|
Mid-brain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the forward-most portion of the brainstem and is associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation. The name comes from the Greek ''mesos'', "middle", and ''enkephalos'', "brain". Structure The principal regions of the midbrain are the tectum, the cerebral aqueduct, tegmentum, and the cerebral peduncles. Rostrally the midbrain adjoins the diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, etc.), while caudally it adjoins the hindbrain (pons, medulla and cerebellum). In the rostral direction, the midbrain noticeably splays laterally. Sectioning of the midbrain is usually performed axially, at one of two levels – that of the superior colliculi, or that of the inferior colliculi. One common technique for remembering the structures of the midbrain involves visualizing these cross-sections (especially at the level of the superior colliculi) as the upside-down face of a bea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
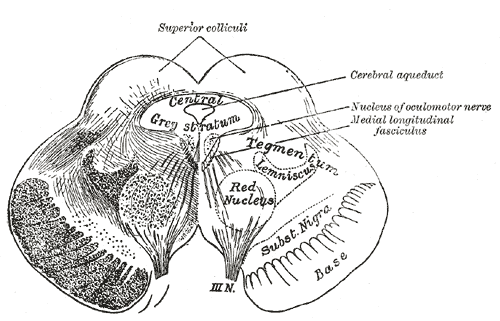
Cerebral Aqueduct
The cerebral aqueduct (aqueductus mesencephali, mesencephalic duct, sylvian aqueduct or aqueduct of Sylvius) is a conduit for cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that connects the third ventricle to the fourth ventricle of the ventricular system of the brain. It is located in the midbrain dorsal to the pons and ventral to the cerebellum. The cerebral aqueduct is surrounded by an enclosing area of gray matter called the periaqueductal gray, or central gray. It was first named after Franciscus Sylvius. Structure Development The cerebral aqueduct, as other parts of the ventricular system of the brain, develops from the central canal of the neural tube, and it originates from the portion of the neural tube that is present in the developing mesencephalon, hence the name "mesencephalic duct." Function The cerebral aqueduct acts like a canal that passes through the midbrain. It connects the third ventricle with the fourth ventricle so that cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) moves between the cereb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Colliculus
The inferior colliculus (IC) (Latin for ''lower hill'') is the principal midbrain nucleus of the auditory pathway and receives input from several peripheral brainstem nuclei in the auditory pathway, as well as inputs from the auditory cortex. The inferior colliculus has three subdivisions: the central nucleus, a dorsal cortex by which it is surrounded, and an external cortex which is located laterally. Its bimodal neurons are implicated in auditory-somatosensory interaction, receiving projections from somatosensory nuclei. This multisensory integration may underlie a filtering of self-effected sounds from vocalization, chewing, or respiration activities. The inferior colliculi together with the superior colliculi form the eminences of the corpora quadrigemina, and also part of the tectal region of the midbrain. The inferior colliculus lies caudal to its counterpart – the superior colliculus – above the trochlear nerve, and at the base of the projection of the medial genicu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Colliculus
In neuroanatomy, the superior colliculus () is a structure lying on the roof of the mammalian midbrain. In non-mammalian vertebrates, the homologous structure is known as the optic tectum, or optic lobe. The adjective form ''tectal'' is commonly used for both structures. In mammals, the superior colliculus forms a major component of the midbrain. It is a paired structure and together with the paired inferior colliculi forms the corpora quadrigemina. The superior colliculus is a layered structure, with a pattern that is similar to all mammals. The layers can be grouped into the superficial layers ( stratum opticum and above) and the deeper remaining layers. Neurons in the superficial layers receive direct input from the retina and respond almost exclusively to visual stimuli. Many neurons in the deeper layers also respond to other modalities, and some respond to stimuli in multiple modalities. The deeper layers also contain a population of motor-related neurons, capable of activat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pons
The pons (from Latin , "bridge") is part of the brainstem that in humans and other bipeds lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum. The pons is also called the pons Varolii ("bridge of Varolius"), after the Italian anatomist and surgeon Costanzo Varolio (1543–75). This region of the brainstem includes neural pathways and tracts that conduct signals from the brain down to the cerebellum and medulla, and tracts that carry the sensory signals up into the thalamus.Saladin Kenneth S.(2007) Anatomy & physiology the unity of form and function. Dubuque, IA: McGraw-Hill Structure The pons is in the brainstem situated between the midbrain and the medulla oblongata, and in front of the cerebellum. A separating groove between the pons and the medulla is the inferior pontine sulcus. The superior pontine sulcus separates the pons from the midbrain. The pons can be broadly divided into two parts: the basilar part of the pons (ventral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tegmentum
The tegmentum (from Latin for "covering") is a general area within the brainstem. The tegmentum is the ventral part of the midbrain and the tectum is the dorsal part of the midbrain. It is located between the ventricular system and distinctive basal or ventral structures at each level. It forms the floor of the midbrain (mesencephalon) whereas the tectum forms the ceiling. It is a multisynaptic network of neurons that is involved in many subconscious homeostatic and reflexive pathways. It is a motor center that relays inhibitory signals to the thalamus and basal nuclei preventing unwanted body movement. The tegmentum area includes various different structures, such as the rostral end of the reticular formation, several nuclei controlling eye movements, the periaqueductal gray matter, the red nucleus, the substantia nigra, and the ventral tegmental area. The tegmentum is the location of several cranial nerve (CN) nuclei. The nuclei of CN III and IV are located in the tegmentu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Peduncle
The cerebral peduncles are the two stalks that attach the cerebrum to the brainstem. They are structures at the front of the midbrain which arise from the ventral pons and contain the large ascending (sensory) and descending (motor) nerve tracts that run to and from the cerebrum from the pons. Mainly, the three common areas that give rise to the cerebral peduncles are the cerebral cortex, the spinal cord and the cerebellum. The region includes the tegmentum, crus cerebri and pretectum. By this definition, the cerebral peduncles are also known as the basis pedunculi, while the large ventral bundle of efferent fibers is referred to as the cerebral crus or the pes pedunculi. The cerebral peduncles are located on either side of the midbrain and are the frontmost part of the midbrain, and act as the connectors between the rest of the midbrain and the thalamic nuclei and thus the cerebrum. As a whole, the cerebral peduncles assist in refining motor movements, learning new motor ski ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pons
The pons (from Latin , "bridge") is part of the brainstem that in humans and other bipeds lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum. The pons is also called the pons Varolii ("bridge of Varolius"), after the Italian anatomist and surgeon Costanzo Varolio (1543–75). This region of the brainstem includes neural pathways and tracts that conduct signals from the brain down to the cerebellum and medulla, and tracts that carry the sensory signals up into the thalamus.Saladin Kenneth S.(2007) Anatomy & physiology the unity of form and function. Dubuque, IA: McGraw-Hill Structure The pons is in the brainstem situated between the midbrain and the medulla oblongata, and in front of the cerebellum. A separating groove between the pons and the medulla is the inferior pontine sulcus. The superior pontine sulcus separates the pons from the midbrain. The pons can be broadly divided into two parts: the basilar part of the pons (ventral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rostral
{{disambiguation ...
Rostral may refer to: Anatomy * Rostral (anatomical term), situated toward the oral or nasal region * Rostral bone, in ceratopsian dinosaurs * Rostral organ, of certain fish * Rostral scale, in snakes and scaled reptiles Other uses * Rostral column, a victory column commemorating a naval military victory See also * * Rostrum (other) Rostrum may refer to: * Any kind of a platform for a speaker: **dais **pulpit * Rostrum (anatomy), a beak, or anatomical structure resembling a beak, as in the mouthparts of many sucking insects * Rostrum (ship), a form of bow on naval ships * Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diencephalon
The diencephalon (or interbrain) is a division of the forebrain (embryonic ''prosencephalon''). It is situated between the telencephalon and the midbrain (embryonic ''mesencephalon''). The diencephalon has also been known as the 'tweenbrain in older literature. It consists of structures that are on either side of the third ventricle, including the thalamus, the hypothalamus, the epithalamus and the subthalamus. The diencephalon is one of the main vesicles of the brain formed during embryogenesis. During the third week of development a neural tube is created from the ectoderm, one of the three primary germ layers. The tube forms three main vesicles during the third week of development: the prosencephalon, the mesencephalon and the rhombencephalon. The prosencephalon gradually divides into the telencephalon and the diencephalon. Structure The diencephalon consists of the following structures: *Thalamus *Hypothalamus including the posterior pituitary *Epithalamus which consists of: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebellar Hemisphere
The cerebellum consists of three parts, a median and two lateral, which are continuous with each other, and are substantially the same in structure. The median portion is constricted, and is called the vermis, from its annulated appearance which it owes to the transverse ridges and furrows upon it; the lateral expanded portions are named the hemispheres. Sections *The "intermediate hemisphere" is also known as the "spinocerebellum". *The "lateral hemisphere" is also known as the " pontocerebellum". *The lateral hemisphere is considered the portion of the cerebellum to develop most recently. Additional images File:Cerebellar hemisphere -- animation.gif, Animation. File:Cerebellar hemisphere --- animation.gif, Close up animation. File:Cerebellar hemisphere by Sanjoy Sanyal.webmsd.webm, Dissection video (45 s). Demonstrating the two cerebellar hemispheres. File:Human cerebellum anterior view description.JPG, Human cerebellum anterior view description (Cerebellar hemisphere is #8) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalamus
The thalamus (from Greek θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter located in the dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of the forebrain). Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all directions, allowing hub-like exchanges of information. It has several functions, such as the relaying of sensory signals, including motor signals to the cerebral cortex and the regulation of consciousness, sleep, and alertness. Anatomically, it is a paramedian symmetrical structure of two halves (left and right), within the vertebrate brain, situated between the cerebral cortex and the midbrain. It forms during embryonic development as the main product of the diencephalon, as first recognized by the Swiss embryologist and anatomist Wilhelm His Sr. in 1893. Anatomy The thalamus is a paired structure of gray matter located in the forebrain which is superior to the midbrain, near the center of the brain, with nerve fibers projecting out to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caudal
...
Caudal may refer to: Anatomy * Caudal (anatomical term) (from Latin ''cauda''; tail), used to describe how close something is to the trailing end of an organism * Caudal artery, the portion of the dorsal aorta of a vertebrate that passes into the tail * Caudal cell mass, the aggregate of undifferentiated cells at the caudal end on the spine * Caudal fin, the tail fin of a fish * Caudal vertebrae, that make up the tail of tailed animals Places * Caudal (comarca), an administrative division of Asturias, Spain * Caudal (river), in northern Spain * Caudal Hills, Antarctica Other uses * Caudal (protein), a family of homeobox transcription factors * Anne-Lise Caudal (born 1984), a French golfer See also * *Cauda (other) The cauda is a characteristic feature of songs in the conductus style of ''a cappella'' music. Cauda may refer to: * a tail-like protrusion of an aphid * Gavdos Gavdos ( el, Γαύδος, ) is the southernmost Greek island, located to the sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |