|
Measurements Of Neutrino Speed
Measurements of neutrino speed have been conducted as tests of special relativity and for the determination of the mass of neutrinos. Astronomical searches investigate whether light and neutrinos emitted simultaneously from a distant source are arriving simultaneously on Earth. Terrestrial searches include time of flight measurements using synchronized clocks, and direct comparison of neutrino speed with the speed of other particles. Since it is established that neutrinos possess mass, the speed of neutrinos of kinetic energies ranging from MeV to GeV should be slightly lower than the speed of light in accordance with special relativity. Existing measurements provided upper limits for deviations from light speed of approximately 10−9, or a few parts per billion. Within the margin of error this is consistent with no deviation at all. Overview It was assumed for a long time in the framework of the standard model of particle physics that neutrinos are massless. Thus, they shou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tests Of Special Relativity
Special relativity is a physical theory that plays a fundamental role in the description of all physical phenomena, as long as gravitation is not significant. Many experiments played (and still play) an important role in its development and justification. The strength of the theory lies in its unique ability to correctly predict to high precision the outcome of an extremely diverse range of experiments. Repeats of many of those experiments are still being conducted with steadily increased precision, with modern experiments focusing on effects such as at the Planck scale and in the neutrino sector. Their results are consistent with the predictions of special relativity. Collections of various tests were given by Jakob Laub, Zhang, Mattingly, Clifford Will, and Roberts/Schleif. Special relativity is restricted to flat spacetime, ''i.e.'', to all phenomena without significant influence of gravitation. The latter lies in the domain of general relativity and the corresponding tests of ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tachyon
A tachyon () or tachyonic particle is a hypothetical particle that always travels faster than light. Physicists believe that faster-than-light particles cannot exist because they are not consistent with the known laws of physics. If such particles did exist they could be used to send signals faster than light. According to the theory of relativity this would violate causality, leading to logical paradoxes such as the grandfather paradox. Tachyons would exhibit the unusual property of increasing in speed as their energy decreases, and would require infinite energy to slow down to the speed of light. No verifiable experimental evidence for the existence of such particles has been found. In the 1967 paper that coined the term, Gerald Feinberg proposed that tachyonic particles could be made from excitations of a quantum field with imaginary mass. However, it was soon realized that Feinberg's model did not in fact allow for superluminal (faster-than-light) particles or signals and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadron
In particle physics, a hadron (; grc, ἁδρός, hadrós; "stout, thick") is a composite subatomic particle made of two or more quarks held together by the strong interaction. They are analogous to molecules that are held together by the electric force. Most of the mass of ordinary matter comes from two hadrons: the proton and the neutron, while most of the mass of the protons and neutrons is in turn due to the binding energy of their constituent quarks, due to the strong force. Hadrons are categorized into two broad families: baryons, made of an odd number of quarks (usually three quarks) and mesons, made of an even number of quarks (usually two quarks: one quark and one antiquark). Protons and neutrons (which make the majority of the mass of an atom) are examples of baryons; pions are an example of a meson. "Exotic" hadrons, containing more than three valence quarks, have been discovered in recent years. A tetraquark state (an exotic meson), named the Z(4430), was discove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaon
KAON (Karlsruhe ontology) is an ontology infrastructure developed by the University of Karlsruhe and the Research Center for Information Technologies in Karlsruhe. Its first incarnation was developed in 2002 and supported an enhanced version of RDF ontologies. Several tools like the graphical ontology editor OIModeler or the KAON Server were based on KAON. There are ontology learning companion tools which take non-annotated natural language text as input: TextToOnto (KAON-based) and Text2Onto (KAON2-based). Text2Onto is based on the Probabilistic Ontology Model (POM). In 2005, the first version of KAON2 was released, offering fast reasoning support for OWL ontologies. KAON2 is not backward-compatible with KAON. KAON2 is developed as a joint effort of the Information Process Engineering (IPE) at the Research Center for Information Technologies (FZI), the Institute of Applied Informatics and Formal Description Methods (AIFB) at the University of Karlsruhe, and the Information Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pion
In particle physics, a pion (or a pi meson, denoted with the Greek letter pi: ) is any of three subatomic particles: , , and . Each pion consists of a quark and an antiquark and is therefore a meson. Pions are the lightest mesons and, more generally, the lightest hadrons. They are unstable, with the charged pions and decaying after a mean lifetime of 26.033 nanoseconds ( seconds), and the neutral pion decaying after a much shorter lifetime of 85 attoseconds ( seconds). Charged pions most often decay into muons and muon neutrinos, while neutral pions generally decay into gamma rays. The exchange of virtual pions, along with vector, rho and omega mesons, provides an explanation for the residual strong force between nucleons. Pions are not produced in radioactive decay, but commonly are in high-energy collisions between hadrons. Pions also result from some matter–antimatter annihilation events. All types of pions are also produced in natural processes wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
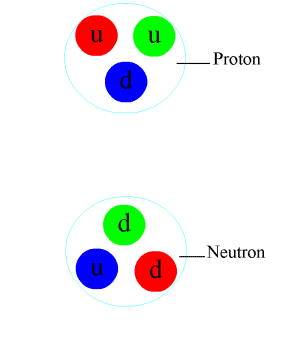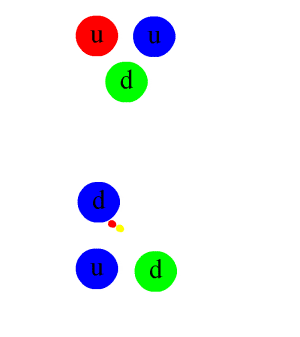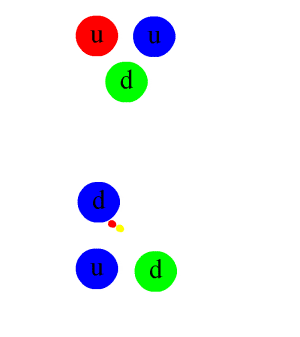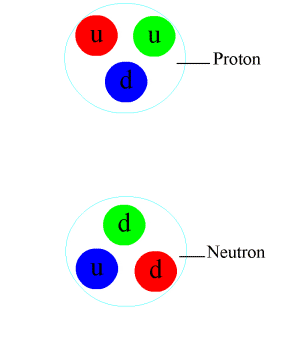
Proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' elementary charge. Its mass is slightly less than that of a neutron and 1,836 times the mass of an electron (the proton–electron mass ratio). Protons and neutrons, each with masses of approximately one atomic mass unit, are jointly referred to as "nucleons" (particles present in atomic nuclei). One or more protons are present in the nucleus of every atom. They provide the attractive electrostatic central force which binds the atomic electrons. The number of protons in the nucleus is the defining property of an element, and is referred to as the atomic number (represented by the symbol ''Z''). Since each element has a unique number of protons, each element has its own unique atomic number, which determines the number of atomic electrons and consequently the chemical characteristics of the element. The word ''proton'' is Greek for "first", and this name was given to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accelerator Neutrino
An accelerator neutrino is a human-generated neutrino or antineutrino obtained using particle accelerators, in which beam of protons is accelerated and collided with a fixed target, producing mesons (mainly pions) which then decay into neutrinos. Depending on the energy of the accelerated protons and whether mesons decay in flight or at rest it is possible to generate neutrinos of a different flavour, energy and angular distribution. Accelerator neutrinos are used to study neutrino interactions and neutrino oscillations taking advantage of high intensity of neutrino beams, as well as a possibility to control and understand their type and kinematic properties to a much greater extent than for neutrinos from other sources. Muon neutrino beam production The process of the muon neutrino or muon antineutrino beam production consists of the following steps: * Acceleration of a primary proton beam in a particle accelerator. * Proton beam collision with a fixed target. In such a collis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muon
A muon ( ; from the Greek letter mu (μ) used to represent it) is an elementary particle similar to the electron, with an electric charge of −1 '' e'' and a spin of , but with a much greater mass. It is classified as a lepton. As with other leptons, the muon is not thought to be composed of any simpler particles; that is, it is a fundamental particle. The muon is an unstable subatomic particle with a mean lifetime of , much longer than many other subatomic particles. As with the decay of the non-elementary neutron (with a lifetime around 15 minutes), muon decay is slow (by subatomic standards) because the decay is mediated only by the weak interaction (rather than the more powerful strong interaction or electromagnetic interaction), and because the mass difference between the muon and the set of its decay products is small, providing few kinetic degrees of freedom for decay. Muon decay almost always produces at least three particles, which must include an electron o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory
Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (Fermilab), located just outside Batavia, Illinois, near Chicago, is a United States Department of Energy national laboratory specializing in high-energy particle physics. Since 2007, Fermilab has been operated by the Fermi Research Alliance, a joint venture of the University of Chicago, and the Universities Research Association (URA). Fermilab is a part of the Illinois Technology and Research Corridor. Fermilab's Main Injector, two miles (3.3 km) in circumference, is the laboratory's most powerful particle accelerator. The accelerator complex that feeds the Main Injector is under upgrade, and construction of the first building for the new PIP-II linear accelerator began in 2020. Until 2011, Fermilab was the home of the 6.28 km (3.90 mi) circumference Tevatron accelerator. The ring-shaped tunnels of the Tevatron and the Main Injector are visible from the air and by satellite. Fermilab aims to become a world center in neutri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Searches For Lorentz Violation
Modern may refer to: History * Modern history ** Early Modern period ** Late Modern period *** 18th century *** 19th century *** 20th century ** Contemporary history * Moderns, a faction of Freemasonry that existed in the 18th century Philosophy and sociology * Modernity, a loosely defined concept delineating a number of societal, economic and ideological features that contrast with "pre-modern" times or societies ** Late modernity Art * Modernism ** Modernist poetry * Modern art, a form of art * Modern dance, a dance form developed in the early 20th century * Modern architecture, a broad movement and period in architectural history * Modern music (other) Geography *Modra, a Slovak city, referred to in the German language as "Modern" Typography * Modern (typeface), a raster font packaged with Windows XP * Another name for the typeface classification known as Didone (typography) * Modern, a generic font family name for fixed-pitch serif and sans serif fonts ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indirect Determinations Of Neutrino Speed
Indirect, the opposite of direct, may refer to: *Indirect approach, a battle strategy *Indirect DNA damage, caused by UV-photons *Indirect agonist or indirect-acting agonist, a substance that enhances the release or action of an endogenous neurotransmitter *Indirect speech, a form of speech *Indirect costs, costs that are not directly accountable to a particular function or product *Indirect self-reference, describes an object referring to itself indirectly *Indirect effect, a principle of European Community Law *Indirect finance, where borrowers borrow funds from the financial market through indirect means *Indirection In computer programming, indirection (also called dereferencing) is the ability to reference something using a name, reference, or container instead of the value itself. The most common form of indirection is the act of manipulating a value throug ..., the ability to reference something in computer programming * Indirect transmission, infections passing from one hos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorentz-violating Neutrino Oscillations
Lorentz-violating neutrino oscillation refers to the quantum phenomenon of neutrino oscillations described in a framework that allows the breakdown of Lorentz invariance. Today, neutrino oscillation or change of one type of neutrino into another is an experimentally verified fact; however, the details of the underlying theory responsible for these processes remain an open issue and an active field of study. The conventional model of neutrino oscillations assumes that neutrinos are massive, which provides a successful description of a wide variety of experiments; however, there are a few oscillation signals that cannot be accommodated within this model, which motivates the study of other descriptions. In a theory with Lorentz violation, neutrinos can oscillate with and without masses and many other novel effects described below appear. The generalization of the theory by incorporating Lorentz violation has shown to provide alternative scenarios to explain all the established experim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |