|
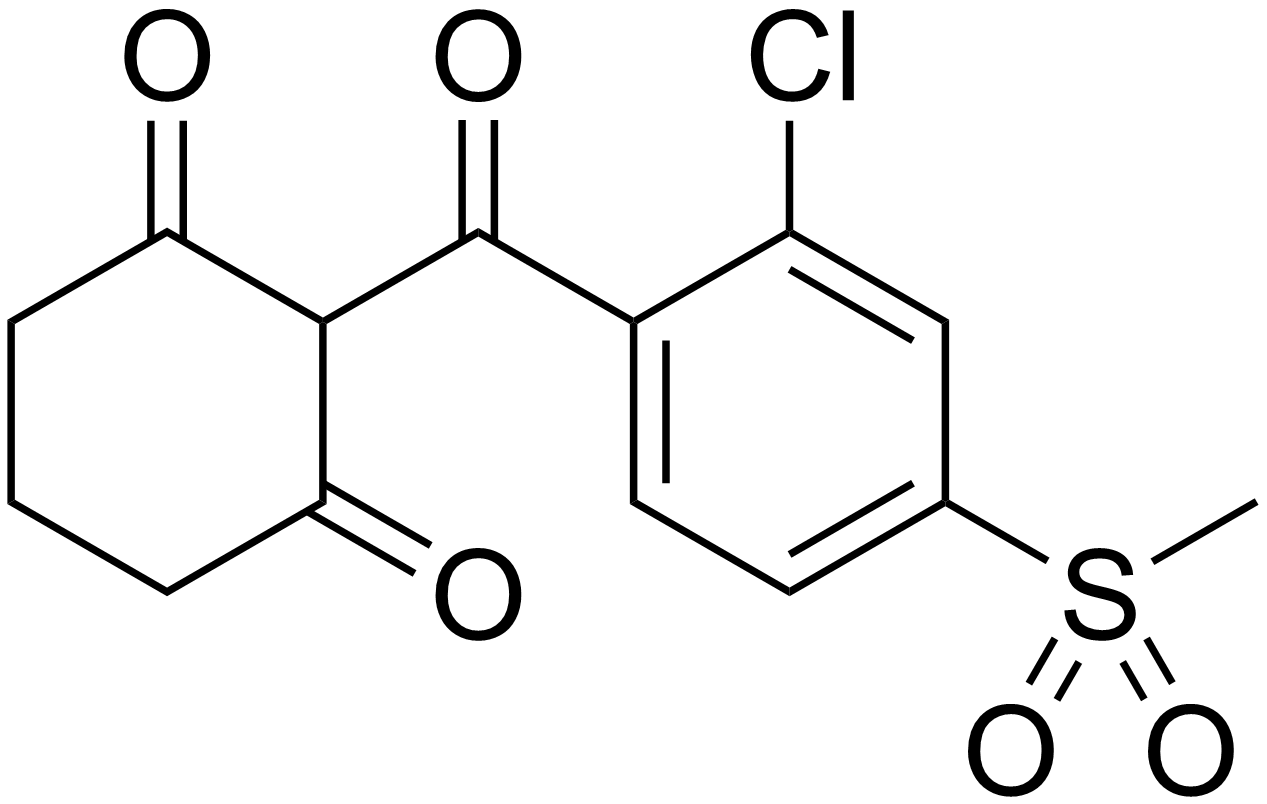
Mesotrione
Mesotrione is the ISO common name for an organic compound that is used as a selective herbicide, especially in maize. A synthetic inspired by the natural substance leptospermone, it inhibits the enzyme 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (HPPD) and is sold under brand names including Callisto and Tenacity. It was first marketed by Syngenta in 2001. History The invention of the triketone class of herbicides had its beginnings in an observation in 1977 of allelopathic weed control near a bottlebrush tree, '' Callistemon citrinus''. Chemists at the Stauffer Chemical Company identified the compound responsible as leptospermone, a known natural product which had not previously been reported as having biological activity. Extensive work on analogues led to the discovery and development of sulcotrione and mesotrione. The triketone herbicides were found to be effective on a wide range of commercially-important weed species and to have both pre- and post-emergence activity. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesotrione Synthesis
Mesotrione is the ISO common name for an organic compound that is used as a selective herbicide, especially in maize. A synthetic inspired by the natural substance leptospermone, it inhibits the enzyme 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (HPPD) and is sold under brand names including Callisto and Tenacity. It was first marketed by Syngenta in 2001. History The invention of the triketone class of herbicides had its beginnings in an observation in 1977 of allelopathic weed control near a bottlebrush tree, '' Callistemon citrinus''. Chemists at the Stauffer Chemical Company identified the compound responsible as leptospermone, a known natural product which had not previously been reported as having biological activity. Extensive work on analogues led to the discovery and development of sulcotrione and mesotrione. The triketone herbicides were found to be effective on a wide range of commercially-important weed species and to have both pre- and post-emergence activity. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptospermone
Leptospermone is a chemical compound (a β-triketone) produced by some members of the myrtle family ('' Myrtaceae''), such as '' Callistemon citrinus'' (Lemon Bottlebrush), a shrub native to Australia, and ''Leptospermum scoparium'' (Manuka), a New Zealand tree from which it gets its name. Modification of this allelopathic chemical to produce mesotrione led to the commercialization of derivative compounds as HPPD inhibitor herbicides. History Leptospermone was first identified in 1927 and was extracted from a variety of plants in 1965, 1966 and 1968. It was first identified as a chemical in ''Callistemon citrinus'' in California in 1977. A biologist at the Western Research Centre of Stauffer Chemical Company noticed that very few plants grew under ''Callistemon citrinus'' bushes. After taking soil samples and creating an array of extracts, one was identified as an herbicide. While it did have herbicidal effects, the rate required for sufficient coverage was too high to be of prac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptospermone
Leptospermone is a chemical compound (a β-triketone) produced by some members of the myrtle family ('' Myrtaceae''), such as '' Callistemon citrinus'' (Lemon Bottlebrush), a shrub native to Australia, and ''Leptospermum scoparium'' (Manuka), a New Zealand tree from which it gets its name. Modification of this allelopathic chemical to produce mesotrione led to the commercialization of derivative compounds as HPPD inhibitor herbicides. History Leptospermone was first identified in 1927 and was extracted from a variety of plants in 1965, 1966 and 1968. It was first identified as a chemical in ''Callistemon citrinus'' in California in 1977. A biologist at the Western Research Centre of Stauffer Chemical Company noticed that very few plants grew under ''Callistemon citrinus'' bushes. After taking soil samples and creating an array of extracts, one was identified as an herbicide. While it did have herbicidal effects, the rate required for sufficient coverage was too high to be of prac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allelopathic
