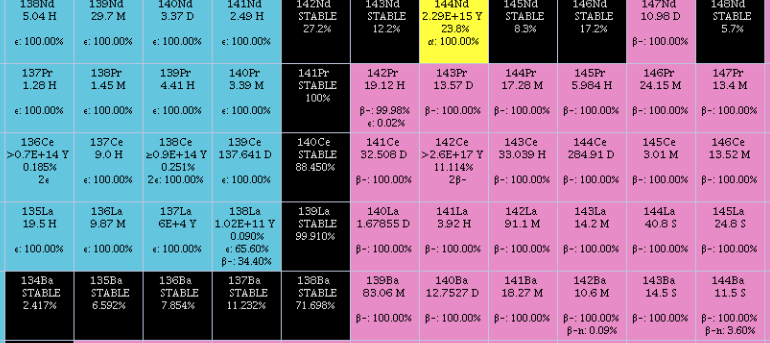
|
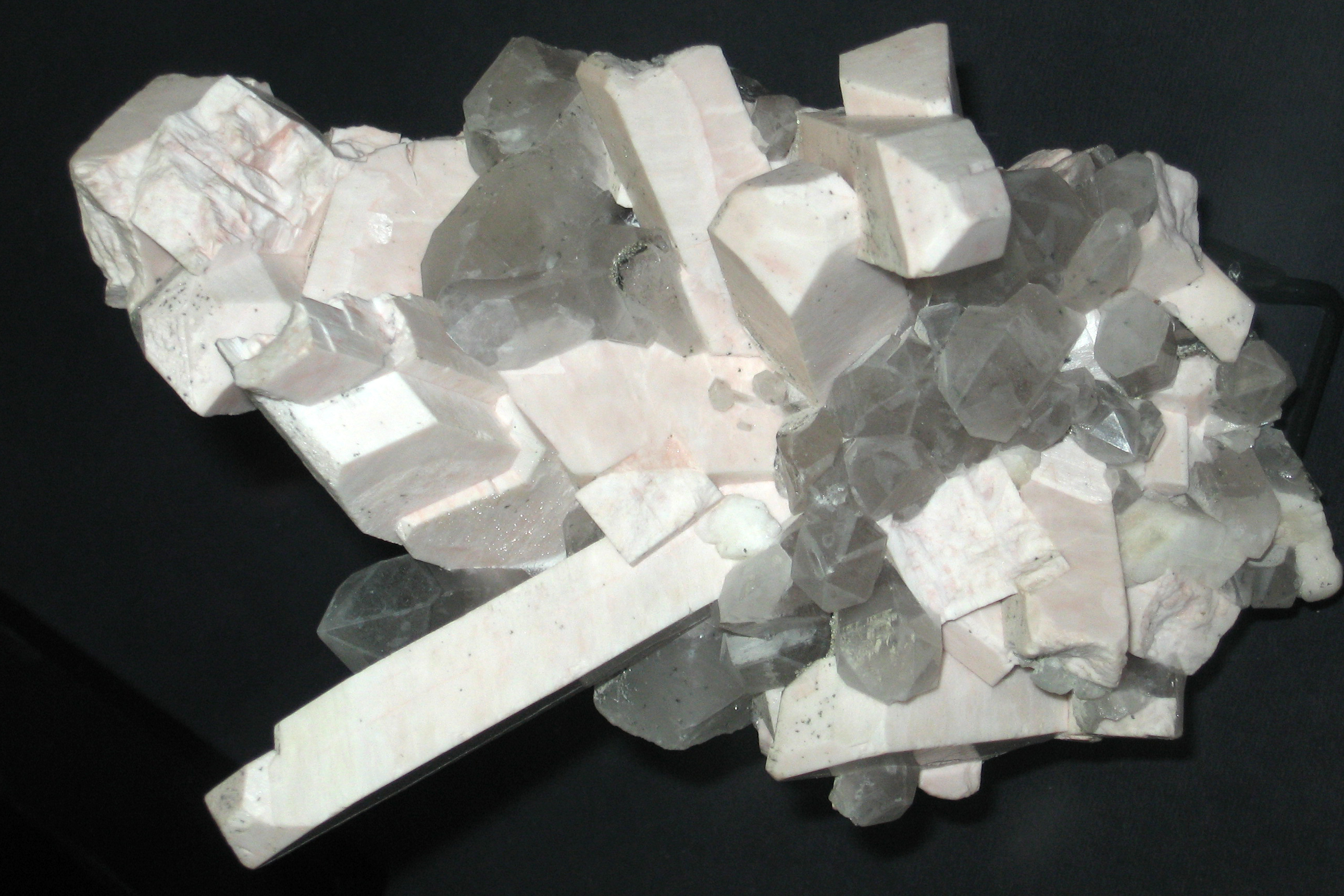
Monazite-(La)
Monazite-(La) is a relatively rare representative of the monazite group, with lanthanum being the dominant rare earth element in its structure. As such, it is the lanthanum analogue of monazite-(Ce), monazite-(Nd), and monazite-(Sm) Monazite-(Sm) is an exceedingly rare representative of the monazite group, with samarium being the dominant rare earth element in its structure. It is the samarium analogue of monazite-(Ce), monazite-(La), and monazite-(Nd) Monazite-(Nd) is a rela .... It is also the phosphorus analogue of gasparite-(La). The group contains simple rare earth phosphate minerals with the general formula of A''T''O4, where A = Ce, La, Nd, or Sm (or, rarely, Bi), and B = P or, rarely, As. The A site may also bear Ca and Th. Mindat, Monazite Group, https://www.mindat.org/min-29313.html References {{reflist Lanthanum minerals Phosphate minerals Monoclinic minerals Minerals in space group 14 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monazite
Monazite is a primarily reddish-brown phosphate mineral that contains rare-earth elements. Due to variability in composition, monazite is considered a group of minerals. The most common species of the group is monazite-(Ce), that is, the cerium-dominant member of the group. It occurs usually in small isolated crystals. It has a hardness of 5.0 to 5.5 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness and is relatively dense, about 4.6 to 5.7 g/cm3. There are five different most common species of monazite, depending on the relative amounts of the rare earth elements in the mineral: * monazite-(Ce), ( Ce, La, Nd, Th) PO4 (the most common member), * monazite-(La), (La,Ce,Nd)PO4, * monazite-(Nd), (Nd,La,Ce)PO4, * monazite-(Sm), ( Sm, Gd,Ce,Th)PO4, * monazite-(Pr), ( Pr,Ce,Nd,Th)PO4. The elements in parentheses are listed in the order of their relative proportion within the mineral: lanthanum is the most common rare-earth element in monazite-(La), and so forth. Silica (SiO2) is present in trace a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanthanum
Lanthanum is a chemical element with the symbol La and atomic number 57. It is a soft, ductile, silvery-white metal that tarnishes slowly when exposed to air. It is the eponym of the lanthanide series, a group of 15 similar elements between lanthanum and lutetium in the periodic table, of which lanthanum is the first and the prototype. Lanthanum is traditionally counted among the rare earth elements. Like most other rare earth elements, the usual oxidation state is +3. Lanthanum has no biological role in humans but is essential to some bacteria. It is not particularly toxic to humans but does show some antimicrobial activity. Lanthanum usually occurs together with cerium and the other rare earth elements. Lanthanum was first found by the Swedish chemist Carl Gustaf Mosander in 1839 as an impurity in cerium nitrate – hence the name ''lanthanum'', from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'to lie hidden'. Although it is classified as a rare earth element, lanthanum is the 28th most abund ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monazite-(Ce)
Monazite-(Ce) is the most common representative of the monazite group. It is the cerium-dominant analogue of monazite-(La), monazite-(Nd), and monazite-(Sm) Monazite-(Sm) is an exceedingly rare representative of the monazite group, with samarium being the dominant rare earth element in its structure. It is the samarium analogue of monazite-(Ce), monazite-(La), and monazite-(Nd) Monazite-(Nd) is a rela .... It is also the phosphorus analogue of gasparite-(Ce). The group contains simple rare earth phosphate minerals with the general formula of A''T''O4, where A = Ce, La, Nd, or Sm (or, rarely, Bi), and B = P or, rarely, As. The A site may also bear Ca and Th. Mindat, Monazite Group, https://www.mindat.org/min-29313.html References {{reflist Cerium minerals Lanthanide minerals Phosphate minerals Monoclinic minerals Minerals in space group 14 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monazite-(Nd)
Monazite-(Nd) is a relatively rare representative of the monazite group, with neodymium being the dominant rare earth element in its structure. This variety of monazite is typically colored bright rose-red. It is the neodymium analogue of monazite-(Ce), monazite-(La), and monazite-(Sm) Monazite-(Sm) is an exceedingly rare representative of the monazite group, with samarium being the dominant rare earth element in its structure. It is the samarium analogue of monazite-(Ce), monazite-(La), and monazite-(Nd) Monazite-(Nd) is a rela .... The group contains simple rare earth phosphate minerals with the general formula of A''T''O4, where A = Ce, La, Nd, or Sm (or, rarely, Bi), and B = P or, rarely, As. The A site may also bear Ca and Th. Mindat, Monazite Group, https://www.mindat.org/min-29313.html References {{reflist Neodymium compounds Phosphate minerals Monoclinic minerals Minerals in space group 14 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monazite-(Sm)
Monazite-(Sm) is an exceedingly rare representative of the monazite group, with samarium being the dominant rare earth element in its structure. It is the samarium analogue of monazite-(Ce), monazite-(La), and monazite-(Nd) Monazite-(Nd) is a relatively rare representative of the monazite group, with neodymium being the dominant rare earth element in its structure. This variety of monazite is typically colored bright rose-red. It is the neodymium analogue of monazite- .... It is only the second known mineral with samarium being the mineral-forming element, after florencite-(Sm). The group contains simple rare earth phosphate minerals with the general formula of A''T''O4, where A = Ce, La, Nd, or Sm (or, rarely, Bi), and B = P or, rarely, As. The A site may also bear Ca and Th. Mindat, Monazite Group, https://www.mindat.org/min-29313.html References {{reflist Samarium minerals Phosphate minerals Monoclinic minerals Minerals in space group 11 Minerals described in 2002 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanthanum Minerals
Lanthanum is a chemical element with the symbol La and atomic number 57. It is a soft, ductile, silvery-white metal that tarnishes slowly when exposed to air. It is the eponym of the lanthanide series, a group of 15 similar elements between lanthanum and lutetium in the periodic table, of which lanthanum is the first and the prototype. Lanthanum is traditionally counted among the rare earth elements. Like most other rare earth elements, the usual oxidation state is +3. Lanthanum has no biological role in humans but is essential to some bacteria. It is not particularly toxic to humans but does show some antimicrobial activity. Lanthanum usually occurs together with cerium and the other rare earth elements. Lanthanum was first found by the Swedish chemist Carl Gustaf Mosander in 1839 as an impurity in cerium nitrate – hence the name ''lanthanum'', from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'to lie hidden'. Although it is classified as a rare earth element, lanthanum is the 28th most abund ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphate Mineral
Phosphate minerals contain the tetrahedrally coordinated phosphate (PO43−) anion along sometimes with arsenate (AsO43−) and vanadate (VO43−) substitutions, and chloride (Cl−), fluoride (F−), and hydroxide (OH−) anions that also fit into the crystal structure. The phosphate class of minerals is a large and diverse group, however, only a few species are relatively common. Applications Phosphate rock has high concentration of phosphate minerals, most commonly of the apatite group. It is the major resource mined to produce phosphate fertilizers for the agriculture sector. Phosphate is also used in animal feed supplements, food preservatives, anti-corrosion agents, cosmetics, fungicides, ceramics, water treatment and metallurgy. The largest use of minerals mined for their phosphate content is the production of fertilizer. Phosphate minerals are often used for control of rust and prevention of corrosion on ferrous materials applied with electrochemical conversion co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoclinic
In crystallography, the monoclinic crystal system is one of the seven crystal systems. A crystal system is described by three vectors. In the monoclinic system, the crystal is described by vectors of unequal lengths, as in the orthorhombic system. They form a parallelogram prism. Hence two pairs of vectors are perpendicular (meet at right angles), while the third pair makes an angle other than 90°. Bravais lattices Two monoclinic Bravais lattices exist: the primitive monoclinic and the base-centered monoclinic. For the base-centered monoclinic lattice, the primitive cell has the shape of an oblique rhombic prism;See , row mC, column Primitive, where the cell parameters are given as a1 = a2, α = β it can be constructed because the two-dimensional centered rectangular base layer can also be described with primitive rhombic axes. Note that the length a of the primitive cell below equals \frac \sqrt of the conventional cell above. Crystal classes The table below org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rare Earth Element
The rare-earth elements (REE), also called the rare-earth metals or (in context) rare-earth oxides or sometimes the lanthanides (yttrium and scandium are usually included as rare earths), are a set of 17 nearly-indistinguishable lustrous silvery-white soft heavy metals. Compounds containing rare earths have diverse applications in electrical and electronic components, lasers, glass, magnetic materials, and industrial processes. Scandium and yttrium are considered rare-earth elements because they tend to occur in the same ore deposits as the lanthanides and exhibit similar chemical properties, but have different electronic and magnetic properties. These metals tarnish slowly in air at room temperature and react slowly with cold water to form hydroxides, liberating hydrogen. They react with steam to form oxides, and at elevated temperature (400°C) ignite spontaneously. These elements and their compounds have no biological function other than in several specialized enzymes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphate Minerals
Phosphate minerals contain the tetrahedrally coordinated phosphate (PO43−) anion along sometimes with arsenate (AsO43−) and vanadate (VO43−) substitutions, and chloride (Cl−), fluoride (F−), and hydroxide (OH−) anions that also fit into the crystal structure. The phosphate class of minerals is a large and diverse group, however, only a few species are relatively common. Applications Phosphate rock has high concentration of phosphate minerals, most commonly of the apatite group. It is the major resource mined to produce phosphate fertilizers for the agriculture sector. Phosphate is also used in animal feed supplements, food preservatives, anti-corrosion agents, cosmetics, fungicides, ceramics, water treatment and metallurgy. The largest use of minerals mined for their phosphate content is the production of fertilizer. Phosphate minerals are often used for control of rust and prevention of corrosion on ferrous materials applied with electrochemical conversion co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoclinic Minerals
In crystallography, the monoclinic crystal system is one of the seven crystal systems. A crystal system is described by three vectors. In the monoclinic system, the crystal is described by vectors of unequal lengths, as in the orthorhombic system. They form a parallelogram prism. Hence two pairs of vectors are perpendicular (meet at right angles), while the third pair makes an angle other than 90°. Bravais lattices Two monoclinic Bravais lattices exist: the primitive monoclinic and the base-centered monoclinic. For the base-centered monoclinic lattice, the primitive cell has the shape of an oblique rhombic prism;See , row mC, column Primitive, where the cell parameters are given as a1 = a2, α = β it can be constructed because the two-dimensional centered rectangular base layer can also be described with primitive rhombic axes. Note that the length a of the primitive cell below equals \frac \sqrt of the conventional cell above. Crystal classes The table below org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |