|
Matrix-assisted Laser Desorption Electrospray Ionization
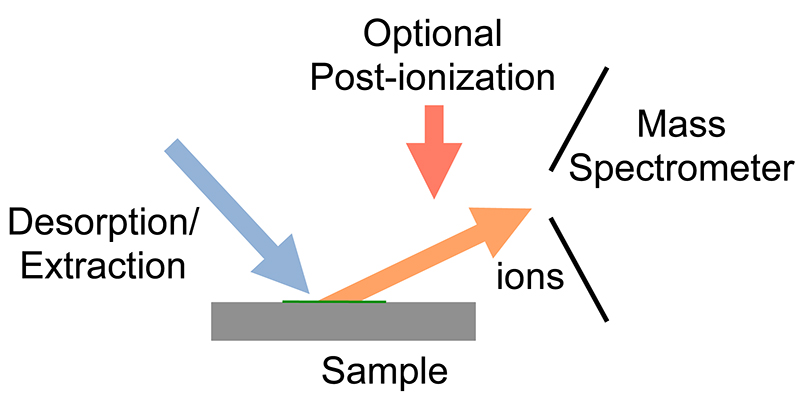
Matrix-assisted laser desorption electrospray ionization (MALDESI) was first introduced in 2006 as a novel Ambient ionization, ambient ionization technique which combines the benefits of Electrospray ionization, electrospray ionization (ESI) and Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI). An Infrared, infrared (IR) or Ultraviolet, ultraviolet (UV) laser can be utilized in MALDESI to Excited state, resonantly excite an endogenous or exogenous matrix. The term ‘Matrix (mass spectrometry), matrix’ refers to any molecule that is present in large excess and absorbs the energy of the laser, thus facilitating desorption of analyte molecules. The original MALDESI design was implemented using common Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization, organic matrices, similar to those used in MALDI, along with a UV laser. The current MALDESI source employs endogenous water or a thin layer of exogenously deposited ice as the energy-absorbing ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambient Ionization
Ambient ionization is a form of ionization in which ions are formed in an ion source outside the mass spectrometer without sample preparation or separation. Ions can be formed by extraction into charged electrospray droplets, thermally desorbed and ionized by chemical ionization, or laser desorbed or ablated and post-ionized before they enter the mass spectrometer. Solid-liquid extraction Solid-liquid extraction based ambient ionization is based on the use of a charged spray, for example electrospray to create a liquid film on the sample surface. Molecules on the surface are extracted into the solvent. The action of the primary droplets hitting the surface produces secondary droplets that are the source of ions for the mass spectrometer. Desorption electrospray ionization (DESI) is one of the original ambient ionization sources and uses an electrospray source to create charged droplets that are directed at a solid sample. The charged droplets pick up the sample through interacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MATLAB
MATLAB (an abbreviation of "MATrix LABoratory") is a proprietary multi-paradigm programming language and numeric computing environment developed by MathWorks. MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementation of algorithms, creation of user interfaces, and interfacing with programs written in other languages. Although MATLAB is intended primarily for numeric computing, an optional toolbox uses the MuPAD symbolic engine allowing access to symbolic computing abilities. An additional package, Simulink, adds graphical multi-domain simulation and model-based design for dynamic and embedded systems. As of 2020, MATLAB has more than 4 million users worldwide. They come from various backgrounds of engineering, science, and economics. History Origins MATLAB was invented by mathematician and computer programmer Cleve Moler. The idea for MATLAB was based on his 1960s PhD thesis. Moler became a math professor at the University of New Mexico and starte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flame Retardant
The term flame retardants subsumes a diverse group of chemicals that are added to manufactured materials, such as plastics and textiles, and surface finishes and coatings. Flame retardants are activated by the presence of an ignition source and are intended to prevent or slow the further development of ignition by a variety of different physical and chemical methods. They may be added as a copolymer during the polymerisation process, or later added to the polymer at a moulding or extrusion process or (particularly for textiles) applied as a topical finish. Mineral flame retardants are typically additive while organohalogen and organophosphorus compounds can be either reactive or additive. Classes Both Reactive and Additive Flame retardants types, can be further separated into four distinct classes: * Minerals such as aluminium hydroxide (ATH), magnesium hydroxide (MDH), huntite and hydromagnesite, various hydrates, red phosphorus, and boron compounds, mostly borates. * Organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell. Neurotransmitters are released from synaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft where they are able to interact with neurotransmitter receptors on the target cell. The neurotransmitter's effect on the target cell is determined by the receptor it binds. Many neurotransmitters are synthesized from simple and plentiful precursors such as amino acids, which are readily available and often require a small number of biosynthetic steps for conversion. Neurotransmitters are essential to the function of complex neural systems. The exact number of unique neurotransmitters in humans is unknown, but more than 100 have been identified. Common neurotransmitters include glutamate, GABA, acetylcholine, glycine and norepinephrine. Mechanism and cycle Synthes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
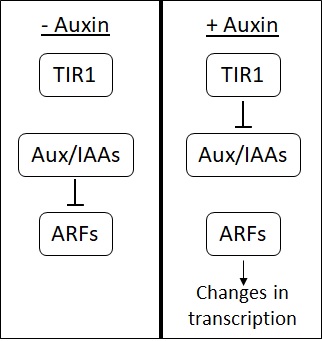
Indole-3-acetic Acid
Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA, 3-IAA) is the most common naturally occurring plant hormone of the auxin class. It is the best known of the auxins, and has been the subject of extensive studies by plant physiologists. IAA is a derivative of indole, containing a carboxymethyl substituent. It is a colorless solid that is soluble in polar organic solvents. Biosynthesis IAA is predominantly produced in cells of the apex (bud) and very young leaves of a plant. Plants can synthesize IAA by several independent biosynthetic pathways. Four of them start from tryptophan, but there is also a biosynthetic pathway independent of tryptophan. Plants mainly produce IAA from tryptophan through indole-3-pyruvic acid. IAA is also produced from tryptophan through indole-3-acetaldoxime in ''Arabidopsis thaliana''. In rats, IAA is a product of both endogenous and colonic microbial metabolism from dietary tryptophan along with tryptophol. This was first observed in rats infected by ''Trypanosoma bruc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auxin
Auxins (plural of auxin ) are a class of plant hormones (or plant-growth regulators) with some morphogen-like characteristics. Auxins play a cardinal role in coordination of many growth and behavioral processes in plant life cycles and are essential for plant body development. The Dutch biologist Frits Warmolt Went first described auxins and their role in plant growth in the 1920s. Kenneth V. Thimann became the first to isolate one of these phytohormones and to determine its chemical structure as indole-3-acetic acid (IAA). Went and Thimann co-authored a book on plant hormones, ''Phytohormones'', in 1937. Overview Auxins were the first of the major plant hormones to be discovered. They derive their name from the Greek word αυξειν (''auxein'' – "to grow/increase"). Auxin is present in all parts of a plant, although in very different concentrations. The concentration in each position is crucial developmental information, so it is subject to tight regulation through both meta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabidopsis
''Arabidopsis'' (rockcress) is a genus in the family Brassicaceae. They are small flowering plants related to cabbage and mustard. This genus is of great interest since it contains thale cress (''Arabidopsis thaliana''), one of the model organisms used for studying plant biology and the first plant to have its entire genome sequenced. Changes in thale cress are easily observed, making it a very useful model. Status Currently, the genus ''Arabidopsis'' has nine species and a further eight subspecies recognised. This delimitation is quite recent and is based on morphological and molecular phylogenies by O'Kane and Al-Shehbaz and others. Their findings confirm the species formerly included in ''Arabidopsis'' made it polyphyletic. The most recent reclassification moves two species previously placed in ''Cardaminopsis'' and ''Hylandra'' and three species of ''Arabis'' into ''Arabidopsis'', but excludes 50 that have been moved into the new genera '' Beringia, Crucihimalaya, Ianhedge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HeLa
HeLa (; also Hela or hela) is an immortalized cell line used in scientific research. It is the oldest and most commonly used human cell line. The line is derived from cervical cancer cells taken on February 8, 1951, named after Henrietta Lacks, a 31-year-old African-American mother of five, who died of cancer on October 4, 1951. The cell line was found to be remarkably durable and prolific, which allows it to be used extensively in scientific study. The cells from Lacks's cancerous cervical tumor were taken without her knowledge or consent, which was common practice in the United States at the time. Cell biologist George Otto Gey found that they could be kept alive, and developed a cell line. Previously, cells cultured from other human cells would only survive for a few days. Cells from Lacks's tumor behaved differently. History Origin In 1951, a patient named Henrietta Lacks was admitted to the Johns Hopkins Hospital with symptoms of irregular vaginal bleeding, and was s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolomics
Metabolomics is the scientific study of chemical processes involving metabolites, the small molecule substrates, intermediates, and products of cell metabolism. Specifically, metabolomics is the "systematic study of the unique chemical fingerprints that specific cellular processes leave behind", the study of their small-molecule metabolite profiles. The metabolome represents the complete set of metabolites in a biological cell, tissue, organ, or organism, which are the end products of cellular processes. Messenger RNA (mRNA), gene expression data, and proteomics, proteomic analyses reveal the set of gene products being produced in the cell, data that represents one aspect of cellular function. Conversely, metabolic profiling can give an instantaneous snapshot of the physiology of that cell, and thus, metabolomics provides a direct "functional readout of the physiological state" of an organism. There are indeed quantifiable correlations between the metabolome and the other cellular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Hence, peptides fall under the broad chemical classes of biological polymers and oligomers, alongside nucleic acids, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, and others. A polypeptide that contains more than approximately 50 amino acids is known as a protein. Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional way, often bound to ligands such as coenzymes and cofactors, or to another protein or other macromolecule such as DNA or RNA, or to complex macromolecular assemblies. Amino acids that have been incorporated into peptides are termed residues. A water molecule is released during formation of each amide bond.. All peptides except cyclic pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing energy, signaling, and acting as structural components of cell membranes. Lipids have applications in the cosmetic and food industries, and in nanotechnology. Lipids may be broadly defined as hydrophobic or amphiphilic small molecules; the amphiphilic nature of some lipids allows them to form structures such as vesicles, multilamellar/unilamellar liposomes, or membranes in an aqueous environment. Biological lipids originate entirely or in part from two distinct types of biochemical subunits or "building-blocks": ketoacyl and isoprene groups. Using this approach, lipids may be divided into eight categories: fatty acyls, glycerolipids, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids, saccharolipids, and polyketides (derived from condensati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass-to-charge Ratio
The mass-to-charge ratio (''m''/''Q'') is a physical quantity relating the ''mass'' (quantity of matter) and the ''electric charge'' of a given particle, expressed in units of kilograms per coulomb (kg/C). It is most widely used in the electrodynamics of charged particles, e.g. in electron optics and ion optics. It appears in the scientific fields of electron microscopy, cathode ray tubes, accelerator physics, nuclear physics, Auger electron spectroscopy, cosmology and mass spectrometry. The importance of the mass-to-charge ratio, according to classical electrodynamics, is that two particles with the same mass-to-charge ratio move in the same path in a vacuum, when subjected to the same electric and magnetic fields. On rare occasions, the thomson has been used as its unit in the field of mass spectrometry. Some disciplines use the charge-to-mass ratio (''Q''/''m'') instead, which is the multiplicative inverse of the mass-to-charge ratio. The CODATA recommended value for an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)