|
Jean-Baptiste Willermoz
Jean-Baptiste Willermoz (10 July 1730 – 29 May 1824) was a French Freemason and Martinist who played an important role in the establishment of various systems of Masonic high-degrees in his time in both France and Germany. Biography Jean-Baptiste Willermoz was born on 10 July 1730 in Lyon. He was the oldest of 12 children. He lived mainly in Lyon. He was the brother of Pierre-Jacques Willermoz, a physician and chemist who also worked on the ''Encyclopédie'' of Diderot and D'Alembert. He was a manufacturer in silk and silver at Rue des Quatre-Chapeaux, and as a volunteer director of charities, he played an important role in the European freemasonry of his time. As such he was initiated at the age of 20 and became Venerable Master of his lodge at 23. As a mystic, passionate about the secret nature of initiation, he contributed to the creation of the Regular Grand Lodge of Masters in Lyon and became its Grand Master in 1761. The Grand Lodge practised the seven Masonic hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyon
Lyon,, ; Occitan: ''Lion'', hist. ''Lionés'' also spelled in English as Lyons, is the third-largest city and second-largest metropolitan area of France. It is located at the confluence of the rivers Rhône and Saône, to the northwest of the French Alps, southeast of Paris, north of Marseille, southwest of Geneva, northeast of Saint-Étienne. The City of Lyon proper had a population of 522,969 in 2019 within its small municipal territory of , but together with its suburbs and exurbs the Lyon metropolitan area had a population of 2,280,845 that same year, the second most populated in France. Lyon and 58 suburban municipalities have formed since 2015 the Metropolis of Lyon, a directly elected metropolitan authority now in charge of most urban issues, with a population of 1,411,571 in 2019. Lyon is the prefecture of the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region and seat of the Departmental Council of Rhône (whose jurisdiction, however, no longer extends over the Metropolis of Lyo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Versailles (city)
Versailles () is a commune in the department of the Yvelines, Île-de-France, renowned worldwide for the Château de Versailles and the gardens of Versailles, designated UNESCO World Heritage Sites. Located in the western suburbs of the French capital, from the centre of Paris, Versailles is a wealthy suburb of Paris with a service-based economy and is a major tourist destination. According to the 2017 census, the population of the city is 85,862 inhabitants, down from a peak of 94,145 in 1975.Population en historique depuis 1968 INSEE A new town founded at the will of King , Versai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cagliostro
Count Alessandro di Cagliostro (, ; 2 June 1743 – 26 August 1795) was the alias of the Italian occultist Giuseppe Balsamo (; in French usually referred to as Joseph Balsamo). Cagliostro was an Italian adventurer and self-styled magician. He became a glamorous figure associated with the royal courts of Europe where he pursued various occult arts, including psychic healing, alchemy and scrying. His reputation lingered for many decades after his death, but continued to deteriorate, as he came to be regarded as a charlatan and impostor, this view fortified by the savage attack of Thomas Carlyle (1795–1881) in 1833, who pronounced him the "Quack of Quacks". Later works—such as that of W.R.H. Trowbridge (1866–1938) in his ''Cagliostro: the Splendour and Misery of a Master of Magic'' (1910), attempted a rehabilitation. Biography Origin The history of Cagliostro is shrouded in rumour, propaganda, and mysticism. Some effort was expended to ascertain his true identity when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph De Maistre
Joseph Marie, comte de Maistre (; 1 April 1753 – 26 February 1821) was a Savoyard philosopher, writer, lawyer, and diplomat who advocated social hierarchy and monarchy in the period immediately following the French Revolution. Despite his close personal and intellectual ties with France, Maistre was throughout his life a subject of the Kingdom of Sardinia, which he served as a member of the Savoy Senate (1787–1792), ambassador to Russia (1803–1817), and minister of state to the court in Turin (1817–1821). A key figure of the Counter-Enlightenment, Maistre regarded monarchy both as a divinely sanctioned institution and as the only stable form of government. He called for the restoration of the House of Bourbon to the throne of France and for the ultimate authority of the Pope in temporal matters. Maistre argued that the rationalist rejection of Christianity was directly responsible for the disorder and bloodshed which followed the French Revolution of 1789. Biography ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
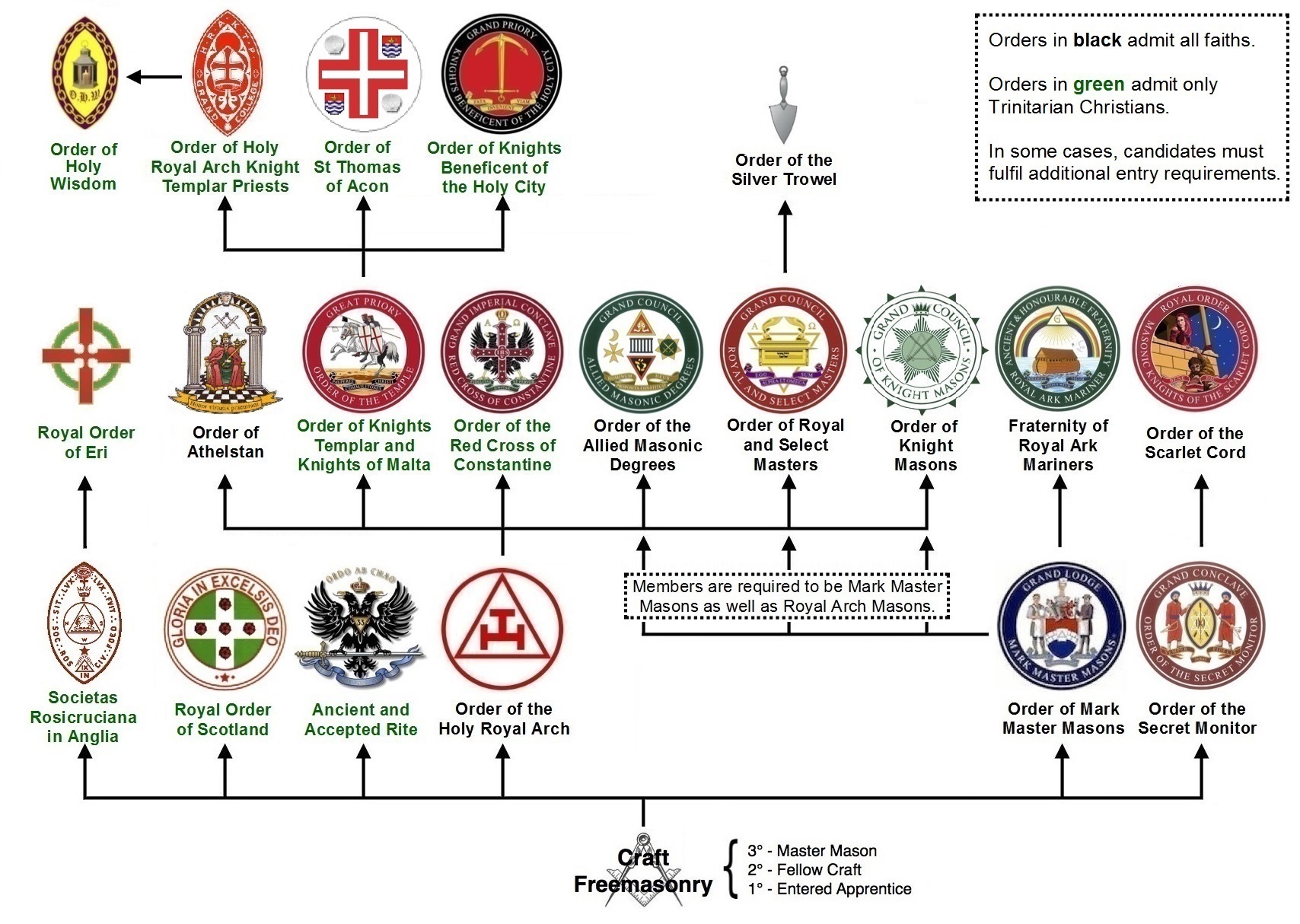
Rectified Scottish Rite
The Rectified Scottish Rite, also known as Order of Knights Beneficent of the Holy City or Knights Benefactor of the Holy City (french: Chevalier bienfaisant de la Cité sainte) is a Christian Masonic rite founded in Lyon (France) in 1778. Origins of this Rite The Rite was mainly elaborated by Jean-Baptiste Willermoz. This famous Mason reformed the French branch of the Rite of Strict Observance at the Congress of Gauls in 1778, including some items coming from the Elect Cohen Order and denying the Templar legacy. This date may be considered as the birth of the Rectified Scottish Rite. It came from several initiatory systems of the 18th century: * The Order of Knight Masons of the Elect Cohens of the Universe, of Martines de Pasqually, * The Templar Strict Observance, Knight Masonry born in Germany in the middle of the 18th century then spread in the rest of Europe, * Scottish Masonry (all the existing higher degrees, when it was not yet structured), * Craft Masonry in 3 deg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Work (Hermeticism)
Great Work ( la, magnum opus) is a term used in Hermeticism and occult traditions descended from it, such as Thelema. Accomplishing the Great Work, symbolized as the creation of the philosopher's stone, represents the culmination of the spiritual path, the attainment of enlightenment, or the rescue of the human soul from the unconscious forces which bind it. The Great Work signifies the spiritual path towards self-transcendence in its entirety. This is the process of bringing unconscious complexes into the conscious awareness, in order to integrate them back into oneself. Ceremonial magic Eliphas Levi Eliphas Levi (1810–1875), one of the first modern ceremonial magicians and inspiration for the Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn, discussed the Great Work at length, giving it a spiritual meaning by analogy to the alchemical of 'perfecting' lead into gold and mortality into immortality: He further defined it as such: Thelema Within Thelema, the Great Work is general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panacea
In Greek mythology, Panacea (Greek ''Πανάκεια'', Panakeia), a goddess of universal remedy, was the daughter of Asclepius and Epione. Panacea and her four sisters each performed a facet of Apollo's art: * Panacea (the goddess of universal health) * Hygieia ("Hygiene", the goddess/personification of health, cleanliness, and sanitation) * Iaso (the goddess of recuperation from illness) * Aceso (the goddess of the healing process) * Aglæa/Ægle (the goddess of beauty, splendor, glory, magnificence, and adornment) Panacea also had four brothers: * Podaleirus, one of the two kings of Tricca, who was skilled in diagnostics * Machaon, the other king of Tricca, who was a master surgeon (these two took part in the Trojan War until Machaon was killed by Penthesilea, queen of the Amazons) * Telesphoros, who devoted his life to serving Asclepius * Aratus, Panacea's half-brother, a Greek hero and the patron/liberator of Sicyon However, portrayals of the family were not always c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosopher's Stone
The philosopher's stone or more properly philosophers' stone (Arabic: حجر الفلاسفة, , la, lapis philosophorum), is a mythic alchemical substance capable of turning base metals such as mercury into gold (, from the Greek , "gold", and , "to make") or silver. It is also called the elixir of life, useful for rejuvenation and for achieving immortality; for many centuries, it was the most sought-after goal in alchemy. The philosopher's stone was the central symbol of the mystical terminology of alchemy, symbolizing perfection at its finest, enlightenment, and heavenly bliss. Efforts to discover the philosopher's stone were known as the Magnum Opus ("Great Work"). History Antiquity The earliest known written mention of the philosopher's stone is in the ''Cheirokmeta'' by Zosimos of Panopolis (c. 300 AD). Alchemical writers assign a longer history. Elias Ashmole and the anonymous author of ''Gloria Mundi'' (1620) claim that its history goes back to Adam, who acquired t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rite Of Strict Observance
The Rite of Strict Observance was a Rite of Freemasonry, a series of progressive degrees that were conferred by the Order of Strict Observance, a Masonic body of the 18th century. History Baron Karl Gotthelf von Hund (1722–1776) introduced a new "Scottish" Rite to Germany, which he renamed "Rectified Masonry" and, after 1764, the "Strict Observance", while referring to the English system of Freemasonry as the "Late Observance." The Rite appealed to German national pride, attracted the non-nobility, and was allegedly directed by "Unknown Superiors". The Strict Observance was particularly devoted to the reform of Masonry, with special reference to the elimination of the occult sciences which at the time were widely practiced in many lodges, and the establishment of cohesion and homogeneity in Masonry through the enforcement of strict discipline, the regulation of functions, etc. By 1768 the Rite of Strict Observance counted some forty lodges. Despite its initial popularity, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Gotthelf Von Hund
Karl Gotthelf, Baron von Hund und Altengrotkau (11 September 1722, Unwürde - 8 November 1776, Meiningen) was a German freemason. In 1751, he founded the Rite of Strict Observance. Childhood and youth Karl Gotthelf von Hund came from Silesia, descended from Henry von Hund und Altengrotkau (ca 1480). Henry's son was Commander of the Order of Malta in Glatz, where in 1518 and 1523 he held the Office of the Governor. Documents from around 1300 show John and Christopher von Hund, but it is not proven that they belong to the line that later became Altengrotkau. Karl Gotthelf's father, Joachim Hildebrand von Hund was chamberlain and Electoral Saxon landowner. The family of von Hund and Altengrotkau owned their estate from 1607 and from 1704 the estate of Upper Kittlitz in Upper Lusatia. Karl's father died very early, so that his still minor son inherited the estate. The guardianship of the son and his mother fell to Caspar Heinrich von Rodewitz. Karl Gotthelf was the youngest of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis-Claude De Saint-Martin
Louis Claude de Saint-Martin (18 January 1743 – 14 October 1803) was a French philosopher, known as ''le philosophe inconnu'', the name under which his works were published; he was an influential of the mystic and human mind evolution and became the inspiration for the founding of the Martinist Order. Léonce de Saint-Martin, composer and organist, was a distant relative of Louis-Claude de Saint-Martin. Life He was born at Amboise, into a family from the lesser nobility of central France. As his father wished, he tried first law and then the army as a profession. While in the garrison at Bordeaux, he came under the influence of Martinez de Pasqually, usually called a Portuguese Jew (although later research has revealed the probability that he was a Spanish Catholic), who taught a species of mysticism drawn from cabbalistic sources, and endeavoured to found thereon a secret cult with magical or theurgical rites. Around September 1768 Saint-Martin was introduced to the El ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)