|
Mammalian Wide Interspersed Repeat
Mammalian-wide interspersed repeats (MIRs) are transposable elements in the genomes of some organisms and belong to the group of Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs). Incidence MIRs are found in all mammals (including marsupials). In human It is estimated that there are around 368,000 MIRs in the human genome. Structure The MIR consensus sequence is 260 basepairs long and has an A/T-rich 3' end. Propagation Like other Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs), MIR elements used the machinery of LINE elements for their propagation in the genome, which took place around 130 million years ago. They cannot retrotranspose anymore since the loss of activity of the required reverse transcriptase A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to generate complementary DNA (cDNA) from an RNA template, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B to replicate their genomes, .... History of disc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
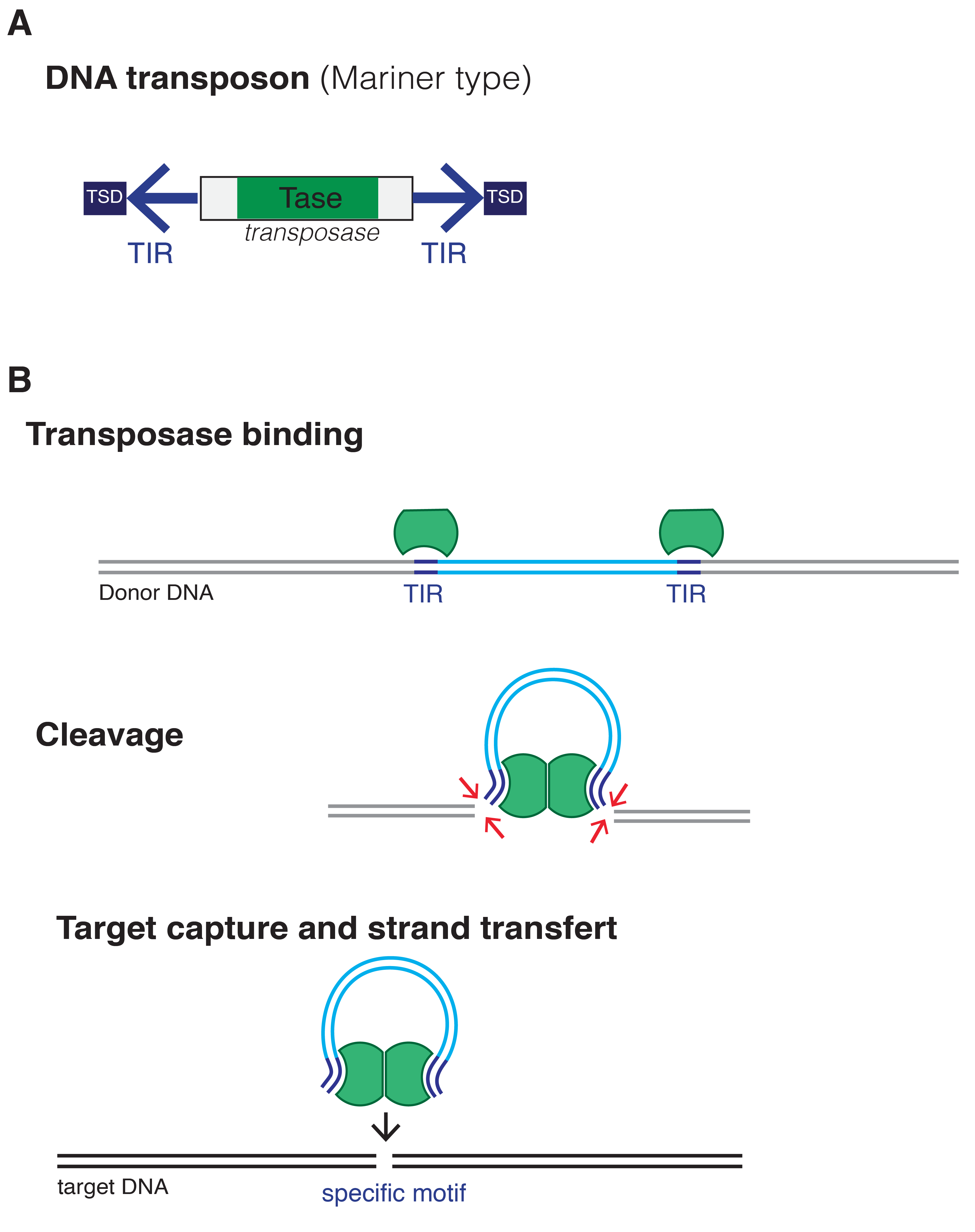
Transposable Elements
A transposable element (TE, transposon, or jumping gene) is a nucleic acid sequence in DNA that can change its position within a genome, sometimes creating or reversing mutations and altering the cell's genetic identity and genome size. Transposition often results in duplication of the same genetic material. Barbara McClintock's discovery of them earned her a Nobel Prize in 1983. Its importance in personalized medicine is becoming increasingly relevant, as well as gaining more attention in data analytics given the difficulty of analysis in very high dimensional spaces. Transposable elements make up a large fraction of the genome and are responsible for much of the C-value, mass of DNA in a eukaryotic cell. Although TEs are selfish genetic elements, many are important in genome function and evolution. Transposons are also very useful to researchers as a means to alter DNA inside a living organism. There are at least two classes of TEs: Class I TEs or retrotransposons generally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short Interspersed Nuclear Element
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) are non-autonomous, non-coding transposable elements (TEs) that are about 100 to 700 base pairs in length. They are a class of retrotransposons, DNA elements that amplify themselves throughout eukaryotic genomes, often through RNA intermediates. SINEs compose about 13% of the mammalian genome. The internal regions of SINEs originate from tRNA and remain highly conserved, suggesting positive pressure to preserve structure and function of SINEs. While SINEs are present in many species of vertebrates and invertebrates, SINEs are often lineage specific, making them useful markers of divergent evolution between species. Copy number variation and mutations in the SINE sequence make it possible to construct phylogenies based on differences in SINEs between species. SINEs are also implicated in certain types of genetic disease in humans and other eukaryotes. In essence, short interspersed nuclear elements are genetic parasites which have evolv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla ( cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, seals, and others). In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade, together with Saur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marsupial
Marsupials are any members of the mammalian infraclass Marsupialia. All extant marsupials are endemic to Australasia, Wallacea and the Americas. A distinctive characteristic common to most of these species is that the young are carried in a pouch. Marsupials include opossums, Tasmanian devils, kangaroos, koalas, wombats, wallabies, bandicoots, and the extinct thylacine. Marsupials represent the clade originating from the last common ancestor of extant metatherians, the group containing all mammals more closely related to marsupials than to placentals. They give birth to relatively undeveloped young that often reside in a pouch located on their mothers' abdomen for a certain amount of time. Close to 70% of the 334 extant species occur on the Australian continent (the mainland, Tasmania, New Guinea and nearby islands). The remaining 30% are found in the Americas—primarily in South America, thirteen in Central America, and one species, the Virginia opossum, in North America, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Genome
The human genome is a complete set of nucleic acid sequences for humans, encoded as DNA within the 23 chromosome pairs in cell nuclei and in a small DNA molecule found within individual mitochondria. These are usually treated separately as the nuclear genome and the mitochondrial genome. Human genomes include both protein-coding DNA sequences and various types of DNA that does not encode proteins. The latter is a diverse category that includes DNA coding for non-translated RNA, such as that for ribosomal RNA, transfer RNA, ribozymes, small nuclear RNAs, and several types of regulatory RNAs. It also includes promoters and their associated gene-regulatory elements, DNA playing structural and replicatory roles, such as scaffolding regions, telomeres, centromeres, and origins of replication, plus large numbers of transposable elements, inserted viral DNA, non-functional pseudogenes and simple, highly-repetitive sequences. Introns make up a large percentage of non-coding DNA. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consensus Sequence
In molecular biology and bioinformatics, the consensus sequence (or canonical sequence) is the calculated order of most frequent residues, either nucleotide or amino acid, found at each position in a sequence alignment. It serves as a simplified representation of the population. It represents the results of multiple sequence alignments in which related sequences are compared to each other and similar sequence motifs are calculated. Such information is important when considering sequence-dependent enzymes such as RNA polymerase.Pierce, Benjamin A. 2002. Genetics : A Conceptual Approach. 1st ed. New York: W.H. Freeman and Co. Biological significance A protein binding site, represented by a consensus sequence, may be a short sequence of nucleotides which is found several times in the genome and is thought to play the same role in its different locations. For example, many transcription factors recognize particular patterns in the promoters of the genes they regulate. In the same way, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Interspersed Nuclear Element
Long interspersed nuclear elements (LINEs) (also known as long interspersed nucleotide elements or long interspersed elements) are a group of non-LTR (long terminal repeat) retrotransposons that are widespread in the genome of many eukaryotes. They make up around 21.1% of the human genome. LINEs make up a family of transposons, where each LINE is about 7,000 base pairs long. LINEs are transcribed into mRNA and translated into protein that acts as a reverse transcriptase. The reverse transcriptase makes a DNA copy of the LINE RNA that can be integrated into the genome at a new site. The only abundant LINE in humans is LINE1. The human genome contains an estimated 100,000 truncated and 4,000 full-length LINE-1 elements. Due to the accumulation of random mutations, the sequence of many LINEs has degenerated to the extent that they are no longer transcribed or translated. Comparisons of LINE DNA sequences can be used to date transposon insertion in the genome. History of discovery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retrotransposition
A transposable element (TE, transposon, or jumping gene) is a nucleic acid sequence in DNA that can change its position within a genome, sometimes creating or reversing mutations and altering the cell's genetic identity and genome size. Transposition often results in duplication of the same genetic material. Barbara McClintock's discovery of them earned her a Nobel Prize in 1983. Its importance in personalized medicine is becoming increasingly relevant, as well as gaining more attention in data analytics given the difficulty of analysis in very high dimensional spaces. Transposable elements make up a large fraction of the genome and are responsible for much of the mass of DNA in a eukaryotic cell. Although TEs are selfish genetic elements, many are important in genome function and evolution. Transposons are also very useful to researchers as a means to alter DNA inside a living organism. There are at least two classes of TEs: Class I TEs or retrotransposons generally functio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reverse Transcriptase
A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to generate complementary DNA (cDNA) from an RNA template, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B to replicate their genomes, by retrotransposon mobile genetic elements to proliferate within the host genome, and by eukaryotic cells to extend the telomeres at the ends of their linear chromosomes. Contrary to a widely held belief, the process does not violate the flows of genetic information as described by the classical central dogma, as transfers of information from RNA to DNA are explicitly held possible. Retroviral RT has three sequential biochemical activities: RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity, ribonuclease H (RNase H), and DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity. Collectively, these activities enable the enzyme to convert single-stranded RNA into double-stranded cDNA. In retroviruses and retrotransposons, this cDNA can then integrate into the host genom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mobile Genetic Elements
Mobile genetic elements (MGEs) sometimes called selfish genetic elements are a type of genetic material that can move around within a genome, or that can be transferred from one species or replicon to another. MGEs are found in all organisms. In humans, approximately 50% of the genome is thought to be MGEs. MGEs play a distinct role in evolution. Gene duplication events can also happen through the mechanism of MGEs. MGEs can also cause mutations in protein coding regions, which alters the protein functions. These mechanisms can also rearrange genes in the host genome generating variation. These mechanism can increase fitness by gaining new or additional functions. An example of MGEs in evolutionary context are that virulence factors and antibiotic resistance genes of MGEs can be transported to share genetic code with neighboring bacteria. However, MGEs can also decrease fitness by introducing disease-causing alleles or mutations. The set of MGEs in an organism is called a mobilome, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(white_background).jpg)