Retroperitoneum on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The retroperitoneal space (retroperitoneum) is the spatium, anatomical space (sometimes a potential space) behind (''retro'') the peritoneum. It has no specific delineating anatomical structures. Organs are retroperitoneal if they have peritoneum on their anterior side only. Structures that are not suspended by mesentery in the abdominal cavity and that lie between the parietal peritoneum and abdominal wall are classified as retroperitoneal.
This is different from organs that are not retroperitoneal, which have peritoneum on their posterior side and are suspended by mesentery in the abdominal cavity.
The retroperitoneum can be further subdivided into the following:
*Perirenal (or perinephric) space
*Anterior pararenal (or paranephric) space
*Posterior pararenal (or paranephric) space
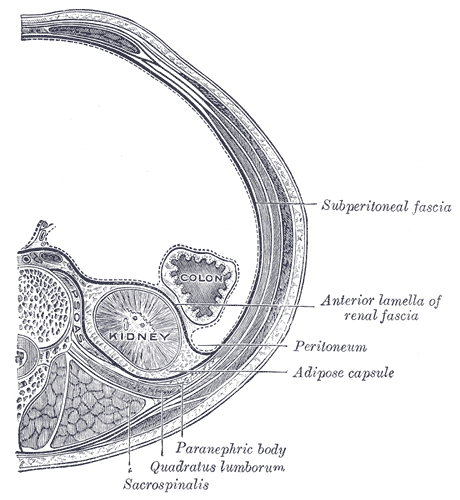
 ;Perirenal space
It is also called the perinephric space. Bounded by the anterior and posterior leaves of the renal fascia. It contains the following structures:
* Adrenal gland
* Kidney
* Renal blood flow, Renal vessels
*Perirenal fat, which is also called the "adipose capsule of the kidney" and may be regarded as being part of the renal capsule
;Perirenal space
It is also called the perinephric space. Bounded by the anterior and posterior leaves of the renal fascia. It contains the following structures:
* Adrenal gland
* Kidney
* Renal blood flow, Renal vessels
*Perirenal fat, which is also called the "adipose capsule of the kidney" and may be regarded as being part of the renal capsuleUniversity of Michigan
- Lab Manual - Kidneys & Retroperitoneum ;Anterior pararenal space Bounded by the posterior layer of peritoneum and the anterior leaf of the renal fascia. It contains the following structures: * Pancreas * Ascending and descending colon (anatomy), colon * Duodenum ;Posterior pararenal space Bounded by the posterior leaf of the renal fascia and the muscles of the posterior abdominal wall. It contains only fat ("pararenal fat"), and is also called the "paranephric body", or "pararenal fat body".
Retroperitoneal structures
Structures that lie behind the peritoneum are termed "retroperitoneal". Organs that were once suspended within the abdominal cavity by mesentery but migrated posterior to the peritoneum during the course of embryogenesis to become retroperitoneal are considered to be secondarily retroperitoneal organs. * Primarily retroperitoneal, meaning the structures were retroperitoneal during the entirety of development: ** urinary *** adrenal glands *** kidneys *** ureter ** circulatory *** aorta *** inferior vena cava ** digestive system, digestive ***anal canal * Secondarily retroperitoneal, meaning the structures initially were suspended in mesentery and later migrated behind the peritoneum during development ** the duodenum, except for the proximal first segment, which is intraperitoneal ** ascending and descending portions of the colon (anatomy), colon (but not the transverse colon, sigmoid and the cecum) ** pancreas, except for the tail, which is intraperitonealSubdivisions

 ;Perirenal space
It is also called the perinephric space. Bounded by the anterior and posterior leaves of the renal fascia. It contains the following structures:
* Adrenal gland
* Kidney
* Renal blood flow, Renal vessels
*Perirenal fat, which is also called the "adipose capsule of the kidney" and may be regarded as being part of the renal capsule
;Perirenal space
It is also called the perinephric space. Bounded by the anterior and posterior leaves of the renal fascia. It contains the following structures:
* Adrenal gland
* Kidney
* Renal blood flow, Renal vessels
*Perirenal fat, which is also called the "adipose capsule of the kidney" and may be regarded as being part of the renal capsule- Lab Manual - Kidneys & Retroperitoneum ;Anterior pararenal space Bounded by the posterior layer of peritoneum and the anterior leaf of the renal fascia. It contains the following structures: * Pancreas * Ascending and descending colon (anatomy), colon * Duodenum ;Posterior pararenal space Bounded by the posterior leaf of the renal fascia and the muscles of the posterior abdominal wall. It contains only fat ("pararenal fat"), and is also called the "paranephric body", or "pararenal fat body".
Clinical significance
Bleeding from a blood vessel or structure in the retroperitoneal such as the aorta or inferior vena cava into the retroperitoneal space can lead to a retroperitoneal hemorrhage. * Retroperitoneal fibrosis * Retroperitoneal lymph node dissection It is also possible to have a cancer, neoplasm in this area, more commonly a metastasis; or very rarely a primary neoplasm. The most common type is a sarcoma followed by lymphoma, germ cell tumor, extragonadal germ cell tumor, and Gastrointestinal stromal tumor, Gastrointestinal stromal tumor/GIST. Examples of tumors include **Primary peritoneal carcinoma, Primary retroperitoneal carcinoma **Pseudomyxoma peritonei **Examples of sarcomas include: **Soft-tissue sarcoma ***liposarcoma ***leiomyosarcoma ***Undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma, a clinically distinct sarcoma of the areaSee also
* IntraperitonealReferences
{{Authority control Abdomen