|
Martinism
Martinism is a form of Christian mysticism and esoteric Christianity concerned with the fall of the first man, his state of material privation from his divine source, and the process of his return, called 'Reintegration'. As a mystical tradition, it was first transmitted through a Masonic high-degree system established around 1740 in France by Martinez de Pasqually, and later propagated in different forms by his two students Louis Claude de Saint-Martin and Jean-Baptiste Willermoz. The term ''Martinism'' applies to both this particular doctrine and the teachings of the reorganized "Martinist Order" founded in 1886 by Augustin Chaboseau and Gérard Encausse (aka Papus). It was not used at the tradition's inception in the 18th century. This confusing disambiguation has been a problem since the late 18th century, where the term ''Martinism'' was already used interchangeably between the teachings of Louis-Claude de Saint-Martin and Martinez de Pasqually, and the works of the firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martinism Red
Martinism is a form of Christian mysticism and esoteric Christianity concerned with the fall of the first man, his state of material privation from his divine source, and the process of his return, called 'Reintegration'. As a mystical tradition, it was first transmitted through a Masonic high-degree system established around 1740 in France by Martinez de Pasqually, and later propagated in different forms by his two students Louis Claude de Saint-Martin and Jean-Baptiste Willermoz. The term ''Martinism'' applies to both this particular doctrine and the teachings of the reorganized "Martinist Order" founded in 1886 by Augustin Chaboseau and Gérard Encausse (aka Papus). It was not used at the tradition's inception in the 18th century. This confusing disambiguation has been a problem since the late 18th century, where the term ''Martinism'' was already used interchangeably between the teachings of Louis-Claude de Saint-Martin and Martinez de Pasqually, and the works of the fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of Knight-Masons Elect Priests Of The Universe
The Order of Knight-Masons Elect Priests of the Universe (french: Ordre des Chevaliers Maçons Élus Coëns de l’Univers) or simply Élus Coëns (sometimes misspelled ‘Elus Cohens’ or ‘Kohens’, Hebrew for ‘Elect Priests’), was a theurgical organisation founded by Martinez de Pasqually. It appeared in France in the second half of the 18th century and is the first branch of Martinist tradition, otherwise known as Martinezism. Doctrine General teaching The Élus Coëns is an esoteric Christian order founded in 1767, with its focus on establishing an invisible church, independent of any earthly structure, to find the path that leads to the hidden knowledge of nature in anticipation of the coming destruction of the material Church. That is to say, by a progressive initiation and a direct knowledge of God to obtain the primordial unity, which was lost since the fall of Adam—the Reintegration—through the practice of theurgy, which relied on complex ceremonia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martinezism
The Order of Knight-Masons Elect Priests of the Universe (french: Ordre des Chevaliers Maçons Élus Coëns de l’Univers) or simply Élus Coëns (sometimes misspelled ‘Elus Cohens’ or ‘Kohens’, Hebrew for ‘Elect Priests’), was a theurgical organisation founded by Martinez de Pasqually. It appeared in France in the second half of the 18th century and is the first branch of Martinist tradition, otherwise known as Martinezism. Doctrine General teaching The Élus Coëns is an esoteric Christian order founded in 1767, with its focus on establishing an invisible church, independent of any earthly structure, to find the path that leads to the hidden knowledge of nature in anticipation of the coming destruction of the material Church. That is to say, by a progressive initiation and a direct knowledge of God to obtain the primordial unity, which was lost since the fall of Adam—the Reintegration—through the practice of theurgy, which relied on complex ceremonia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treatise On The Reintegration Of Beings
The ''Treatise on the Reintegration of Beings into Their Original Estate, Virtues and Powers both Spiritual and Divine'' (french: Traité de la Réintégration des êtres dans leurs premières propriétés, vertus et puissance spirituelles et divines) is a book written by Martinès de Pasqually—a theurgist and theosopher of uncertain origin—in 1772–1773. Initially, the book was intended as an internal document and doctrine for the Order of Knight-Masons Elect Priests of the Universe, which was founded by Martinès de Pasqually. After the death of Pasqually, the book outgrew the narrow framework of the Order, having influenced the spiritual and philosophical life of its time. It continues to influence occultism, mysticism, and spiritual philosophy as several Martinist organisations and orders around the world consider it one of the fundamental books of their tradition. Characteristic The theosopher Pasqually wanted to understand the world from the religion, through inne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martinez De Pasqually
Jacques de Livron Joachim de la Tour de la Casa Martinez de Pasqually (1727?–1774) was a theurgist and theosopher of uncertain origin. He was the founder of the l'Ordre de Chevaliers Maçons Élus Coëns de l'Univers - Commonly referred to as the 'Elus Cohens' in 1761. He was the tutor, initiator and friend of Louis-Claude de Saint-Martin and Jean-Baptiste Willermoz. Biography Martinez de Pasqually, whose biography is continually being researched, due to the lack of documentation, appears in the history of French freemasonry in 1754. His exact date and place of birth, as well as his true nationality is unknown. A number of authors proposed that he was a Spanish Jew but later researches counter that this was unlikely. Certain similarities between Pasqually's theurgy and Portuguese hermetic thought led philosopher Sampaio Bruno (1857-1915) to argue that he was probably of Portuguese origin.Sampaio Bruno, José Pereira de (1904), O Encoberto. Porto: Livraria Moreira In 1772 P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Baptiste Willermoz
Jean-Baptiste Willermoz (10 July 1730 – 29 May 1824) was a French Freemason and Martinist who played an important role in the establishment of various systems of Masonic high-degrees in his time in both France and Germany. Biography Jean-Baptiste Willermoz was born on 10 July 1730 in Lyon. He was the oldest of 12 children. He lived mainly in Lyon. He was the brother of Pierre-Jacques Willermoz, a physician and chemist who also worked on the ''Encyclopédie'' of Diderot and D'Alembert. He was a manufacturer in silk and silver at Rue des Quatre-Chapeaux, and as a volunteer director of charities, he played an important role in the European freemasonry of his time. As such he was initiated at the age of 20 and became Venerable Master of his lodge at 23. As a mystic, passionate about the secret nature of initiation, he contributed to the creation of the Regular Grand Lodge of Masters in Lyon and became its Grand Master in 1761. The Grand Lodge practised the seven Masonic hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Ambelain
Robert Ambelain (2 September 1907 – 27 May 1997) was a French essayist. He was involved in the esoteric Masonic Martinist movement and claimed to have revived the Primitive Scottish Rite. He has written several works, such as ''The Masonic Secret'', in which he tells the most relevant aspects of Masonic lodges. The reawakening of the Élus Coëns In 1943, Robert Ambelain, whose mystical name was ''Aurifer'', revived the Order of the '' Élus Coëns.'' The other two esotericists who signed the Charter to revive the Order were Robert Amadou (1924 – 2006) and Roger Ménard. Georges Bogé de Lagrèze (1882-1946) was elected Grand Master and Ambelain his Deputy Grand Master. The degrees of this new Order were the Operative degrees of the original ''Élus Coëns'', reconstituted with the scarce material Ambelain had in his hands. The name of the Order was later changed in ''“Ordre Martiniste des Élus Cohens”'', where candidates were also initiated into the usual thre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Claude De Saint-Martin
Louis Claude de Saint-Martin (18 January 1743 – 14 October 1803) was a French philosopher, known as ''le philosophe inconnu'', the name under which his works were published; he was an influential of the mystic and human mind evolution and became the inspiration for the founding of the Martinist Order. Léonce de Saint-Martin, composer and organist, was a distant relative of Louis-Claude de Saint-Martin. Life He was born at Amboise, into a family from the lesser nobility of central France. As his father wished, he tried first law and then the army as a profession. While in the garrison at Bordeaux, he came under the influence of Martinez de Pasqually, usually called a Portuguese Jew (although later research has revealed the probability that he was a Spanish Catholic), who taught a species of mysticism drawn from cabbalistic sources, and endeavoured to found thereon a secret cult with magical or theurgical rites. Around September 1768 Saint-Martin was introduced to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
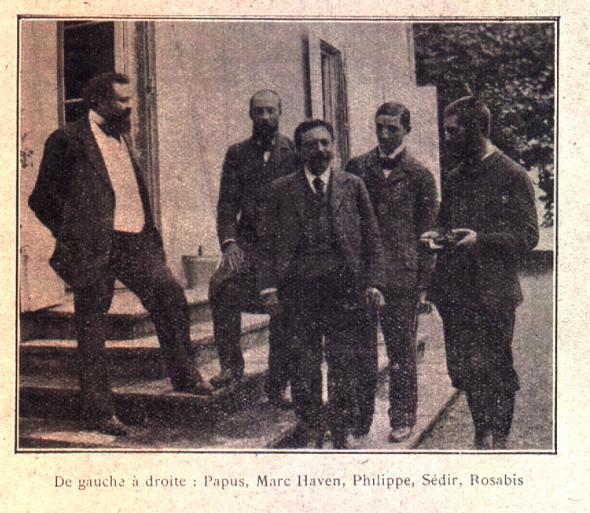
Gérard Encausse
Gérard Anaclet Vincent Encausse (July 13, 1865 – 25 October 1916), whose esotericism, esoteric pseudonyms were Papus and Tau Vincent, was a French people, French physician, hypnotist, and popularizer of occultism, who founded the modern martinism, Martinist Order. Early life Gerard Encausse was born at A Coruña in Galicia (Spain) on July 13, 1865, of a Spanish mother and a French father, Louis Encausse, a chemist. His family moved to Paris when he was four years old, and he received his education there. As a young man, Encausse spent a great deal of time at the Bibliothèque Nationale studying the Kabbalah, occult tarot, magic (paranormal), magic and alchemy, and the writings of Eliphas Levi, Eliphas Lévi. He joined the French Theosophical Society shortly after it was founded by Madame Blavatsky in 1884–1885, but he resigned soon after joining because he disliked the Society's emphasis on Eastern occultism. Career Overview In 1888, he co-founded his own group, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis-Claude De Saint-Martin
Louis Claude de Saint-Martin (18 January 1743 – 14 October 1803) was a French philosopher, known as ''le philosophe inconnu'', the name under which his works were published; he was an influential of the mystic and human mind evolution and became the inspiration for the founding of the Martinist Order. Léonce de Saint-Martin, composer and organist, was a distant relative of Louis-Claude de Saint-Martin. Life He was born at Amboise, into a family from the lesser nobility of central France. As his father wished, he tried first law and then the army as a profession. While in the garrison at Bordeaux, he came under the influence of Martinez de Pasqually, usually called a Portuguese Jew (although later research has revealed the probability that he was a Spanish Catholic), who taught a species of mysticism drawn from cabbalistic sources, and endeavoured to found thereon a secret cult with magical or theurgical rites. Around September 1768 Saint-Martin was introduced to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willermozism
The Rectified Scottish Rite, also known as Order of Knights Beneficent of the Holy City or Knights Benefactor of the Holy City (french: Chevalier bienfaisant de la Cité sainte) is a Christian Masonic rite founded in Lyon (France) in 1778. Origins of this Rite The Rite was mainly elaborated by Jean-Baptiste Willermoz. This famous Mason reformed the French branch of the Rite of Strict Observance at the Congress of Gauls in 1778, including some items coming from the Elect Cohen Order and denying the Templar legacy. This date may be considered as the birth of the Rectified Scottish Rite. It came from several initiatory systems of the 18th century: * The Order of Knight Masons of the Elect Cohens of the Universe, of Martines de Pasqually, * The Templar Strict Observance, Knight Masonry born in Germany in the middle of the 18th century then spread in the rest of Europe, * Scottish Masonry (all the existing higher degrees, when it was not yet structured), * Craft Masonry in 3 de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustin Chaboseau
Augustin Chaboseau (17 June 1868 – 2 January 1946) is the original organizer and promulgation officer of the Traditional Martinist Order (TMO), Occultist and Historian. Notably, his founding was in partnership with Papus in 1888. In his early years, he had the necessary talents, skills and abilities that led him to become a medical doctor and it was with the knowledge gained from working with the responsibility of saving people's lives that he was able to successful transition into his work with the TMO. He has contributed to numerous journals and is the author of an essay on Buddhist philosophy Buddhist philosophy refers to the philosophical investigations and systems of inquiry that developed among various schools of Buddhism in India following the parinirvana of The Buddha and later spread throughout Asia. The Buddhist path combin ... (1891) and a History of Brittany before the thirteenth century (1926), World War I interior ministry. References {{DEFAULTSORT: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |