|
Minimum Bactericidal Concentration
The minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) is the lowest concentration of an antibacterial agent required to kill a particular bacterium. It can be determined from broth dilution minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) tests by subculturing to agar plates that do not contain the test agent. The MBC is identified by determining the lowest concentration of antibacterial agent that reduces the viability of the initial bacterial inoculum by ≥99.9%. The MBC is complementary to the MIC; whereas the MIC test demonstrates the lowest level of antimicrobial agent that inhibits growth, the MBC demonstrates the lowest level of antimicrobial agent that results in microbial death. This means that even if a particular MIC shows inhibition, plating the bacteria onto agar might still result in organism proliferation because the antimicrobial did not cause death. Antibacterial agents are usually regarded as bactericidal if the MBC is no more than four times the MIC. Because the MBC test uses colony ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibacterial
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of such infections. They may either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the common cold or influenza; drugs which inhibit viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals rather than antibiotics. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against microbes, but in the usual medical usage, antibiotics (such as penicillin) are those produced naturally (by one microorganism fighting another), whereas non-antibiotic antibacterials (such as sulfonamides and antiseptics) ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
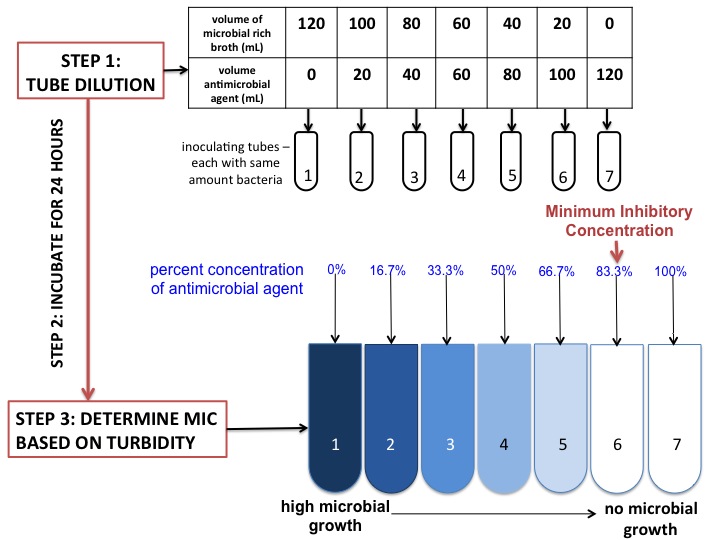
Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
In microbiology, the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) is the lowest concentration of a chemical, usually a drug, which prevents visible growth of a bacterium or bacteria. MIC depends on the microorganism, the affected human being (in vivo only), and the antibiotic itself. It is often expressed in micrograms per milliliter (μg/mL) or milligrams per liter (mg/L). The MIC is determined by preparing solutions of the chemical in vitro at increasing concentrations, incubating the solutions with separate batches of cultured bacteria, and measuring the results using agar dilution or broth microdilution. Results have been graded into susceptible (often called sensitive), increased exposure, or resistant to a particular antimicrobial by using a breakpoint. Breakpoints are agreed upon values, published in guidelines of a reference body, such as the U.S. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI), the British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (BSAC) or the European Committee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agar Plate
An agar plate is a Petri dish that contains a growth medium solidified with agar, used to culture microorganisms. Sometimes selective compounds are added to influence growth, such as antibiotics. Individual microorganisms placed on the plate will grow into individual colonies, each a clone genetically identical to the individual ancestor organism (except for the low, unavoidable rate of mutation). Thus, the plate can be used either to estimate the concentration of organisms in a liquid culture or a suitable dilution of that culture using a colony counter, or to generate genetically pure cultures from a mixed culture of genetically different organisms. Several methods are available to plate out cells. One technique is known as "streaking". In this technique, a drop of the culture on the end of a thin, sterile loop of wire, sometimes known as an inoculator, is streaked across the surface of the agar leaving organisms behind, a higher number at the beginning of the streak and a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinical And Laboratory Standards Institute
The Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) is a volunteer-driven, membership-supported, not-for-profit, standards development organization. CLSI promotes the development and use of voluntary laboratory consensus standards and guidelines within the health care community. History In 1968, 31 clinicians and laboratory scientists representing 15 organizations met to develop a formal consensus process for standardization. In 1977, CLSI was accredited by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) as a voluntary consensus standards organization. At about the same time, CLSI became the home of the National Reference System for the Clinical Laboratory (NRSCL), a collection of broadly understood reference systems intended to improve the comparability of test results, consistent with the needs of medical practice. CLSI is a global association of 1,500+ member organizations and individual members, as well as more than 2,000 volunteers. Until 2005, CLSI was called the Natio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bactericidal
A bactericide or bacteriocide, sometimes abbreviated Bcidal, is a substance which kills bacteria. Bactericides are disinfectants, antiseptics, or antibiotics. However, material surfaces can also have bactericidal properties based solely on their physical surface structure, as for example biomaterials like insect wings. Disinfectants The most used disinfectants are those applying *active chlorine (i.e., hypochlorites, chloramines, dichloroisocyanurate and trichloroisocyanurate, wet chlorine, chlorine dioxide, etc.), *active oxygen (peroxides, such as peracetic acid, potassium persulfate, sodium perborate, sodium percarbonate, and urea perhydrate), *iodine (povidone-iodine, Lugol's solution, iodine tincture, iodinated nonionic surfactants), *concentrated alcohols (mainly ethanol, 1-propanol, called also n-propanol and 2-propanol, called isopropanol and mixtures thereof; further, 2-phenoxyethanol and 1- and 2-phenoxypropanols are used), * phenolic substances (such as phenol ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colony-forming Unit
In microbiology, colony-forming unit (CFU, cfu or Cfu) is a unit which estimates the number of microbial cells (bacteria, fungi, viruses etc.) in a sample that are viable, able to multiply via binary fission under the controlled conditions. Counting with colony-forming units requires culturing the microbes and counts only viable cells, in contrast with microscopic examination which counts all cells, living or dead. The visual appearance of a colony in a cell culture requires significant growth, and when counting colonies, it is uncertain if the colony arose from one cell or a group of cells. Expressing results as colony-forming units reflects this uncertainty. Theory The purpose of plate counting is to estimate the number of cells present based on their ability to give rise to colonies under specific conditions of nutrient medium, temperature and time. Theoretically, one viable cell can give rise to a colony through replication. However, solitary cells are the exception in na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavonoids
Flavonoids (or bioflavonoids; from the Latin word ''flavus'', meaning yellow, their color in nature) are a class of polyphenolic secondary metabolites found in plants, and thus commonly consumed in the diets of humans. Chemically, flavonoids have the general structure of a 15-carbon skeleton, which consists of two phenyl rings (A and B) and a heterocyclic ring (C, the ring containing the embedded oxygen). This carbon structure can be abbreviated C6-C3-C6. According to the IUPAC nomenclature, they can be classified into: *flavonoids or bioflavonoids *isoflavonoids, derived from 3-phenyl chromen-4-one (3-phenyl-1,4-benzopyrone) structure *neoflavonoids, derived from 4-phenylcoumarine (4-phenyl-1,2-benzopyrone) structure The three flavonoid classes above are all ketone-containing compounds and as such, anthoxanthins ( flavones and flavonols). This class was the first to be termed bioflavonoids. The terms flavonoid and bioflavonoid have also been more loosely used to describe non- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |