Marsupial on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Marsupials are any members of the mammalian infraclass Marsupialia. All extant marsupials are endemic to Australasia, Wallacea and the
 Marsupials have the typical characteristics of mammals—e.g., mammary glands, three middle ear bones, and true hair. There are, however, striking differences as well as a number of anatomical features that separate them from
Marsupials have the typical characteristics of mammals—e.g., mammary glands, three middle ear bones, and true hair. There are, however, striking differences as well as a number of anatomical features that separate them from
 Marsupials' reproductive systems differ markedly from those of placental mammals. During embryonic development, a choriovitelline placenta forms in all marsupials. In bandicoots, an additional chorioallantoic placenta forms, although it lacks the chorionic villi found in
Marsupials' reproductive systems differ markedly from those of placental mammals. During embryonic development, a choriovitelline placenta forms in all marsupials. In bandicoots, an additional chorioallantoic placenta forms, although it lacks the chorionic villi found in
 Most male marsupials, except for macropods and
Most male marsupials, except for macropods and
 Female marsupials have two lateral
Female marsupials have two lateral
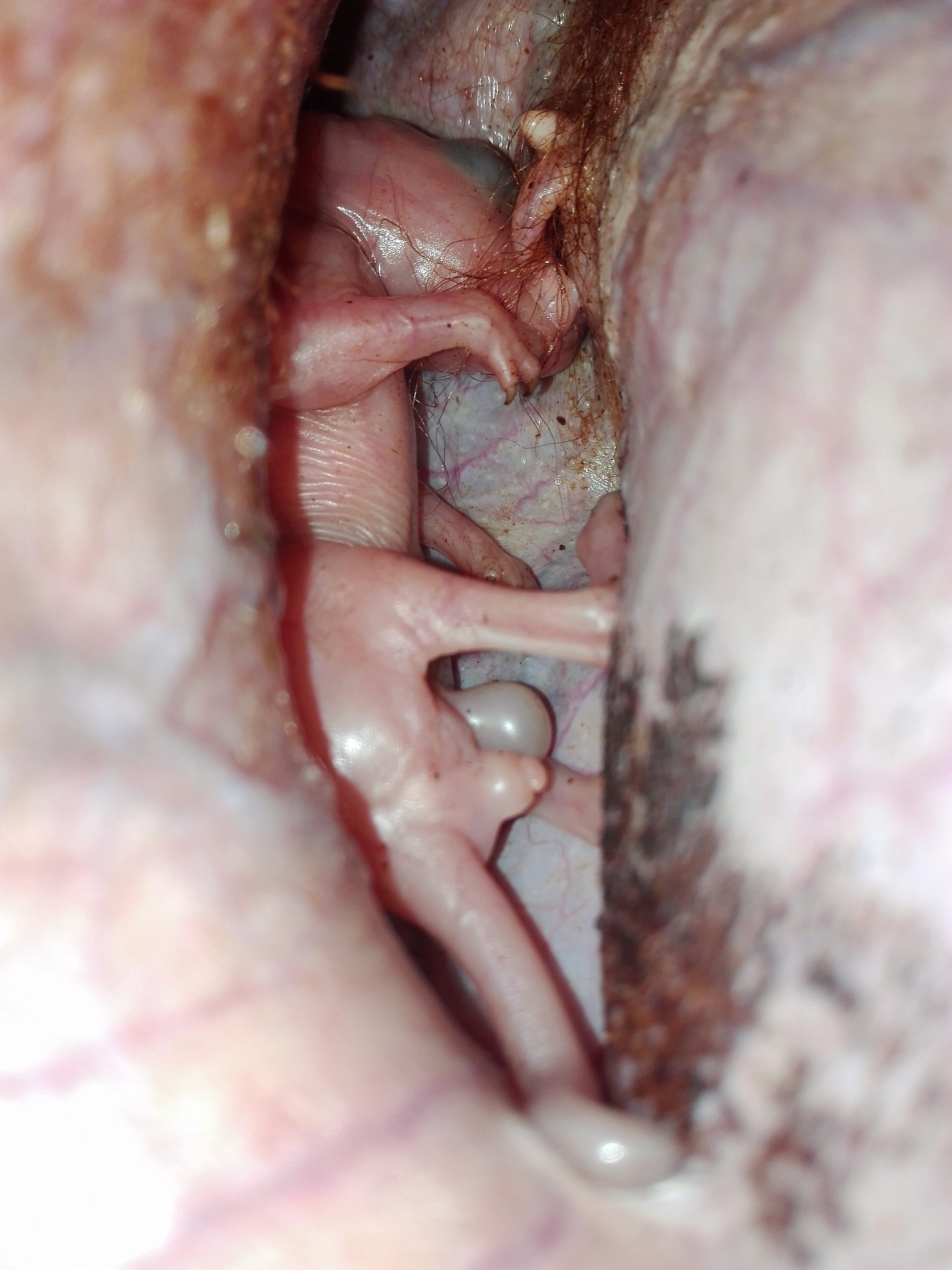 Prenatal development differs between marsupials and placental mammals. Key aspects of the first stages of placental mammal embryo development, such as the inner cell mass and the process of compaction, are not found in marsupials. The cleavage stages of marsupial development are very variable between groups and aspects of marsupial early development are not yet fully understood.
An early birth removes a developing marsupial from its mother's body much sooner than in placental mammals; thus marsupials have not developed a complex placenta to protect the embryo from its mother's immune system. Though early birth puts the tiny newborn marsupial at a greater environmental risk, it significantly reduces the dangers associated with long pregnancies, as there is no need to carry a large fetus to full term in bad seasons. Marsupials are extremely
Prenatal development differs between marsupials and placental mammals. Key aspects of the first stages of placental mammal embryo development, such as the inner cell mass and the process of compaction, are not found in marsupials. The cleavage stages of marsupial development are very variable between groups and aspects of marsupial early development are not yet fully understood.
An early birth removes a developing marsupial from its mother's body much sooner than in placental mammals; thus marsupials have not developed a complex placenta to protect the embryo from its mother's immune system. Though early birth puts the tiny newborn marsupial at a greater environmental risk, it significantly reduces the dangers associated with long pregnancies, as there is no need to carry a large fetus to full term in bad seasons. Marsupials are extremely
 The relationships among the three extant divisions of mammals ( monotremes, marsupials, and placentals) were long a matter of debate among taxonomists. Most morphological evidence comparing traits such as number and arrangement of teeth and structure of the reproductive and waste elimination systems as well as most genetic and molecular evidence favors a closer evolutionary relationship between the marsupials and placental mammals than either has with the monotremes.
The relationships among the three extant divisions of mammals ( monotremes, marsupials, and placentals) were long a matter of debate among taxonomists. Most morphological evidence comparing traits such as number and arrangement of teeth and structure of the reproductive and waste elimination systems as well as most genetic and molecular evidence favors a closer evolutionary relationship between the marsupials and placental mammals than either has with the monotremes.
 The ancestors of marsupials, part of a larger group called metatherians, probably split from those of placental mammals (
The ancestors of marsupials, part of a larger group called metatherians, probably split from those of placental mammals (
Marsupials in the age of genomics
''Annu Rev Genom Hum Genet'' The ancestral number of chromosomes has been estimated to be 2n = 14. A new hypothesis suggests that South American microbiotheres resulted from a back-dispersal from eastern Gondwana due to new cranial and post-cranial marsupial fossils from the ''Djarthia murgonensis'' from the early Eocene Tingamarra Local Fauna in Australia that indicate the ''Djarthia murgonensis'' is the most plesiomorphic, the oldest unequivocal australidelphian, and may be the ancestral morphotype of the Australian marsupial radiation.
First marsupial genome released. Most differences between the opossom and placental mammals stem from non-coding DNA
{{Authority control Extant Paleocene first appearances
Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
. A distinctive characteristic common to most of these species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
is that the young are carried in a pouch. Marsupials include opossums, Tasmanian devils, kangaroos, koala
The koala or, inaccurately, koala bear (''Phascolarctos cinereus''), is an arboreal herbivorous marsupial native to Australia. It is the only extant representative of the family Phascolarctidae and its closest living relatives are the w ...
s, wombats, wallabies, bandicoot
Bandicoots are a group of more than 20 species of small to medium-sized, terrestrial, largely nocturnal marsupial omnivores in the order Peramelemorphia. They are endemic to the Australia–New Guinea region, including the Bismarck Archipelago t ...
s, and the extinct thylacine
The thylacine ( , or , also ) (''Thylacinus cynocephalus'') is an extinct carnivorous marsupial that was native to the Australian mainland and the islands of Tasmania and New Guinea. The last known live animal was captured in 1930 in Tasma ...
.
Marsupials represent the clade originating from the last common ancestor of extant metatherians, the group containing all mammals more closely related to marsupials than to placentals. They give birth to relatively undeveloped young that often reside in a pouch located on their mothers' abdomen for a certain amount of time. Close to 70% of the 334 extant species occur on the Australian continent
The continent of Australia, sometimes known in technical contexts by the names Sahul (), Australia-New Guinea, Australinea, Meganesia, or Papualand to distinguish it from the country of Australia, is located within the Southern and East ...
(the mainland, Tasmania
)
, nickname =
, image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdi ...
, New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torr ...
and nearby islands). The remaining 30% are found in the Americas—primarily in South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sout ...
, thirteen in Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
, and one species, the Virginia opossum
The Virginia opossum (''Didelphis virginiana''), also known as the North American opossum, is the only opossum living north of Mexico, its range extending south into Central America. It is the northernmost marsupial in the world. In the United S ...
, in North America, north of Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
.
The word ''marsupial'' comes from '' marsupium'', the technical term for the abdominal pouch. It, in turn, is borrowed from the Latin and ultimately from the ancient Greek , meaning "pouch".
Taxonomy
Marsupials are taxonomically identified as members of mammalian infraclass Marsupialia, first described as a family under the order Pollicata by German zoologistJohann Karl Wilhelm Illiger
Johann Karl Wilhelm Illiger (19 November 1775 – 10 May 1813) was a German entomologist and zoologist.
Illiger was the son of a merchant in Braunschweig. He studied under the entomologist Johann Hellwig, and later worked on the zoological colle ...
in his 1811 work ''Prodromus Systematis Mammalium et Avium''. However, James Rennie, author of ''The Natural History of Monkeys, Opossums and Lemurs'' (1838), pointed out that the placement of five different groups of mammals – monkeys, lemur
Lemurs ( ) (from Latin ''lemures'' – ghosts or spirits) are wet-nosed primates of the superfamily Lemuroidea (), divided into 8 families and consisting of 15 genera and around 100 existing species. They are endemic to the island of Madagas ...
s, tarsiers, aye-ayes and marsupials (with the exception of kangaroos, that were placed under the order Salientia) – under a single order (Pollicata) did not appear to have a strong justification. In 1816, French zoologist George Cuvier classified all marsupials under the order Marsupialia. In 1997, researcher J. A. W. Kirsch and others accorded infraclass rank to Marsupialia.
Classification
Marsupialia is further divided as follows: – Extinct * Order Didelphimorphia (93 species) - see list of didelphimorphs ** Family Didelphidae: opossums * Order Paucituberculata (seven species) ** FamilyCaenolestidae
The family Caenolestidae contains the seven surviving species of shrew opossum: small, shrew-like marsupials that are confined to the Andes mountains of South America. The order is thought to have diverged from the ancestral marsupial line very e ...
: shrew opossum
The family Caenolestidae contains the seven surviving species of shrew opossum: small, shrew-like marsupials that are confined to the Andes mountains of South America. The order is thought to have diverged from the ancestral marsupial line very e ...
s
* Superorder Australidelphia
** Order Microbiotheria
Microbiotheria is an australidelphian marsupial order that encompasses two families, Microbiotheriidae and Woodburnodontidae, and is represented by only one extant species, the monito del monte, and a number of extinct species known from fossi ...
(one extant species)
*** Family Microbiotheriidae
Microbiotheriidae is a family of australidelphian marsupials represented by only one extant species, the monito del monte, and a number of extinct species known from fossils in South America, Western Antarctica, and northeastern Australia.
Micr ...
: monitos del monte
** Order † Yalkaparidontia (''incertae sedis'')
** Order Dasyuromorphia (73 species)
*** Family †Thylacinidae
Thylacinidae is an extinct family of carnivorous, superficially dog-like marsupials from the order Dasyuromorphia. The only species to survive into modern times was the thylacine (''Thylacinus cynocephalus''), which became extinct in 1936.
The ...
: thylacine
The thylacine ( , or , also ) (''Thylacinus cynocephalus'') is an extinct carnivorous marsupial that was native to the Australian mainland and the islands of Tasmania and New Guinea. The last known live animal was captured in 1930 in Tasma ...
*** Family Dasyuridae
The Dasyuridae are a family of marsupials native to Australia and New Guinea, including 71 extant species divided into 17 genera. Many are small and mouse-like or shrew-like, giving some of them the name marsupial mice or marsupial shrews, but th ...
: antechinuses, quoll
Quolls (; genus ''Dasyurus'') are carnivorous marsupials native to Australia and New Guinea. They are primarily nocturnal and spend most of the day in a den. Of the six species of quoll, four are found in Australia and two in New Guinea. Anoth ...
s, dunnart
Dunnart is a common name for species of the genus ''Sminthopsis'', narrow-footed marsupials the size of a European mouse. They have a largely insectivorous diet.
Taxonomy
The genus name ''Sminthopsis'' was published by Oldfield Thomas in 18 ...
s, Tasmanian devil, and relatives
*** Family Myrmecobiidae: numbat
** Order Notoryctemorphia (two species)
*** Family Notoryctidae: marsupial mole
Marsupial moles, the Notoryctidae , are highly specialized marsupial mammals, known from two species found at the Australian interior.
* ''Notoryctes typhlops'' (southern marsupial mole, known as the ''itjaritjari'' by the Pitjantjatjara and Yan ...
s
** Order Peramelemorphia (27 species)
*** Family Thylacomyidae: bilbies
*** Family †Chaeropodidae: pig-footed bandicoots
*** Family Peramelidae: bandicoot
Bandicoots are a group of more than 20 species of small to medium-sized, terrestrial, largely nocturnal marsupial omnivores in the order Peramelemorphia. They are endemic to the Australia–New Guinea region, including the Bismarck Archipelago t ...
s and allies
** Order Diprotodontia
Diprotodontia (, from Greek "two forward teeth") is the largest extant order of marsupials, with about 155 species, including the kangaroos, wallabies, possums, koala, wombats, and many others. Extinct diprotodonts include the hippopotamus-sized ...
(136 species)
*** Suborder Vombatiformes
The Vombatiformes are one of the three suborders of the large marsupial order Diprotodontia. Seven of the nine known families within this suborder are extinct; only the families Phascolarctidae, with the koala, and Vombatidae, with three extan ...
**** Family Vombatidae: wombats
**** Family Phascolarctidae: koala
The koala or, inaccurately, koala bear (''Phascolarctos cinereus''), is an arboreal herbivorous marsupial native to Australia. It is the only extant representative of the family Phascolarctidae and its closest living relatives are the w ...
s
**** Family Diprotodontidae: giant wombats
**** Family Palorchestidae: marsupial tapirs
**** Family Thylacoleonidae: marsupial lions
*** Suborder Phalangeriformes
Phalangeriformes is a paraphyletic suborder of about 70 species of small to medium-sized arboreal marsupials native to Australia, New Guinea, and Sulawesi. The species are commonly known as possums, gliders, and cuscus. The common name "possum ...
**** Family Acrobatidae: feathertail glider and feather-tailed possum
**** Family Burramyidae
The pygmy possums are a family of small possums that together form the marsupial family Burramyidae. The five extant species of pygmy possum are grouped into two genera. Four of the species are endemic to Australia, with one species also co-occu ...
: pygmy possums
**** Family †Ektopodon
''Ektopodon'' is an extinct genus of marsupial, and is the type genus of the family Ektopodontidae which occurred in forested environments in South Australia, Queensland and Victoria. The last species of this group went extinct in the early Plei ...
tidae: sprite possum
''Ektopodon'' is an extinct genus of marsupial, and is the type genus of the family Ektopodontidae which occurred in forested environments in South Australia, Queensland and Victoria. The last species of this group went extinct in the early Plei ...
s
**** Family Petauridae
Petauridae is a family of possums containing 13 species: four species of trioks and striped possum (genus ''Dactylopsila''), eight species of wrist-winged glider (genus ''Petaurus''), and Leadbeater's possum (''Gymnobelideus leadbeateri''), whic ...
: striped possum
The striped possum or common striped possum (''Dactylopsila trivirgata'') is a member of the marsupial family Petauridae. it is found mainly in New Guinea. The species is black with three white stripes running head to tail, and its head has whi ...
, Leadbeater's possum
Leadbeater's possum (''Gymnobelideus leadbeateri'') is a critically endangered possum largely restricted to small pockets of alpine ash, mountain ash, and snow gum forests in the Central Highlands of Victoria, Australia, north-east of Melbou ...
, yellow-bellied glider, sugar glider
The sugar glider (''Petaurus breviceps'') is a small, omnivorous, arboreal, and nocturnal gliding possum belonging to the marsupial infraclass. The common name refers to its predilection for sugary foods such as sap and nectar and its abili ...
, mahogany glider, squirrel glider
The squirrel glider (''Petaurus norfolcensis'') is a nocturnal gliding possum. The squirrel glider is one of the wrist-winged gliders of the genus ''Petaurus''.
Habitat
This species' home range extends from Bordertown near the South Australia ...
**** Family Phalangeridae
The Phalangeridae are a family of mostly nocturnal marsupials native to Australia, New Guinea, and Eastern Indonesia, including the cuscuses, brushtail possums, and their close relatives. Considered a type of possum, most species are arboreal, ...
: brushtail possums and cuscus
Cuscus ( or ) is the common name generally given to the species within the four genera of Australasian possum of the family Phalangeridae with the most tropical distribution:
* ''Ailurops''
* ''Phalanger''
* ''Spilocuscus''
* ''Strigocuscus'' ...
es
**** Family Pseudocheiridae: ringtailed possums and relatives
**** Family Tarsipedidae: honey possum
*** Suborder Macropodiformes
The Macropodiformes , also known as macropods, are one of the three suborders of the large marsupial order Diprotodontia. They may in fact be nested within one of the suborders, Phalangeriformes. Kangaroos, wallabies and allies, bettongs, potoro ...
**** Family Macropodidae
Macropodidae is a family of marsupials that includes kangaroos, wallabies, tree-kangaroos, wallaroos, pademelons, quokkas, and several other groups. These genera are allied to the suborder Macropodiformes, containing other macropods, and ar ...
: kangaroos, wallabies, and relatives
**** Family Potoroidae: potoroos, rat kangaroos, bettongs
**** Family Hypsiprymnodontidae: musky rat-kangaroo
The musky rat-kangaroo (''Hypsiprymnodon moschatus'') is a small marsupial found only in the rainforests of northeastern Australia. First described in the later 19th century, the only other species are known from fossil specimens. They are simil ...
**** Family Balbaridae: basal quadrupedal kangaroos
Phylogenetic relationships
Comprising over 300 extant species, several attempts have been made to accurately interpret thephylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ...
relationships among the different marsupial orders. Studies differ on whether Didelphimorphia or Paucituberculata is the sister group to all other marsupials. Though the order Microbiotheria
Microbiotheria is an australidelphian marsupial order that encompasses two families, Microbiotheriidae and Woodburnodontidae, and is represented by only one extant species, the monito del monte, and a number of extinct species known from fossi ...
(which has only one species, the monito del monte
The monito del monte or colocolo opossum, ''Dromiciops gliroides'', also called ''chumaihuén'' in Mapudungun, is a diminutive marsupial native only to southwestern South America (Argentina and Chile). It is the only extant species in the ancient ...
) is found in South America, morphological similarities suggest it is closely related to Australian marsupials. Molecular analyses in 2010 and 2011 identified Microbiotheria as the sister group to all Australian marsupials. However, the relations among the four Australidelphid orders are not as well understood. The cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to ...
below, depicting the relationships among the various marsupial orders, is based on a 2015 phylogenetic study.
DNA evidence supports a South American origin for marsupials, with Australian marsupials arising from a single Gondwanan migration of marsupials from South America, across Antarctica, to Australia. There are many small arboreal
Arboreal locomotion is the locomotion of animals in trees. In habitats in which trees are present, animals have evolved to move in them. Some animals may scale trees only occasionally, but others are exclusively arboreal. The habitats pose nu ...
species in each group. The term " opossum" is used to refer to American species (though "possum" is a common abbreviation), while similar Australian species are properly called "possums".
Anatomy
 Marsupials have the typical characteristics of mammals—e.g., mammary glands, three middle ear bones, and true hair. There are, however, striking differences as well as a number of anatomical features that separate them from
Marsupials have the typical characteristics of mammals—e.g., mammary glands, three middle ear bones, and true hair. There are, however, striking differences as well as a number of anatomical features that separate them from eutheria
Eutheria (; from Greek , 'good, right' and , 'beast'; ) is the clade consisting of all therian mammals that are more closely related to placentals than to marsupials.
Eutherians are distinguished from noneutherians by various phenotypic tra ...
ns.
In addition to the front pouch, which contains multiple teat
A teat is the projection from the mammary glands of mammals from which milk flows or is ejected for the purpose of feeding young. In many mammals the teat projects from the udder. The number of teats varies by mammalian species and often corr ...
s for the sustenance of their young, marsupials have other common structural features. Ossified
Ossification (also called osteogenesis or bone mineralization) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in t ...
patellae are absent in most modern marsupials (though a small number of exceptions are reported) and epipubic bone
Epipubic bones are a pair of bones projecting forward from the pelvic bones of modern marsupials, monotremes and fossil mammals like multituberculates, and even basal eutherians (the ancestors of placental mammals, who lack them).
They first ...
s are present. Marsupials (and monotremes) also lack a gross communication (corpus callosum
The corpus callosum (Latin for "tough body"), also callosal commissure, is a wide, thick nerve tract, consisting of a flat bundle of commissural fibers, beneath the cerebral cortex in the brain. The corpus callosum is only found in placental m ...
) between the right and left brain hemispheres.
Skull and teeth
The skull has peculiarities in comparison to placental mammals. In general, the skull is relatively small and tight. Holes (''foramen lacrimale'') are located in the front of the orbit. The cheekbone is enlarged and extends farther to the rear. The angular extension (''processus angularis'') of the lower jaw is bent toward the center. Another feature is the hard palate which, in contrast to the placental mammals' foramina, always have more openings. The teeth differ from that of placental mammals, so that alltaxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular nam ...
except wombats have a different number of incisors in the upper and lower jaws. The early marsupials had a dental formula from , that is, per quadrant; they have five (maxillary) or four (mandibular) incisors, one canine, three premolars and four molars, for a total of 50 teeth. Some taxa, such as the opossum, have the original number of teeth. In other groups the number of teeth is reduced. The dental formula for Macropodidae
Macropodidae is a family of marsupials that includes kangaroos, wallabies, tree-kangaroos, wallaroos, pademelons, quokkas, and several other groups. These genera are allied to the suborder Macropodiformes, containing other macropods, and ar ...
(kangaroos and wallabies etc.) is 3/1 – (0 or 1)/0 – 2/2 – 4/4. Marsupials in many cases have 40 to 50 teeth, significantly more than placental mammals. The second set of teeth grows in only at the 3rd premolar site and back; all teeth more anterior to that erupt initially as permanent teeth.
Torso
Few general characteristics describe their skeleton. In addition to unique details in the construction of the ankle, epipubic bones (''ossa epubica'') are observed projecting forward from the pubic bone of the pelvis. Since these are present in males and pouchless species, it is believed that they originally had nothing to do with reproduction, but served in the muscular approach to the movement of the hind limbs. This could be explained by an original feature of mammals, as theseepipubic bone
Epipubic bones are a pair of bones projecting forward from the pelvic bones of modern marsupials, monotremes and fossil mammals like multituberculates, and even basal eutherians (the ancestors of placental mammals, who lack them).
They first ...
s are also found in monotremes. Marsupial reproductive organs differ from the placental mammals. For them, the reproductive tract is doubled. The females have two uteri and two vaginas, and before birth, a birth canal forms between them, the median vagina. The males have a split or double penis lying in front of the scrotum.
A pouch is present in most, but not all, species. Many marsupials have a permanent bag, whereas in others the pouch develops during gestation, as with the shrew opossum
The family Caenolestidae contains the seven surviving species of shrew opossum: small, shrew-like marsupials that are confined to the Andes mountains of South America. The order is thought to have diverged from the ancestral marsupial line very e ...
, where the young are hidden only by skin folds or in the fur of the mother. The arrangement of the pouch is variable to allow the offspring to receive maximum protection. Locomotive kangaroos have a pouch opening at the front, while many others that walk or climb on all fours have the opening in the back. Usually, only females have a pouch, but the male water opossum
The water opossum (''Chironectes minimus''), also locally known as the yapok (), is a marsupial of the family Didelphidae.* It is the only living member of its genus, ''Chironectes''. This semiaquatic creature is found in and near freshwater ...
has a pouch that is used to accommodate his genitalia while swimming or running.
General and convergences
Marsupials have adapted to many habitats, reflected in the wide variety in their build. The largest living marsupial, thered kangaroo
The red kangaroo (''Osphranter rufus'') is the largest of all kangaroos, the largest terrestrial mammal native to Australia, and the largest extant marsupial. It is found across mainland Australia, except for the more fertile areas, such as sou ...
, grows up to in height and in weight, but extinct genera, such as '' Diprotodon'', were significantly larger and heavier. The smallest members of this group are the marsupial mice
The Dasyuridae are a family of marsupials native to Australia and New Guinea, including 71 extant species divided into 17 genera. Many are small and mouse-like or shrew-like, giving some of them the name marsupial mice or marsupial shrews, but th ...
, which often reach only in body length.
Some species resemble placental mammals and are examples of convergent evolution
Convergent evolution is the independent evolution of similar features in species of different periods or epochs in time. Convergent evolution creates analogous structures that have similar form or function but were not present in the last com ...
. This convergence is evident in both brain evolution and behaviour. The extinct ''Thylacine
The thylacine ( , or , also ) (''Thylacinus cynocephalus'') is an extinct carnivorous marsupial that was native to the Australian mainland and the islands of Tasmania and New Guinea. The last known live animal was captured in 1930 in Tasma ...
'' strongly resembled the placental wolf, hence one of its nicknames "Tasmanian wolf". The ability to glide evolved in both marsupials (as with sugar glider
The sugar glider (''Petaurus breviceps'') is a small, omnivorous, arboreal, and nocturnal gliding possum belonging to the marsupial infraclass. The common name refers to its predilection for sugary foods such as sap and nectar and its abili ...
s) and some placental mammals (as with flying squirrels), which developed independently. Other groups such as the kangaroo, however, do not have clear placental counterparts, though they share similarities in lifestyle and ecological niches with ruminant
Ruminants (suborder Ruminantia) are hoofed herbivorous grazing or browsing mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microbial actions. The ...
s.
Body temperature
Marsupials, along with monotremes ( platypuses andechidnas
Echidnas (), sometimes known as spiny anteaters, are quill-covered monotremes (egg-laying mammals) belonging to the family Tachyglossidae . The four extant species of echidnas and the platypus are the only living mammals that lay eggs and the ...
), typically have lower body temperatures than similarly sized placental mammals ( eutherians).
Reproductive system
 Marsupials' reproductive systems differ markedly from those of placental mammals. During embryonic development, a choriovitelline placenta forms in all marsupials. In bandicoots, an additional chorioallantoic placenta forms, although it lacks the chorionic villi found in
Marsupials' reproductive systems differ markedly from those of placental mammals. During embryonic development, a choriovitelline placenta forms in all marsupials. In bandicoots, an additional chorioallantoic placenta forms, although it lacks the chorionic villi found in eutherian
Eutheria (; from Greek , 'good, right' and , 'beast'; ) is the clade consisting of all therian mammals that are more closely related to placentals than to marsupials.
Eutherians are distinguished from noneutherians by various phenotypic tra ...
placentas.
The evolution of reproduction in marsupials, and speculation about the ancestral state of mammalian reproduction, have engaged discussion since the end of the 19th century. Both sexes possess a cloaca, which is connected to a urogenital sac used to store waste before expulsion. The bladder of marsupials functions as a site to concentrate urine and empties into the common urogenital sinus in both females and males.
Male reproductive system
 Most male marsupials, except for macropods and
Most male marsupials, except for macropods and marsupial mole
Marsupial moles, the Notoryctidae , are highly specialized marsupial mammals, known from two species found at the Australian interior.
* ''Notoryctes typhlops'' (southern marsupial mole, known as the ''itjaritjari'' by the Pitjantjatjara and Yan ...
s, have a bifurcated penis, separated into two columns, so that the penis has two ends corresponding to the females' two vaginas. The penis is used only during copulation, and is separate from the urinary tract
The urinary system, also known as the urinary tract or renal system, consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and the urethra. The purpose of the urinary system is to eliminate waste from the body, regulate blood volume and blood pressure, c ...
. It curves forward when erect, and when not erect, it is retracted into the body in an S-shaped curve. Neither marsupials nor monotremes possess a baculum. The shape of the glans penis
In male human anatomy, the glans penis, commonly referred to as the glans, is the bulbous structure at the distal end of the human penis that is the human male's most sensitive erogenous zone and their primary anatomical source of sexual pl ...
varies among marsupial species.
The male thylacine
The thylacine ( , or , also ) (''Thylacinus cynocephalus'') is an extinct carnivorous marsupial that was native to the Australian mainland and the islands of Tasmania and New Guinea. The last known live animal was captured in 1930 in Tasma ...
had a pouch that acted as a protective sheath, covering his external reproductive organs while running through thick brush.
The shape of the urethral grooves of the males' genitalia is used to distinguish between '' Monodelphis brevicaudata'', '' Monodelphis domestica'', and '' Monodelphis americana''. The grooves form 2 separate channels that form the ventral and dorsal folds of the erectile tissue. Several species of dasyurid marsupials can also be distinguished by their penis morphology.
The only accessory sex glands marsupials possess are the prostate and bulbourethral glands. Male marsupials have 1-3 pairs of bulbourethral glands. There are no ampullae of vas deferens, seminal vesicle
The seminal vesicles (also called vesicular glands, or seminal glands) are a pair of two convoluted tubular glands that lie behind the urinary bladder of some male mammals. They secrete fluid that partly composes the semen.
The vesicles are 5� ...
s or coagulating glands. The prostate is proportionally larger in marsupials than in placental mammals. During the breeding season, the male tammar wallaby
The tammar wallaby (''Notamacropus eugenii''), also known as the dama wallaby or darma wallaby, is a small macropod native to South and Western Australia. Though its geographical range has been severely reduced since European colonisation, the ...
's prostate and bulbourethral gland enlarge. However, there does not appear to be any seasonal difference in the weight of the testes.
Female reproductive system
 Female marsupials have two lateral
Female marsupials have two lateral vagina
In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hymen ...
s, which lead to separate uteri, but both open externally through the same orifice. A third canal, the median vagina, is used for birth. This canal can be transitory or permanent. Some marsupial species are able to store sperm in the oviduct after mating.
Marsupials give birth at a very early stage of development; after birth, newborn marsupials crawl up the bodies of their mothers and attach themselves to a teat, which is located on the underside of the mother, either inside a pouch called the marsupium, or open to the environment. Mothers often lick their fur to leave a trail of scent for the newborn to follow to increase chances of making it into the marsupium. There they remain for a number of weeks, attached to the teat. The offspring are eventually able to leave the marsupium for short periods, returning to it for warmth, protection, and nourishment.
=Early development
= Prenatal development differs between marsupials and placental mammals. Key aspects of the first stages of placental mammal embryo development, such as the inner cell mass and the process of compaction, are not found in marsupials. The cleavage stages of marsupial development are very variable between groups and aspects of marsupial early development are not yet fully understood.
An early birth removes a developing marsupial from its mother's body much sooner than in placental mammals; thus marsupials have not developed a complex placenta to protect the embryo from its mother's immune system. Though early birth puts the tiny newborn marsupial at a greater environmental risk, it significantly reduces the dangers associated with long pregnancies, as there is no need to carry a large fetus to full term in bad seasons. Marsupials are extremely
Prenatal development differs between marsupials and placental mammals. Key aspects of the first stages of placental mammal embryo development, such as the inner cell mass and the process of compaction, are not found in marsupials. The cleavage stages of marsupial development are very variable between groups and aspects of marsupial early development are not yet fully understood.
An early birth removes a developing marsupial from its mother's body much sooner than in placental mammals; thus marsupials have not developed a complex placenta to protect the embryo from its mother's immune system. Though early birth puts the tiny newborn marsupial at a greater environmental risk, it significantly reduces the dangers associated with long pregnancies, as there is no need to carry a large fetus to full term in bad seasons. Marsupials are extremely altricial
In biology, altricial species are those in which the young are underdeveloped at the time of birth, but with the aid of their parents mature after birth. Precocial species are those in which the young are relatively mature and mobile from the mome ...
animals, needing to be intensely cared for immediately following birth (cf.
The abbreviation ''cf.'' (short for the la, confer/conferatur, both meaning "compare") is used in writing to refer the reader to other material to make a comparison with the topic being discussed. Style guides recommend that ''cf.'' be used onl ...
precocial
In biology, altricial species are those in which the young are underdeveloped at the time of birth, but with the aid of their parents mature after birth. Precocial species are those in which the young are relatively mature and mobile from the mome ...
).
Because newborn marsupials must climb up to their mother's teats, their front limbs and facial structures are much more developed than the rest of their bodies at the time of birth. This requirement has been argued to have resulted in the limited range of locomotor adaptations in marsupials compared to placentals. Marsupials must develop grasping forepaws during their early youth, making the evolutive transition from these limbs into hooves, wing
A wing is a type of fin that produces lift while moving through air or some other fluid. Accordingly, wings have streamlined cross-sections that are subject to aerodynamic forces and act as airfoils. A wing's aerodynamic efficiency is e ...
s, or flippers, as some groups of placental mammals have done, more difficult. However, several marsupials do possess atypical forelimb morphologies, such as the hooved forelimbs of the pig-footed bandicoot, suggesting that the range of forelimb specialization is not as limited as assumed.
An infant marsupial is known as a joey. Marsupials have a very short gestation period—usually around four to five weeks, but as low as 12 days for some species—and the joey is born in an essentially fetal
A fetus or foetus (; plural fetuses, feti, foetuses, or foeti) is the unborn offspring that develops from an animal embryo. Following embryonic development the fetal stage of development takes place. In human prenatal development, fetal develo ...
state. The blind, furless, miniature newborn, the size of a jelly bean
Jelly beans are small bean shaped sugar candies with soft candy shells and thick gel interiors (see gelatin and jelly). The confection is primarily made of sugar and sold in a wide variety of colors and flavors.
History
It has been clai ...
, crawls across its mother's fur to make its way into the pouch, where it latches onto a teat
A teat is the projection from the mammary glands of mammals from which milk flows or is ejected for the purpose of feeding young. In many mammals the teat projects from the udder. The number of teats varies by mammalian species and often corr ...
for food. It will not re-emerge for several months, during which time it is fully reliant on its mother's milk for essential nutrients, growth factors and immunological defence. After this period, the joey begins to spend increasing lengths of time out of the pouch, feeding and learning survival skills. However, it returns to the pouch to sleep, and if danger threatens, it will seek refuge in its mother's pouch for safety.
Joeys stay in the pouch for up to a year in some species, or until the next joey is born. A marsupial joey is unable to regulate its own body temperature and relies upon an external heat source. Until the joey is well furred and old enough to leave the pouch, a pouch temperature of must be constantly maintained.
Joeys are born with "oral shields". In species without pouches or with rudimentary pouches these are more developed than in forms with well-developed pouches, implying a role in maintaining the young attached to the mother's teat.
Geography
In Australasia, marsupials are found in Australia, Tasmania and New Guinea; throughout theMaluku Islands
The Maluku Islands (; Indonesian: ''Kepulauan Maluku'') or the Moluccas () are an archipelago in the east of Indonesia. Tectonically they are located on the Halmahera Plate within the Molucca Sea Collision Zone. Geographically they are located ...
, Timor and Sulawesi to the west of New Guinea, and in the Bismarck Archipelago (including the Admiralty Islands
The Admiralty Islands are an archipelago group of 18 islands in the Bismarck Archipelago, to the north of New Guinea in the South Pacific Ocean. These are also sometimes called the Manus Islands, after the largest island.
These rainforest-co ...
) and Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and north-west of Vanuatu. It has a land area of , and a population of approx. 700,000. Its capit ...
to the east of New Guinea.
In America, marsupials are found throughout South America, excluding the central/southern Andes and parts of Patagonia; and through Central America and south-central Mexico, with a single species (the Virginia opossum
The Virginia opossum (''Didelphis virginiana''), also known as the North American opossum, is the only opossum living north of Mexico, its range extending south into Central America. It is the northernmost marsupial in the world. In the United S ...
''Didelphis virginiana'') widespread in the eastern United States and along the Pacific coast.
Interaction with Europeans
The first American marsupial (and marsupial in general) that a European encountered was the common opossum. Vicente Yáñez Pinzón, commander of the ''Niña
''La Niña'' ( Spanish for ''The Girl'') was one of the three Spanish ships used by Italian explorer Christopher Columbus in his first voyage to the West Indies in 1492. As was tradition for Spanish ships of the day, she bore a female saint's n ...
'' on Christopher Columbus' first voyage in the late fifteenth century, collected a female opossum with young in her pouch off the South American coast. He presented them to the Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
monarchs, though by then the young were lost and the female had died. The animal was noted for its strange pouch or "second belly", and how the offspring reached the pouch was a mystery.
On the other hand, it was the Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
who first described Australasian marsupials. António Galvão, a Portuguese administrator in Ternate
Ternate is a city in the Indonesian province of North Maluku and an island in the Maluku Islands. It was the ''de facto'' provincial capital of North Maluku before Sofifi on the nearby coast of Halmahera became the capital in 2010. It is off the ...
(1536–40), wrote a detailed account of the northern common cuscus (''Phalanger orientalis''):
From the start of the 17th century more accounts of marsupials arrived. For instance, a 1606 record of an animal, killed on the southern coast of New Guinea, described it as "in the shape of a dog, smaller than a greyhound", with a snakelike "bare scaly tail" and hanging testicles. The meat tasted like venison, and the stomach contained ginger leaves. This description appears to closely resemble the dusky pademelon
The dusky pademelon or dusky wallaby (''Thylogale brunii'') is a species of marsupial in the family Macropodidae. It is found in the Aru and Kai islands and the Trans-Fly savanna and grasslands ecoregion of New Guinea. Its natural habitats are ...
(''Thylogale brunii''), in which case this would be the earliest European record of a member of the kangaroo family (Macropodidae
Macropodidae is a family of marsupials that includes kangaroos, wallabies, tree-kangaroos, wallaroos, pademelons, quokkas, and several other groups. These genera are allied to the suborder Macropodiformes, containing other macropods, and ar ...
).
Evolutionary history

 The relationships among the three extant divisions of mammals ( monotremes, marsupials, and placentals) were long a matter of debate among taxonomists. Most morphological evidence comparing traits such as number and arrangement of teeth and structure of the reproductive and waste elimination systems as well as most genetic and molecular evidence favors a closer evolutionary relationship between the marsupials and placental mammals than either has with the monotremes.
The relationships among the three extant divisions of mammals ( monotremes, marsupials, and placentals) were long a matter of debate among taxonomists. Most morphological evidence comparing traits such as number and arrangement of teeth and structure of the reproductive and waste elimination systems as well as most genetic and molecular evidence favors a closer evolutionary relationship between the marsupials and placental mammals than either has with the monotremes.
 The ancestors of marsupials, part of a larger group called metatherians, probably split from those of placental mammals (
The ancestors of marsupials, part of a larger group called metatherians, probably split from those of placental mammals (eutheria
Eutheria (; from Greek , 'good, right' and , 'beast'; ) is the clade consisting of all therian mammals that are more closely related to placentals than to marsupials.
Eutherians are distinguished from noneutherians by various phenotypic tra ...
ns) during the mid-Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
period, though no fossil evidence of metatherians themselves are known from this time. From DNA and protein analyses, the time of divergence of the two lineages has been estimated to be around 100 to 120 mya. Fossil metatherians are distinguished from eutherians by the form of their teeth; metatherians possess four pairs of molar teeth in each jaw, whereas eutherian mammals (including true placentals) never have more than three pairs. Using this criterion, the earliest known metatherian was thought to be ''Sinodelphys szalayi
''Sinodelphys'' is an extinct eutherian from the Early Cretaceous, estimated to be 125 million years old. It was discovered and described in 2003 in rocks of the Yixian Formation in Liaoning Province, China, by a team of scientists including Zhe ...
'', which lived in China around 125 mya. However ''Sinodelphys'' was later reinterpreted as an early member of Eutheria
Eutheria (; from Greek , 'good, right' and , 'beast'; ) is the clade consisting of all therian mammals that are more closely related to placentals than to marsupials.
Eutherians are distinguished from noneutherians by various phenotypic tra ...
. The unequivocal oldest known metatherians are now 110 million years old fossils from western North America. Metatherians were widespread in North America and Asia during the Late Cretaceous, but suffered a severe decline during the end-Cretaceous extinction event.
Cladogram from Wilson et al. (2016)
In 2022 a study provided strong evidence that the earliest known marsupial was ''Deltatheridium
''Deltatheridium'' (meaning ''triangle beast'' or ''delta beast'') is an extinct species of metatherian. It lived in what is now Mongolia during the Upper Cretaceous, ''circa'' 80 million years ago. A study in 2022 strongly suggested that De ...
'' known from specimens from the Campanian
The Campanian is the fifth of six ages of the Late Cretaceous Epoch on the geologic timescale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). In chronostratigraphy, it is the fifth of six stages in the Upper Cretaceous Series. Campani ...
age of the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', ...
in Mongolia. This study placed both ''Deltatheridium'' and '' Pucadelphys'' as sister taxa
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree.
Definition
The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram:
Taxon A and ...
to the modern large American opossums.
Marsupials spread to South America from North America during the Paleocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''pal ...
, possibly via the Aves Ridge. Northern Hemisphere metatherians, which were of low morphological and species diversity compared to contemporary placental mammals, eventually became extinct during the Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
epoch.
In South America, the opossums
Opossums () are members of the marsupial order Didelphimorphia () endemic to the Americas. The largest order of marsupials in the Western Hemisphere, it comprises 93 species in 18 genera. Opossums originated in South America and entered North A ...
evolved and developed a strong presence, and the Paleogene also saw the evolution of shrew opossum
The family Caenolestidae contains the seven surviving species of shrew opossum: small, shrew-like marsupials that are confined to the Andes mountains of South America. The order is thought to have diverged from the ancestral marsupial line very e ...
s (Paucituberculata) alongside non-marsupial metatherian predators such as the borhyaenids and the saber-toothed ''Thylacosmilus
''Thylacosmilus'' is an extinct genus of saber-toothed metatherian mammals that inhabited South America from the Late Miocene to Pliocene epochs. Though ''Thylacosmilus'' looks similar to the " saber-toothed cats", it was not a felid, like the ...
''. South American niches for mammalian carnivores were dominated by these marsupial and sparassodont
Sparassodonta (from Greek to tear, rend; and , gen. , ' tooth) is an extinct order of carnivorous metatherian mammals native to South America, related to modern marsupials. They were once considered to be true marsupials, but are now though ...
metatherians, which seem to have competitively excluded South American placentals from evolving carnivory. While placental predators were absent, the metatherians did have to contend with avian ( terror bird) and terrestrial crocodylomorph competition. Marsupials were excluded in turn from large herbivore niches in South America by the presence of native placental ungulates (now extinct) and xenarthrans (whose largest forms are also extinct). South America and Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest cont ...
remained connected until 35 mya, as shown by the unique fossils found there. North and South America were disconnected until about three million years ago, when the Isthmus of Panama formed. This led to the Great American Interchange. Sparassodonts disappeared for unclear reasons – again, this has classically assumed as competition from carnivoran placentals, but the last sparassodonts co-existed with a few small carnivorans like procyonids and canines, and disappeared long before the arrival of macropredatory forms like felines, while didelphimorphs (opossums) invaded Central America, with the Virginia opossum
The Virginia opossum (''Didelphis virginiana''), also known as the North American opossum, is the only opossum living north of Mexico, its range extending south into Central America. It is the northernmost marsupial in the world. In the United S ...
reaching as far north as Canada.
Marsupials reached Australia via Antarctica during the Early Eocene, around 50 mya, shortly after Australia had split off. This suggests a single dispersion event of just one species, most likely a relative to South America's monito del monte
The monito del monte or colocolo opossum, ''Dromiciops gliroides'', also called ''chumaihuén'' in Mapudungun, is a diminutive marsupial native only to southwestern South America (Argentina and Chile). It is the only extant species in the ancient ...
(a microbiothere, the only New World australidelphian). This progenitor may have rafted across the widening, but still narrow, gap between Australia and Antarctica. The journey must not have been easy; South American ungulate and xenarthran remains have been found in Antarctica, but these groups did not reach Australia.
In Australia, marsupials radiated into the wide variety seen today, including not only omnivorous and carnivorous forms such as were present in South America, but also into large herbivores. Modern marsupials appear to have reached the islands of New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torr ...
and Sulawesi relatively recently via Australia. A 2010 analysis of retroposon
Retroposons are repetitive DNA fragments which are inserted into chromosomes after they had been reverse transcribed from any RNA molecule.
Difference between retroposons and retrotransposons
In contrast to retrotransposons, retroposons never ...
insertion sites in the nuclear DNA
Nuclear DNA (nDNA), or nuclear deoxyribonucleic acid, is the DNA contained within each cell nucleus of a eukaryotic organism. It encodes for the majority of the genome in eukaryotes, with mitochondrial DNA and plastid DNA coding for the rest. I ...
of a variety of marsupials has confirmed all living marsupials have South American ancestors. The branching sequence of marsupial orders indicated by the study puts Didelphimorphia in the most basal position, followed by Paucituberculata, then Microbiotheria, and ending with the radiation of Australian marsupials. This indicates that Australidelphia arose in South America, and reached Australia after Microbiotheria split off.
In Australia, terrestrial placental mammals disappeared early in the Cenozoic (their most recent known fossils being 55 million-year-old teeth resembling those of condylarth
Condylarthra is an informal group – previously considered an order – of extinct placental mammals, known primarily from the Paleocene and Eocene epochs. They are considered early, primitive ungulates. It is now largely considered to be a waste ...
s) for reasons that are not clear, allowing marsupials to dominate the Australian ecosystem. Extant native Australian terrestrial placental mammals (such as hopping mice) are relatively recent immigrants, arriving via island hopping from Southeast Asia.
Genetic analysis suggests a divergence date between the marsupials and the placentals at .Graves JA, Renfree MB (201Marsupials in the age of genomics
''Annu Rev Genom Hum Genet'' The ancestral number of chromosomes has been estimated to be 2n = 14. A new hypothesis suggests that South American microbiotheres resulted from a back-dispersal from eastern Gondwana due to new cranial and post-cranial marsupial fossils from the ''Djarthia murgonensis'' from the early Eocene Tingamarra Local Fauna in Australia that indicate the ''Djarthia murgonensis'' is the most plesiomorphic, the oldest unequivocal australidelphian, and may be the ancestral morphotype of the Australian marsupial radiation.
See also
* Marsupial lawn * MetatheriaNotes
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * Frith, H. J. and J. H. Calaby. Kangaroos. New York: Humanities Press, 1969. * * * * * * * *External links
* *First marsupial genome released. Most differences between the opossom and placental mammals stem from non-coding DNA
{{Authority control Extant Paleocene first appearances