|
Misinformation Related To Vaccination
Misinformation related to immunization circulates in mass media and social media in spite of the fact that there is no serious hesitancy or debate within mainstream medical and scientific circles about the benefits of vaccination. Intentional spreading of false information and conspiracy theories have also been propagated by the general public and celebrities. Misinformation related to vaccination fuels vaccine hesitancy and thereby results in disease outbreaks. Although opposition to vaccination has existed for centuries, the internet and social media have recently facilitated the spread of vaccine-related misinformation. Unsubstantiated safety concerns related to vaccines are often presented on the internet as scientific information. Extent A survey by the Royal Society for Public Health found that 50% of the parents of children under the age of five regularly encountered misinformation related to vaccination on social media. On Twitter, bots, masked as legitimate users were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Misinformation
Misinformation is incorrect or misleading information. It differs from disinformation, which is ''deliberately'' deceptive. Rumors are information not attributed to any particular source, and so are unreliable and often unverified, but can turn out to be either true or false. Even if later retracted, misinformation can continue to influence actions and memory. People may be more prone to believe misinformation because they are emotionally connected to what they are listening to or are reading. The role of social media has made information readily available to us at anytime, and it connects vast groups of people along with their information at one time. Advances in technology has impacted the way we communicate information and the way misinformation is spread. Misinformation has impacts on our societies' ability to receive information which then influences our communities, politics, and medical field. History Early examples include the insults and smears spread among political rival ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA Vaccine
An mRNA vaccine is a type of vaccine that uses a copy of a molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA) to produce an immune response. The vaccine delivers molecules of antigen-encoding mRNA into immune cells, which use the designed mRNA as a blueprint to build foreign protein that would normally be produced by a pathogen (such as a virus) or by a cancer cell. These protein molecules stimulate an adaptive immune response that teaches the body to identify and destroy the corresponding pathogen or cancer cells. The mRNA is delivered by a co-formulation of the RNA encapsulated in lipid nanoparticles that protect the RNA strands and help their absorption into the cells. Reactogenicity, the tendency of a vaccine to produce adverse reactions, is similar to that of conventional non-RNA vaccines. People susceptible to an autoimmune response may have an adverse reaction to messenger RNA vaccines. The advantages of mRNA vaccines over traditional vaccines are ease of design, speed and lower cost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group are vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) and vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol). The major natural source of the vitamin is synthesis of cholecalciferol in the lower layers of epidermis of the skin through a chemical reaction that is dependent on sun exposure (specifically UVB radiation). Cholecalciferol and ergocalciferol can be ingested from the diet and supplements. Only a few foods, such as the flesh of fatty fish, naturally contain significant amounts of vitamin D. In the U.S. and other countries, cow's milk and plant-derived milk substitutes are fortified with vitamin D, as are many breakfast cereals. Mushrooms exposed to ultraviolet light contribute useful amounts of vitamin D2. Dietary recommendations typically assume that all of a person's vitamin D is taken ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic table. In some respects, zinc is chemically similar to magnesium: both elements exhibit only one normal oxidation state (+2), and the Zn2+ and Mg2+ ions are of similar size.The elements are from different metal groups. See periodic table. Zinc is the 24th most abundant element in Earth's crust and has five stable isotopes. The most common zinc ore is sphalerite (zinc blende), a zinc sulfide mineral. The largest workable lodes are in Australia, Asia, and the United States. Zinc is refined by froth flotation of the ore, roasting, and final extraction using electricity ( electrowinning). Zinc is an essential trace element for humans, animals, plants and for microorganisms and is necessary for prenatal and postnatal development. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quercetin
Quercetin is a plant flavonol from the flavonoid group of polyphenols. It is found in many fruits, vegetables, leaves, seeds, and grains; capers, red onions, and kale are common foods containing appreciable amounts of it. It has a bitter flavor and is used as an ingredient in dietary supplements, beverages, and foods. Occurrence Quercetin is a flavonoid widely distributed in nature. The name has been used since 1857, and is derived from ''quercetum'' (oak forest), after the oak genus ''Quercus''. It is a naturally occurring polar auxin transport inhibitor. Quercetin is one of the most abundant dietary flavonoids, with an average daily consumption of 25–50 milligrams. In red onions, higher concentrations of quercetin occur in the outermost rings and in the part closest to the root, the latter being the part of the plant with the highest concentration. One study found that organically grown tomatoes had 79% more quercetin than non-organically grown fruit. Quercetin is presen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homeopathy
Homeopathy or homoeopathy is a pseudoscientific system of alternative medicine. It was conceived in 1796 by the German physician Samuel Hahnemann. Its practitioners, called homeopaths, believe that a substance that causes symptoms of a disease in healthy people can cure similar symptoms in sick people; this doctrine is called '' similia similibus curentur'', or "like cures like". Homeopathic preparations are termed ''remedies'' and are made using homeopathic dilution. In this process, the selected substance is repeatedly diluted until the final product is chemically indistinguishable from the diluent. Often not even a single molecule of the original substance can be expected to remain in the product. Between each dilution homeopaths may hit and/or shake the product, claiming this makes the diluent remember the original substance after its removal. Practitioners claim that such preparations, upon oral intake, can treat or cure disease. All relevant scientific knowledge about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
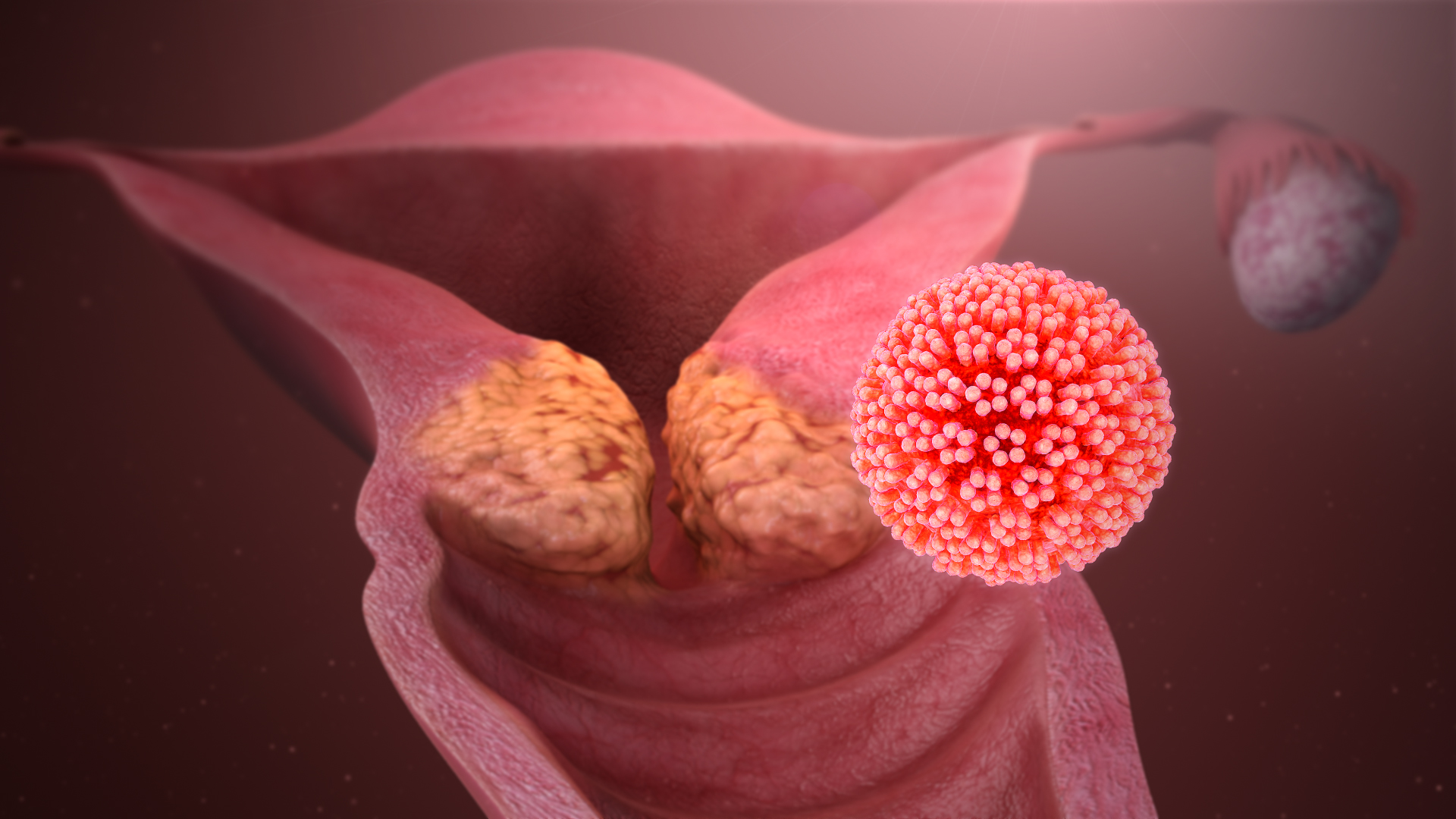
Human Papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the ''Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and results in either warts or precancerous lesions. These lesions, depending on the site affected, increase the risk of cancer of the cervix, vulva, vagina, penis, anus, mouth, tonsils, or throat. Nearly all cervical cancer is due to HPV and two strains – HPV16 and HPV18 – account for 70% of cases. HPV16 is responsible for almost 90% of HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers. Between 60% and 90% of the other cancers listed above are also linked to HPV. HPV6 and HPV11 are common causes of genital warts and laryngeal papillomatosis. An HPV infection is caused by ''human papillomavirus'', a DNA virus from the papillomavirus family. Over 170 types have been described. An individual can become infected with more than one type of HPV, and the dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society For Maternal-Fetal Medicine
The Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine was established in 1977 and is a not-for-profit organization of over 5,000 members that are dedicated to improving maternal and child outcomes. The organization's headquarters is located in Washington, D.C. Board certified maternal-fetal medicine physicians have an additional two to three years training in maternal-fetal medicine (MFM) and are involved in the latest advancements in maternal and fetal care. Because of their additional training, MFM's are considered high-risk pregnancy experts. The Society's primary objectives are to promote and expand research and education in maternal-fetal medicine. Mission and Vision With feedback from the membership, the SMFM Board of Directors revised the vision, mission, and strategic plan of the organization in 2022. The new strategic plan focuses on three goal areas: advocacy and partnerships; member engagement and support; and knowledge, education, and research. Within each goal area, there are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Society For Reproductive Medicine
The American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) is a nonprofit, multidisciplinary organization for advancement of the science and practice of reproductive medicine. The society has its headquarters in Washington, D.C and its administrative office in Birmingham, Alabama. History and activities Founded in 1944 by a small group of fertility experts who met in Chicago, the initial name was the American Society for the Study of Sterility, later the American Fertility Society (AFS). Though primarily an American organization, it had members from over 100 countries as of 2020. The society hosts an annual scientific congress, as well as courses, seminars, workshops and publications. Special interest groups are focused on a range of reproductive medicine topics. ASRM has an Ethics Committee that provides guidance on ethical issues. The ASRM Practice Committee issues clinical guidelines and reports. World Health Organization NSA status In May 2014, the ASRM became an associated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American College Of Obstetricians And Gynecologists
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) is a professional association of physicians specializing in obstetrics and gynecology in the United States. Several Latin American countries are also represented within Districts of the organization. It is a 501(c)(3) organization with a membership of more than 60,000 obstetrician-gynecologists and women's health care professionals. It was founded in 1951. __TOC__ Background A companion 501(c)(6) organization, the American ''Congress'' of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, was founded in 2008 and became operational in 2010. The two organizations coexist, and member individuals automatically belong to both. Both are not-for-profit. The College as a 501(c)(3) focuses on education (with limited political work), whereas the Congress as a 501(c)(6) is allowed to advocate for members' interests in terms of the business of medicine (BOM) through lobbying and other political work. Their main advocacy focuses on women's reprod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syncytin-1
Syncytin-1 also known as enverin is a protein found in humans and other primates that is encoded by the ERVW-1 gene ( endogenous retrovirus group W envelope member 1). Syncytin-1 is a cell-cell fusion protein whose function is best characterized in placental development. The placenta in turn aids in embryo attachment to the uterus and establishment of a nutrient supply. The gene encoding this protein is an endogenous retroviral element that is the remnant of an ancient retroviral infection integrated into the primate germ line. In the case of syncytin-1 (which is found in humans, apes, and Old World but not New World monkeys), this integration likely occurred more than 25 million years ago. Syncytin-1 is one of two known syncytin proteins expressed in catarrhini primates (the other being syncytin-2) and one of many viral genomes incorporated on multiple occasions over evolutionary time in diverse mammalian species. ERVW-1 is located within ERVWE1, a full length provirus on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronavirus Spike Protein
Spike (S) glycoprotein (sometimes also called spike protein, formerly known as E2) is the largest of the four major structural proteins found in coronaviruses. The spike protein assembles into trimers that form large structures, called spikes or peplomers, that project from the surface of the virion. The distinctive appearance of these spikes when visualized using negative stain transmission electron microscopy, "recalling the solar corona", gives the virus family its name. The function of the spike glycoprotein is to mediate viral entry into the host cell by first interacting with molecules on the exterior cell surface and then fusing the viral and cellular membranes. Spike glycoprotein is a class I fusion protein that contains two regions, known as S1 and S2, responsible for these two functions. The S1 region contains the receptor-binding domain that binds to receptors on the cell surface. Coronaviruses use a very diverse range of receptors; SARS-CoV (which causes SARS) an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |