|
Monoalphabetic Substitution Cipher
In cryptography, a substitution cipher is a method of encrypting in which units of plaintext are replaced with the ciphertext, in a defined manner, with the help of a key; the "units" may be single letters (the most common), pairs of letters, triplets of letters, mixtures of the above, and so forth. The receiver deciphers the text by performing the inverse substitution process to extract the original message. Substitution ciphers can be compared with transposition ciphers. In a transposition cipher, the units of the plaintext are rearranged in a different and usually quite complex order, but the units themselves are left unchanged. By contrast, in a substitution cipher, the units of the plaintext are retained in the same sequence in the ciphertext, but the units themselves are altered. There are a number of different types of substitution cipher. If the cipher operates on single letters, it is termed a simple substitution cipher; a cipher that operates on larger groups of letters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptography
Cryptography, or cryptology (from grc, , translit=kryptós "hidden, secret"; and ''graphein'', "to write", or ''-logia'', "study", respectively), is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of adversarial behavior. More generally, cryptography is about constructing and analyzing protocols that prevent third parties or the public from reading private messages. Modern cryptography exists at the intersection of the disciplines of mathematics, computer science, information security, electrical engineering, digital signal processing, physics, and others. Core concepts related to information security (data confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation) are also central to cryptography. Practical applications of cryptography include electronic commerce, chip-based payment cards, digital currencies, computer passwords, and military communications. Cryptography prior to the modern age was effectively synony ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency Distribution
In statistics, the frequency (or absolute frequency) of an event i is the number n_i of times the observation has occurred/recorded in an experiment or study. These frequencies are often depicted graphically or in tabular form. Types The cumulative frequency is the total of the absolute frequencies of all events at or below a certain point in an ordered list of events. The (or empirical probability) of an event is the absolute frequency normalized by the total number of events: : f_i = \frac = \frac. The values of f_i for all events i can be plotted to produce a frequency distribution. In the case when n_i = 0 for certain i, pseudocounts can be added. Depicting frequency distributions A frequency distribution shows us a summarized grouping of data divided into mutually exclusive classes and the number of occurrences in a class. It is a way of showing unorganized data notably to show results of an election, income of people for a certain region, sales of a product wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplomacy
Diplomacy comprises spoken or written communication by representatives of states (such as leaders and diplomats) intended to influence events in the international system.Ronald Peter Barston, ''Modern diplomacy'', Pearson Education, 2006, p. 1 Diplomacy is the main instrument of foreign policy which represents the broader goals and strategies that guide a state's interactions with the rest of the world. International treaties, agreements, alliances, and other manifestations of international relations are usually the result of diplomatic negotiations and processes. Diplomats may also help to shape a state by advising government officials. Modern diplomatic methods, practices, and principles originated largely from 17th-century European custom. Beginning in the early 20th century, diplomacy became professionalized; the 1961 Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations, ratified by most of the world's sovereign states, provides a framework for diplomatic procedures, methods, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis XIV Of France
, house = Bourbon , father = Louis XIII , mother = Anne of Austria , birth_date = , birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France , death_date = , death_place = Palace of Versailles, Versailles, France , burial_date = 9 September 1715 , burial_place = Basilica of Saint-Denis , religion = Catholicism ( Gallican Rite) , signature = Louis XIV Signature.svg Louis XIV (Louis Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 14 May 1643 until his death in 1715. His reign of 72 years and 110 days is the longest of any sovereign in history whose date is verifiable. Although Louis XIV's France was emblematic of the age of absolutism in Europe, the King surrounded himself with a variety of significant political, military, and cultural figures, such as Bossuet, Colbert, Le Brun, Le Nôtre, Lully, Mazarin, Molière, Racine, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
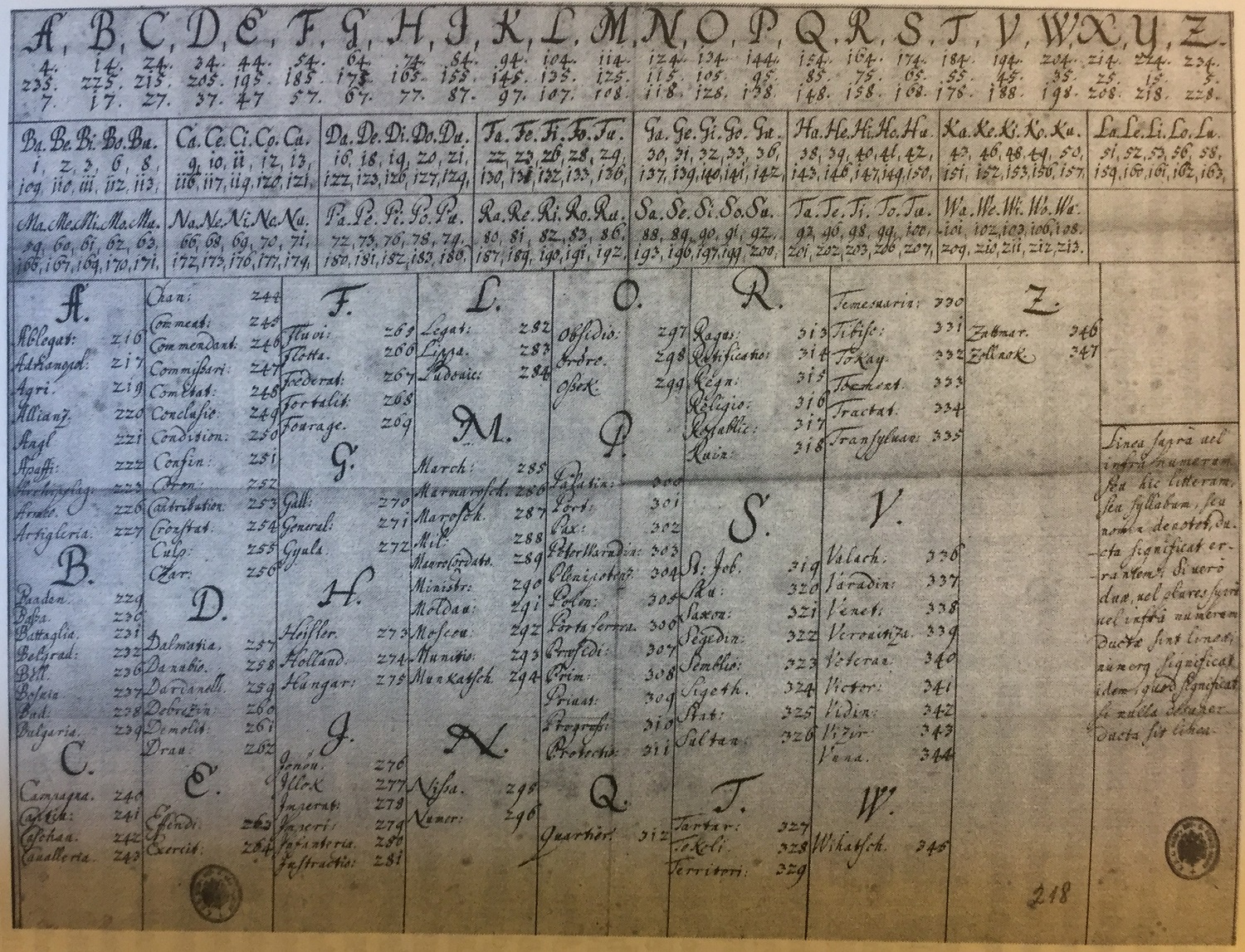
Great Cipher
The Great Cipher ( French: ''Grand chiffre'') was a nomenclator cipher developed by the Rossignols, several generations of whom served the French monarchs as cryptographers. The Great Cipher was so named because of its excellence and because it was reputed to be unbreakable. Modified forms were in use by the French Peninsular army until the summer of 1811. After it fell out of current use, many documents in the French archives were unreadable until it was decoded. Historical background Antoine Rossignol's cryptographic skills became known in 1626, when an encrypted letter was taken from a messenger leaving the city of Réalmont, controlled by the Huguenots and surrounded by the French army. The letter stated that the Huguenots would not be able to hold on to the city for much longer, and by the end of the day, Rossignol had successfully deciphered it. The French returned the letter with the deciphered message and forced the Huguenots to surrender. He and his son, Bonaventure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rossignols
The Rossignols, a family of French cryptographers and cryptanalysts, included Antoine Rossignol (1600–1682), Bonaventure Rossignol and Antoine-Bonaventure Rossignol. The family name means "nightingale" in French. As early as 1406, the word ''rossignol'' has served as the French term for "skeleton key" or for any tool which opens that which is locked. Antoine Rossignol In 1626, Henri II of Bourbon, Prince de Condé laid siege to the Huguenot city of Réalmont. The besiegers intercepted a coded letter leaving the city. Rossignol, then a 26-year-old mathematician, had a local reputation for his interest in cryptography. He quickly broke the Huguenot cipher, revealing a plea to their allies for ammunition to replenish the city's almost exhausted supplies. The next day, the besiegers presented the clear text of the message to the commander of Réalmont, along with a demand for surrender. The Huguenots surrendered immediately. This brought Rossignol to the attention of Louis X ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codeword
In communication, a code word is an element of a standardized code or protocol. Each code word is assembled in accordance with the specific rules of the code and assigned a unique meaning. Code words are typically used for reasons of reliability, clarity, brevity, or secrecy. See also * Code word (figure of speech) * Coded set * Commercial code (communications) * Compartmentalization (information security) * Duress code * Error correction and detection * Marine VHF radio * Password * Safeword * Spelling alphabet A spelling alphabet ( also called by various other names) is a set of words used to represent the letters of an alphabet in oral communication, especially over a two-way radio or telephone. The words chosen to represent the letters sound sufficie ... References * * *UNHCR Procedure for Radio Communication External links UNHCR Procedure for Radio Communication Data transmission Cryptography {{crypto-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Code (cryptography)
In cryptology, a code is a method used to encrypt a message that operates at the level of meaning; that is, words or phrases are converted into something else. A code might transform "change" into "CVGDK" or "cocktail lounge". The U.S. National Security Agency defined a code as "A substitution cryptosystem in which the plaintext elements are primarily words, phrases, or sentences, and the code equivalents (called "code groups") typically consist of letters or digits (or both) in otherwise meaningless combinations of identical length."A History of U.S. Communications Security; the David G. Boak Lectures National Security Agency (NSA), Volumes I, 1973, Volumes II 1981, partially released 2008, additional portions declassified October 14, 2015 A ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cipher
In cryptography, a cipher (or cypher) is an algorithm for performing encryption or decryption—a series of well-defined steps that can be followed as a procedure. An alternative, less common term is ''encipherment''. To encipher or encode is to convert information into cipher or code. In common parlance, "cipher" is synonymous with " code", as they are both a set of steps that encrypt a message; however, the concepts are distinct in cryptography, especially classical cryptography. Codes generally substitute different length strings of characters in the output, while ciphers generally substitute the same number of characters as are input. There are exceptions and some cipher systems may use slightly more, or fewer, characters when output versus the number that were input. Codes operated by substituting according to a large codebook which linked a random string of characters or numbers to a word or phrase. For example, "UQJHSE" could be the code for "Proceed to the follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babington Postscript
Babington may refer to: *Babington family *Babington (surname) * Babington, Somerset, England, a small village between Radstock and Frome * Babington House, an example of Georgian architecture in Somerset, England * Babington Academy, a school in Leicester, England * Babington's tea room, a traditional English tearoom in Rome *Babingtonite, mineral named after William Babington * Babington Path, a road in Hong Kong See also *Babington Plot The Babington Plot was a plan in 1586 to assassinate Queen Elizabeth I, a Protestant, and put Mary, Queen of Scots, her Catholic cousin, on the English throne. It led to Mary's execution, a result of a letter sent by Mary (who had been im ..., a 16th-century conspiracy in England * Babbington {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicity Distance
In cryptography, unicity distance is the length of an original ciphertext needed to break the cipher by reducing the number of possible spurious keys to zero in a brute force attack. That is, after trying every possible key, there should be just one decipherment that makes sense, i.e. expected amount of ciphertext needed to determine the key completely, assuming the underlying message has redundancy. Claude Shannon defined the unicity distance in his 1949 paper " Communication Theory of Secrecy Systems". Consider an attack on the ciphertext string "WNAIW" encrypted using a Vigenère cipher with a five letter key. Conceivably, this string could be deciphered into any other string—RIVER and WATER are both possibilities for certain keys. This is a general rule of cryptanalysis: with no additional information it is impossible to decode this message. Of course, even in this case, only a certain number of five letter keys will result in English words. Trying all possible keys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |