|
Medial Frontal Gyrus
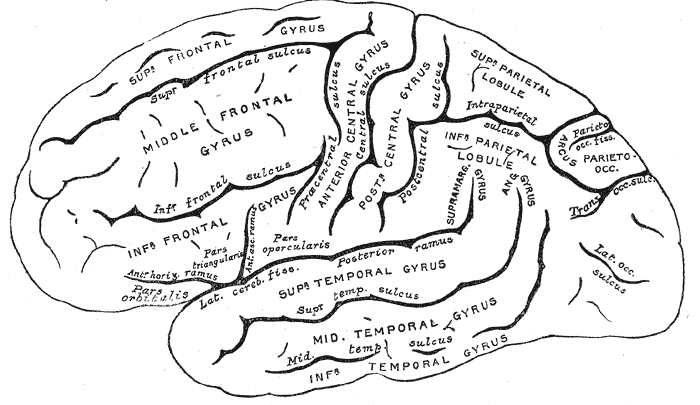
The superior frontal gyrus is situated above the superior frontal sulcus and is continued on to the medial surface of the hemisphere, the medial frontal gyrus. The medial and superior frontal gyri are two of the frontal gyri of the frontal lobe The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a groove betwe .... The portion on the lateral surface of the hemisphere is usually more or less completely subdivided into an upper and a lower part by an antero-posterior sulcus, the paramedial sulcus, which, however, is frequently interrupted by bridging gyri. There is some evidence that it plays a role in executive mechanisms. References Gyri Frontal lobe {{neuroanatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Frontal Gyrus
In neuroanatomy, the superior frontal gyrus (SFG, also marginal gyrus) is a gyrus – a ridge on the brain's cerebral cortex – which makes up about one third of the frontal lobe. It is bounded laterally by the superior frontal sulcus. The superior frontal gyrus is one of the frontal gyri. Function Self-awareness In fMRI experiments, Goldberg ''et al.'' have found evidence that the superior frontal gyrus is involved in self-awareness, in coordination with the action of the sensory system. Laughter In 1998, neurosurgeon Itzhak Fried described a 16-year-old female patient (referred to as "patient AK") who laughed when her SFG was stimulated with electric current during treatment for epilepsy. Electrical stimulation was applied to the cortical surface of AK's left frontal lobe while an attempt was made to locate the focus of her epileptic seizures (which were never accompanied by laughter). Fried identified a 2 cm by 2 cm area on the left SFG where stimulation produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Frontal Sulcus
The superior frontal sulcus is a sulcus between the superior frontal gyrus and the middle frontal gyrus. See also * Inferior frontal sulcus The inferior frontal sulcus is a sulcus between the middle frontal gyrus and the inferior frontal gyrus. See also * Superior frontal sulcus Additional images File:Inferior frontal sulcus animation small.gif, Animation. Inferior frontal sulcus ... Additional images File:Human brain superior-lateral view description.JPG, Human brain seen from top. Superior frontal sulcus labelled as #7. Sulci (neuroanatomy) Frontal lobe {{neuroanatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontal Gyri
The frontal gyri are four gyri of the frontal lobe in the brain. These are four horizontally oriented, parallel convolutions, of the frontal lobe. The other main gyrus of the frontal lobe is the precentral gyrus which is vertically oriented, and runs parallel with the precentral sulcus. The uppermost of the four gyri is the superior frontal gyrus, below this is the middle frontal gyrus, and below this is the inferior frontal gyrus. Continuing from the superior frontal gyrus on the lateral surface, into the uppermost part of the medial surface of the hemisphere is the medial frontal gyrus. The inferior frontal gyrus includes Broca's area. The lowest part of the inferior frontal gyrus rests on the orbital part of the frontal bone. Gyri Superior The superior frontal gyrus makes up about a third of the frontal lobe. It is bounded laterally by the superior frontal sulcus. Medial Middle It has been recently found that this region participates during linguistic tasks. More ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontal Lobe
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a groove between tissues called the central sulcus and from the temporal lobe by a deeper groove called the lateral sulcus (Sylvian fissure). The most anterior rounded part of the frontal lobe (though not well-defined) is known as the frontal pole, one of the three poles of the cerebrum. The frontal lobe is covered by the frontal cortex. The frontal cortex includes the premotor cortex, and the primary motor cortex – parts of the motor cortex. The front part of the frontal cortex is covered by the prefrontal cortex. There are four principal gyri in the frontal lobe. The precentral gyrus is directly anterior to the central sulcus, running parallel to it and contains the primary motor cortex, which controls voluntary movements of specific body parts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyrus
In neuroanatomy, a gyrus (pl. gyri) is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulci (depressions or furrows; sg. ''sulcus''). Gyri and sulci create the folded appearance of the brain in humans and other mammals. Structure The gyri are part of a system of folds and ridges that create a larger surface area for the human brain and other mammalian brains. Because the brain is confined to the skull, brain size is limited. Ridges and depressions create folds allowing a larger cortical surface area, and greater cognitive function, to exist in the confines of a smaller cranium. Development The human brain undergoes gyrification during fetal and neonatal development. In embryonic development, all mammalian brains begin as smooth structures derived from the neural tube. A cerebral cortex without surface convolutions is lissencephalic, meaning 'smooth-brained'. As development continues, gyri and sulci begin to take shape on the fetal brain, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyri
In neuroanatomy, a gyrus (pl. gyri) is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulci (depressions or furrows; sg. ''sulcus''). Gyri and sulci create the folded appearance of the brain in humans and other mammals. Structure The gyri are part of a system of folds and ridges that create a larger surface area for the human brain and other mammalian brains. Because the brain is confined to the skull, brain size is limited. Ridges and depressions create folds allowing a larger cortical surface area, and greater cognitive function, to exist in the confines of a smaller cranium. Development The human brain undergoes gyrification during fetal and neonatal development. In embryonic development, all mammalian brains begin as smooth structures derived from the neural tube. A cerebral cortex without surface convolutions is lissencephalic, meaning 'smooth-brained'. As development continues, gyri and sulci begin to take shape on the fetal brain, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |