makes up most of the present-day administrative region. Name The name "La Mancha" is probably derived from the Arabic word المنشأ ''al-mansha'', meaning "birthplace" or "fountainhead". The name of the city of Almansa in Albacete shares that origin. The word ''mancha'' in Spanish literally means ''spot'', ''stain'', or ''patch'', but no apparent link exists between this word and the name of the region. Geography The largest plain in Spain, La Mancha is made up of a plateau averaging 500 to 600 metr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg , image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg , national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond") , national_anthem = (English: "Royal March") , image_map = , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Madrid , coordinates = , largest_city = Madrid , languages_type = Official language , languages = Spanish language, Spanish , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = , ethnic_groups_ref = , religion = , religion_ref = , religion_year = 2020 , demonym = , government_type = Unitary state, Unitary Parliamentary system, parliamentary constitutional monarchy , leader_title1 = Monarchy of Spain, Monarch , leader_name1 = Felipe VI , leader_title2 = Prime Minister of Spain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age Europe
The European Bronze Age is characterized by bronze artifacts and the use of bronze implements. The regional Bronze Age succeeds the Neolithic and Copper Age and is followed by the Iron Age. It starts with the Aegean Bronze Age in 3200 BC (succeeded by the Beaker culture), and spans the entire 2nd millennium BC (Unetice culture, Tumulus culture, Nordic Bronze Age, Terramare culture, Urnfield culture and Lusatian culture) in Northern Europe, lasting until c. 600 BC. History Aegean The Aegean Bronze Age begins around 3200 BC when civilizations first established a far-ranging trade network. This network imported tin and charcoal to Cyprus, where copper was mined and alloyed with the tin to produce bronze. Bronze objects were then exported far and wide and supported the trade. Isotopic analysis of the tin in some Mediterranean bronze objects indicates it came from as far away as Great Britain. Knowledge of navigation was well developed at this time and reached a peak of skill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Of Levante
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such as arsenic or silicon. These additions produce a range of alloys that may be harder than copper alone, or have other useful properties, such as ultimate tensile strength, strength, ductility, or machinability. The three-age system, archaeological period in which bronze was the hardest metal in widespread use is known as the Bronze Age. The beginning of the Bronze Age in western Eurasia and India is conventionally dated to the mid-4th millennium BCE (~3500 BCE), and to the early 2nd millennium BCE in China; elsewhere it gradually spread across regions. The Bronze Age was followed by the Iron Age starting from about 1300 BCE and reaching most of Eurasia by about 500 BCE, although bronze continued to be much more widely used than it is in mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sierra Morena
The Sierra Morena is one of the main systems of mountain ranges in Spain. It stretches for 450 kilometres from east to west across the south of the Iberian Peninsula, forming the southern border of the ''Meseta Central'' plateau and providing the watershed between the valleys of the Guadiana to the north and the west, and the Guadalquivir to the south. Its highest summit is 1,332 m high Bañuela. Other notable peaks are Corral de Borros 1,312 m and Cerro de la Estrella 1,298 m. The name ''Sierra Morena'' has a strong legendary reputation in Spanish culture and tradition, with myths about bandits ''(Los bandidos de Sierra Morena)'', a giant snake ''(El Saetón de Sierra Morena)'' and a child brought up by wolves (Marcos Rodríguez Pantoja), among others. This range is also mentioned in the famous Mexican song "Cielito Lindo" and in one of the most well known traditional Spanish songs, "Soy Minero", interpreted by Antonio Molina. Description The Sierra Morena stretches f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aridification
Aridification is the process of a region becoming increasingly arid, or dry. It refers to long term change, rather than seasonal variation. It is often measured as the reduction of average soil moisture content. It can be caused by reduced precipitation, increased evaporation, lowering of water tables, and changes in ground cover acting individually or in combination. Its major consequences include reduced agricultural production, soil degradation, ecosystem changes and decreased water catchment runoff. Some researchers have found that the Colorado River basin and other parts of western North America are currently undergoing aridification. See also * Arid * Arid Forest Research Institute * Desert * Global warming * Groundwater * Soil moisture * Water balance * Water content * Water cycle The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle, is a biogeochemical cycle that describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Argar
El Argar is an Early Bronze Age culture that was based in Antas, Almería, within modern Spain. It is believed to have been active from about 2200 B.C. to 1500 B.C.Lull et al."Emblems and spaces of power during the Argaric Bronze Age at La Almoloya, Murcia," ''Antiquity'', Cambridge University Press, 11 March 2021 The people developed sophisticated pottery and ceramic techniques that they traded with other Mediterranean tribes. The civilization of El Argar extended to all the province of Almería, north onto the central Meseta, to most of the region of Murcia and westward into the provinces of Granada and Jaen, controlling an area similar in size to modern Belgium. Its cultural and possibly political influence was much wider. Its influence has been found in eastern and southwestern Iberia (Algarve), and it likely affected other regions as well. Some authors have suggested that El Argar was a unified state. Material culture El Argar is the cultural center of the Early and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleohydrogeology
Historical geology or palaeogeology is a discipline that uses the principles and methods of geology to reconstruct the geological history of Earth. Historical geology examines the vastness of geologic time, measured in billions of years, and investigates changes in the Earth, gradual and sudden, over this deep time. It focuses on geological processes, such as plate tectonics, that have changed the Earth's surface and subsurface over time and the use of methods including stratigraphy, structural geology, paleontology, and sedimentology to tell the sequence of these events. It also focuses on the evolution of life during different time periods in the geologic time scale. Historical development During the 17th century, Nicolas Steno was the first to observe and propose a number of basic principles of historical geology, including three key stratigraphic principles: the law of superposition, the principle of original horizontality, and the principle of lateral continuity. 18th-century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)