Allelopathy is a biological phenomenon by which an organism produces one or more biochemicals that influence the germination, growth, survival, and reproduction of other organisms. These biochemicals are known as allelochemicals and can have beneficial (positive allelopathy) or detrimental (negative allelopathy) effects on the target organisms and the community. Allelopathy is often used narrowly to describe chemically-mediated competition between plants; however, it is sometimes defined more broadly as chemically-mediated competition between any type of organisms. Allelochemicals are a subset of secondary metabolites, which are not directly required for metabolism (i.e. growth, development and reproduction) of the allelopathic organism. Allelopathic interactions are an important factor in determining species distribution and abundance within plant communities, and are also thought to be important in the success of many invasive plants. For specific examples, see black walnut (' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1,3-Cyclohexanedione
1,3-Cyclohexanedione is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4(CO)2. It is one of three isomeric cyclohexanediones. It is a colorless compound that occurs naturally. It is the substrate for cyclohexanedione hydrolase. The compound exists mainly as the enol tautomer. Synthesis, structure, and reactivity 1,3-Cyclohexanedione is produced by semi-hydrogenation of resorcinol: :C6H4(OH)2 + H2 → C6H8O2 1,3-Cyclohexanedione exists in solution predominantly as the enol tautomer. : It reacts under acid catalysis with alcohols to 3-alkoxyenones. Its pKa is 5.26. Treatment of the sodium salt of the enolate with methyl iodide gives 2-methyl-1,3-cyclohexanedione, which also exists predominantly as the enol. Derivatives Dimedone (5,5-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexanedione) is a well established reagent. Several herbicides against grasses are formal derivatives of 1,3-cyclohexanedione. Examples of commercial products include cycloxydim, clethodim, tralkoxydim, butroxydim, prof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Organization For Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ) is an international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries. Membership requirements are given in Article 3 of the ISO Statutes. ISO was founded on 23 February 1947, and (as of November 2022) it has published over 24,500 international standards covering almost all aspects of technology and manufacturing. It has 809 Technical committees and sub committees to take care of standards development. The organization develops and publishes standardization in all technical and nontechnical fields other than electrical and electronic engineering, which is handled by the IEC.Editors of Encyclopedia Britannica. 3 June 2021.International Organization for Standardization" ''Encyclopedia Britannica''. Retrieved 2022-04-26. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, and works in 167 countries . The three official languages of the ISO are English, Fren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Chemical Industries
Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) was a British chemical company. It was, for much of its history, the largest manufacturer in Britain. It was formed by the merger of four leading British chemical companies in 1926. Its headquarters were at Millbank in London. ICI was a constituent of the FT 30 and later the FTSE 100 indices. ICI made general chemicals, plastics, paints, pharmaceuticals and speciality products, including food ingredients, speciality polymers, electronic materials, fragrances and flavourings. In 2008, it was acquired by AkzoNobel, which immediately sold parts of ICI to Henkel and integrated ICI's remaining operations within its existing organisation. History Development of the business (1926–1944) The company was founded in December 1926 from the merger of four companies: Brunner Mond, Nobel Explosives, the United Alkali Company, and British Dyestuffs Corporation. It established its head office at Millbank in London in 1928. Competing with DuPont a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enol
In organic chemistry, alkenols (shortened to enols) are a type of reactive structure or intermediate in organic chemistry that is represented as an alkene ( olefin) with a hydroxyl group attached to one end of the alkene double bond (). The terms ''enol'' and ''alkenol'' are portmanteaus deriving from "-ene"/"alkene" and the "-ol" suffix indicating the hydroxyl group of alcohols, dropping the terminal "-e" of the first term. Generation of enols often involves removal of a hydrogen adjacent (α-) to the carbonyl group—i.e., deprotonation, its removal as a proton, . When this proton is not returned at the end of the stepwise process, the result is an anion termed an enolate (see images at right). The enolate structures shown are schematic; a more modern representation considers the molecular orbitals that are formed and occupied by electrons in the enolate. Similarly, generation of the enol often is accompanied by "trapping" or masking of the hydroxy group as an ether, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
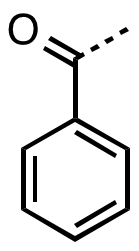
Benzoyl Group
In organic chemistry, benzoyl (, ) is the functional group with the formula C6H5CO-. It can be viewed as benzaldehyde missing one hydrogen. The term "benzoyl" should not be confused with benzyl, which has the formula C6H5CH2. The benzoyl group is given the symbol "Bz". Benzyl is commonly abbreviated "Bn". Sources Benzoyl chloride is a favored source of benzoyl groups, being used to prepare benzoyl ketones, benzamides (benzoyl amides), and benzoate esters. The source of many naturally occurring benzoyl compounds is the thioester benzoyl-CoA. Irradiation of benzil generates benzoyl radicals, which have the formula PhCO. Benzoyl compounds Many ketones contain the benzoyl group. They have the formula C6H5CO–R, an important example being benzophenone. Benzoyl esters and amides are common in organic chemistry. The esters are used as a protecting groups in organic synthesis, which can be easily removed by hydrolysis in dilute basic solution. Benzoyl-β-D-glucoside is a natura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabidopsis Thaliana
''Arabidopsis thaliana'', the thale cress, mouse-ear cress or arabidopsis, is a small flowering plant native to Eurasia and Africa. ''A. thaliana'' is considered a weed; it is found along the shoulders of roads and in disturbed land. A winter annual with a relatively short lifecycle, ''A. thaliana'' is a popular model organism in plant biology and genetics. For a complex multicellular eukaryote, ''A. thaliana'' has a relatively small genome around 135 mega base pairs. It was the first plant to have its genome sequenced, and is a popular tool for understanding the molecular biology of many plant traits, including flower development and light sensing. Description ''Arabidopsis thaliana'' is an annual (rarely biennial) plant, usually growing to 20–25 cm tall. The leaves form a rosette at the base of the plant, with a few leaves also on the flowering stem. The basal leaves are green to slightly purplish in color, 1.5–5 cm long, and 2–10 mm broad, with an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monocotyledon
Monocotyledons (), commonly referred to as monocots, (Lilianae ''sensu'' Chase & Reveal) are grass and grass-like flowering plants (angiosperms), the seeds of which typically contain only one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. They constitute one of the major groups into which the flowering plants have traditionally been divided; the rest of the flowering plants have two cotyledons and are classified as dicotyledons, or dicots. Monocotyledons have almost always been recognized as a group, but with various taxonomic ranks and under several different names. The APG III system of 2009 recognises a clade called "monocots" but does not assign it to a taxonomic rank. The monocotyledons include about 60,000 species, about a quarter of all angiosperms. The largest family in this group (and in the flowering plants as a whole) by number of species are the orchids (family Orchidaceae), with more than 20,000 species. About half as many species belong to the true grasses ( Poaceae), which are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides. Biosynthesis is usually synonymous with anabolism. The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |