|
Mesentery
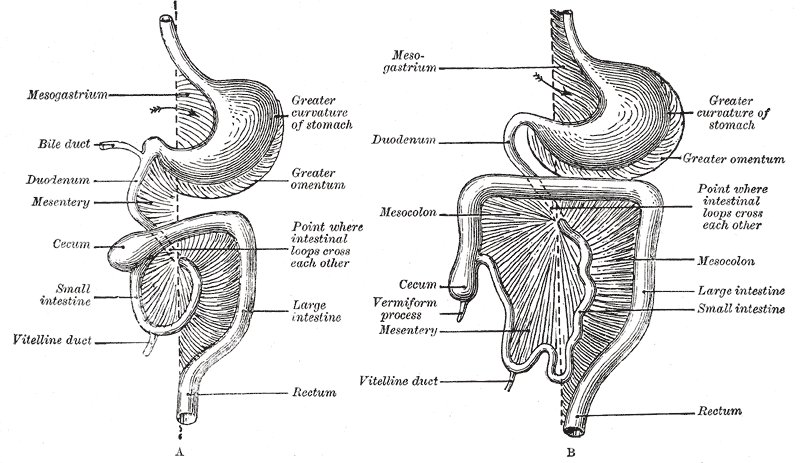
The mesentery is an organ that attaches the intestines to the posterior abdominal wall in humans and is formed by the double fold of peritoneum. It helps in storing fat and allowing blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves to supply the intestines, among other functions. The mesocolon was thought to be a fragmented structure, with all named parts—the ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid mesocolons, the mesoappendix, and the mesorectum—separately terminating their insertion into the posterior abdominal wall. However, in 2012, new microscopic and electron microscopic examinations showed the mesocolon to be a single structure derived from the duodenojejunal flexure and extending to the distal mesorectal layer. Thus, the mesentery is an internal organ. Structure The mesentery of the small intestine arises from the root of the mesentery (or mesenteric root) and is the part connected with the structures in front of the vertebral column. The root is narrow, about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mesothelium supported by a thin layer of connective tissue. This peritoneal lining of the cavity supports many of the abdominal organs and serves as a conduit for their blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves. The abdominal cavity (the space bounded by the vertebrae, abdominal muscles, diaphragm, and pelvic floor) is different from the intraperitoneal space (located within the abdominal cavity but wrapped in peritoneum). The structures within the intraperitoneal space are called "intraperitoneal" (e.g., the stomach and intestines), the structures in the abdominal cavity that are located behind the intraperitoneal space are called " retroperitoneal" (e.g., the kidneys), and those structures below the intraperitoneal space are calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Omentum
The greater omentum (also the great omentum, omentum majus, gastrocolic omentum, epiploon, or, especially in animals, caul) is a large apron-like fold of visceral peritoneum that hangs down from the stomach. It extends from the greater curvature of the stomach, passing in front of the small intestines and doubles back to ascend to the transverse colon before reaching to the posterior abdominal wall. The greater omentum is larger than the lesser omentum, which hangs down from the liver to the lesser curvature. The common anatomical term "epiploic" derives from "epiploon", from the Greek ''epipleein'', meaning to float or sail on, since the greater omentum appears to float on the surface of the intestines. It is the first structure observed when the abdominal cavity is opened anteriorly (from the front). Structure The greater omentum is the larger of the two peritoneal folds. It consists of a double sheet of peritoneum, folded on itself so that it has four layers. The two layer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retroperitoneum
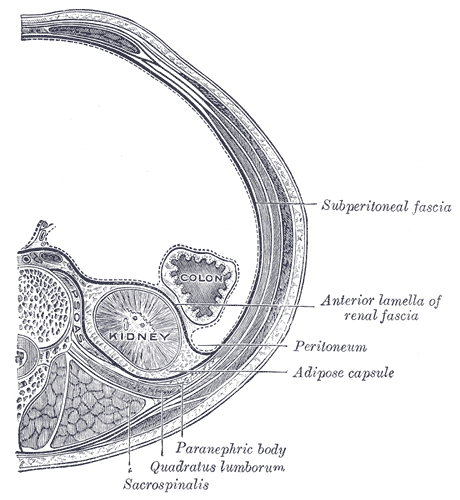
The retroperitoneal space (retroperitoneum) is the anatomical space (sometimes a potential space) behind (''retro'') the peritoneum. It has no specific delineating anatomical structures. Organs are retroperitoneal if they have peritoneum on their anterior side only. Structures that are not suspended by mesentery in the abdominal cavity and that lie between the parietal peritoneum and abdominal wall are classified as retroperitoneal. This is different from organs that are not retroperitoneal, which have peritoneum on their posterior side and are suspended by mesentery in the abdominal cavity. The retroperitoneum can be further subdivided into the following: *Perirenal (or perinephric) space *Anterior pararenal (or paranephric) space *Posterior pararenal (or paranephric) space Retroperitoneal structures Structures that lie behind the peritoneum are termed "retroperitoneal". Organs that were once suspended within the abdominal cavity by mesentery but migrated posterior to the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vermiform Appendix
The appendix (or vermiform appendix; also cecal r caecalappendix; vermix; or vermiform process) is a finger-like, blind-ended tube connected to the cecum, from which it develops in the embryo. The cecum is a pouch-like structure of the large intestine, located at the junction of the small and the large intestines. The term " vermiform" comes from Latin and means "worm-shaped". The appendix was once considered a vestigial organ, but this view has changed since the early 2000s. Research suggests that the appendix may serve an important purpose. In particular, it may serve as a reservoir for beneficial gut bacteria. Structure The human appendix averages in length but can range from . The diameter of the appendix is , and more than is considered a thickened or inflamed appendix. The longest appendix ever removed was long. The appendix is usually located in the lower right quadrant of the abdomen, near the right hip bone. The base of the appendix is located beneath the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ileum
The ileum () is the final section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms posterior intestine or distal intestine may be used instead of ileum. Its main function is to absorb vitamin B12, bile salts, and whatever products of digestion that were not absorbed by the jejunum. The ileum follows the duodenum and jejunum and is separated from the cecum by the ileocecal valve (ICV). In humans, the ileum is about 2–4 m long, and the pH is usually between 7 and 8 (neutral or slightly basic). ''Ileum ''is derived from the Greek word ''eilein'', meaning "to twist up tightly". Structure The ileum is the third and final part of the small intestine. It follows the jejunum and ends at the ileocecal junction, where the terminal ileum communicates with the cecum of the large intestine through the ileocecal valve. The ileum, along with the jejunum, is susp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ (anatomy), organ in the human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract where most of the #Absorption, absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the pancreatic duct to aid in digestion. The small intestine is about long and folds many times to fit in the abdomen. Although it is longer than the large intestine, it is called the small intestine because it is narrower in diameter. The small intestine has three distinct regions – the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. The duodenum, the shortest, is where preparation for absorption through small finger-like protrusions called intestinal villus, villi begins. The jejunum is specialized for the absorption through its lining by enterocytes: small nutrient particles which have been previously digested by enzymes in the duodenum. The main function of the ileum is to absorb vitamin B12, vita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intestine
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores ( ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore ( osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The human gastrointestinal tract consists of the esophagus, stomach, and intestines, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigmoid Colon
The sigmoid colon (or pelvic colon) is the part of the large intestine that is closest to the rectum and anus. It forms a loop that averages about in length. The loop is typically shaped like a Greek letter sigma (ς) or Latin letter S (thus '' sigma'' + '' -oid''). This part of the colon normally lies within the pelvis, but due to its freedom of movement it is liable to be displaced into the abdominal cavity. Structure The sigmoid colon begins at the superior aperture of the lesser pelvis, where it is continuous with the iliac colon, and passes transversely across the front of the sacrum to the right side of the pelvis. It then curves on itself and turns toward the left to reach the middle line at the level of the third piece of the sacrum, where it bends downward and ends in the rectum. Its function is to expel solid and gaseous waste from the gastrointestinal tract. The curving path it takes toward the anus allows it to store gas in the superior arched portion, enab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Large Intestine
The large intestine, also known as the large bowel, is the last part of the gastrointestinal tract and of the digestive system in tetrapods. Water is absorbed here and the remaining waste material is stored in the rectum as feces before being removed by defecation. The colon is the longest portion of the large intestine, and the terms are often used interchangeably but most sources define the large intestine as the combination of the cecum, colon, rectum, and anal canal. Some other sources exclude the anal canal. In humans, the large intestine begins in the right iliac region of the pelvis, just at or below the waist, where it is joined to the end of the small intestine at the cecum, via the ileocecal valve. It then continues as the colon ascending the abdomen, across the width of the abdominal cavity as the transverse colon, and then descending to the rectum and its endpoint at the anal canal. Overall, in humans, the large intestine is about long, which is abo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colectomy
Colectomy ('' col-'' + '' -ectomy'') is bowel resection of the large bowel ( colon). It consists of the surgical removal of any extent of the colon, usually segmental resection (partial colectomy). In extreme cases where the entire large intestine is removed, it is called total colectomy, and proctocolectomy ('' procto-'' + ''colectomy'') denotes that the rectum is included. Indications Some of the most common indications for colectomy are: * Colon cancer * Diverticulitis and diverticular disease of the large intestine * Trauma * Inflammatory bowel disease such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease. Colectomy neither cures nor eliminates Crohn's disease, instead only removing part of the entire diseased large intestine. A colectomy is considered a "cure" for ulcerative colitis because the disease attacks only the large intestine and therefore will not be able to flare up again if the entire large intestine (cecum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duodenojejunal Flexure
The duodenojejunal flexure or duodenojejunal junction is the border between the duodenum and the jejunum. Structure The ascending portion of the duodenum ascends on the left side of the aorta, as far as the level of the upper border of the second lumbar vertebra. At this point, it turns abruptly forward to merge with the jejunum, forming the duodenojejunal flexure. This forms the beginning of the jejunum. The duodenojejunal flexure is surrounded by the suspensory muscle of the duodenum. It is retroperitoneal, so is less mobile than the jejunum that comes after it, helping to stabilise the jejunum. The duodenojejunal flexure lies in front of the left psoas major muscle, the left renal artery, and the left renal vein. It is covered in front, and partly at the sides, by peritoneum continuous with the left portion of the mesentery. Clinical significance The ligament of Treitz, a peritoneal fold, from the right crus of diaphragm, is an identification point for the duodenojejunal flex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton). The pelvic region of the trunk includes the bony pelvis, the pelvic cavity (the space enclosed by the bony pelvis), the pelvic floor, below the pelvic cavity, and the perineum, below the pelvic floor. The pelvic skeleton is formed in the area of the back, by the sacrum and the coccyx and anteriorly and to the left and right sides, by a pair of hip bones. The two hip bones connect the spine with the lower limbs. They are attached to the sacrum posteriorly, connected to each other anteriorly, and joined with the two femurs at the hip joints. The gap enclosed by the bony pelvis, called the pelvic cavity, is the section of the body underneath the abdomen and mainly consists of the reproductive organs (sex organs) and the rectum, while the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |