|
Magneto-encephalography
Magnetoencephalography (MEG) is a functional neuroimaging technique for mapping brain activity by recording magnetic fields produced by electrical currents occurring naturally in the brain, using very sensitive magnetometers. Arrays of SQUIDs (superconducting quantum interference devices) are currently the most common magnetometer, while the SERF (spin exchange relaxation-free) magnetometer is being investigated for future machines. Applications of MEG include basic research into perceptual and cognitive brain processes, localizing regions affected by pathology before surgical removal, determining the function of various parts of the brain, and neurofeedback. This can be applied in a clinical setting to find locations of abnormalities as well as in an experimental setting to simply measure brain activity. History MEG signals were first measured by University of Illinois physicist David Cohen in 1968, before the availability of the SQUID, using a copper induction coil as the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Neuroimaging
Functional neuroimaging is the use of neuroimaging technology to measure an aspect of brain function, often with a view to understanding the relationship between activity in certain brain areas and specific mental functions. It is primarily used as a research tool in cognitive neuroscience, cognitive psychology, neuropsychology, and social neuroscience. Overview Common methods of functional neuroimaging include * Positron emission tomography (PET) * Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) * Electroencephalography (EEG) * Magnetoencephalography (MEG) * Functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) * Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) * Functional ultrasound imaging (fUS) PET, fMRI, fNIRS and fUS can measure localized changes in cerebral blood flow related to neural activity. These changes are referred to as ''activations''. Regions of the brain which are activated when a subject performs a particular task may play a role in the neural computations which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
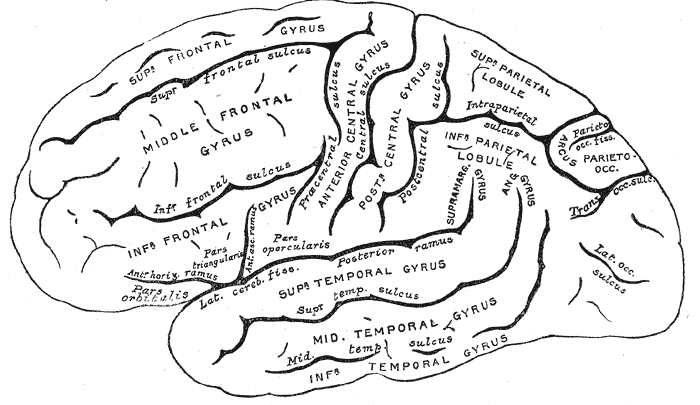
Cerebral Cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consisting of allocortex. It is separated into two cortices, by the longitudinal fissure that divides the cerebrum into the left and right cerebral hemispheres. The two hemispheres are joined beneath the cortex by the corpus callosum. The cerebral cortex is the largest site of neural integration in the central nervous system. It plays a key role in attention, perception, awareness, thought, memory, language, and consciousness. The cerebral cortex is part of the brain responsible for cognition. In most mammals, apart from small mammals that have small brains, the cerebral cortex is folded, providing a greater surface area in the confined volume of the cranium. Apart from minimising brain and cranial volume, cortical folding is crucial for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Shielding
In electrical engineering, electromagnetic shielding is the practice of reducing or blocking the electromagnetic field (EMF) in a space with barriers made of conductive or magnetic materials. It is typically applied to enclosures, for isolating electrical devices from their surroundings, and to cables to isolate wires from the environment through which the cable runs (). Electromagnetic shielding that blocks radio frequency (RF) electromagnetic radiation is also known as RF shielding. EMF shielding serves to minimize electromagnetic interference. The shielding can reduce the coupling of radio waves, electromagnetic fields, and electrostatic fields. A conductive enclosure used to block electrostatic fields is also known as a '' Faraday cage''. The amount of reduction depends very much upon the material used, its thickness, the size of the shielded volume and the frequency of the fields of interest and the size, shape and orientation of holes in a shield to an incident electro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth's Magnetic Field
Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from Earth's interior out into space, where it interacts with the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. The magnetic field is generated by electric currents due to the motion of convection currents of a mixture of molten iron and nickel in Earth's outer core: these convection currents are caused by heat escaping from the core, a natural process called a geodynamo. The magnitude of Earth's magnetic field at its surface ranges from . As an approximation, it is represented by a field of a magnetic dipole currently tilted at an angle of about 11° with respect to Earth's rotational axis, as if there were an enormous bar magnet placed at that angle through the center of Earth. The North geomagnetic pole actually represents the South pole of Earth's magnetic field, and conversely the South geomagnetic pole corresponds to the north pole of Earth's magneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Action Potentials
An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls. This depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize. Action potentials occur in several types of animal cells, called excitable cells, which include neurons, muscle cells, and in some plant cells. Certain endocrine cells such as pancreatic beta cells, and certain cells of the anterior pituitary gland are also excitable cells. In neurons, action potentials play a central role in cell-cell communication by providing for—or with regard to saltatory conduction, assisting—the propagation of signals along the neuron's axon toward synaptic boutons situated at the ends of an axon; these signals can then connect with other neurons at synapses, or to motor cells or glands. In other types of cells, their main function is to activate intracellular processes. In muscle cells, for example, an action potential is the first step in the chain of event ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Processing and Ronald W. Schafer, the principles of signal processing can be found in the classical numerical analysis techniques of the 17th century. They further state that the digital re ...
Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing '' signals'', such as sound, images, and scientific measurements. Signal processing techniques are used to optimize transmissions, digital storage efficiency, correcting distorted signals, subjective video quality and to also detect or pinpoint components of interest in a measured signal. History According to Alan V. Oppenheim Alan Victor Oppenheim''Alan Victor Oppenheim'' was elected in 1987 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulcus (neuroanatomy)
In neuroanatomy, a sulcus (Latin: "furrow", pl. ''sulci'') is a depression or groove in the cerebral cortex. It surrounds a gyrus (pl. gyri), creating the characteristic folded appearance of the brain in humans and other mammals. The larger sulci are usually called fissures. Structure Sulci, the grooves, and gyri, the folds or ridges, make up the folded surface of the cerebral cortex. Larger or deeper sulci are termed fissures, and in many cases the two terms are interchangeable. The folded cortex creates a larger surface area for the brain in humans and other mammals. When looking at the human brain, two-thirds of the surface are hidden in the grooves. The sulci and fissures are both grooves in the cortex, but they are differentiated by size. A sulcus is a shallower groove that surrounds a gyrus. A fissure is a large furrow that divides the brain into lobes and also into the two hemispheres as the longitudinal fissure. Importance of expanded surface area As the surfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyramidal Cell
Pyramidal cells, or pyramidal neurons, are a type of multipolar neuron found in areas of the brain including the cerebral cortex, the hippocampus, and the amygdala. Pyramidal neurons are the primary excitation units of the mammalian prefrontal cortex and the corticospinal tract. Pyramidal neurons are also one of two cell types where the characteristic sign, Negri bodies, are found in post-mortem rabies infection. Pyramidal neurons were first discovered and studied by Santiago Ramón y Cajal. Since then, studies on pyramidal neurons have focused on topics ranging from neuroplasticity to cognition. Structure File:GFPneuron.png, Pyramidal neuron visualized by green fluorescent protein (gfp) File:Hippocampal-pyramidal-cell.png, A hippocampal pyramidal cell One of the main structural features of the pyramidal neuron is the conic shaped soma, or cell body, after which the neuron is named. Other key structural features of the pyramidal cell are a single axon, a large apical d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right-hand Rule
In mathematics and physics, the right-hand rule is a common mnemonic for understanding orientation of axes in three-dimensional space. It is also a convenient method for quickly finding the direction of a cross-product of 2 vectors. Most of the various left-hand and right-hand rules arise from the fact that the three axes of three-dimensional space have two possible orientations. One can see this by holding one's hands outward and together, palms up, with the thumbs out-stretched to the right and left, and the fingers making a curling motion from straight outward to pointing upward. (Note the picture to right is not an illustration of this.) The curling motion of the fingers represents a movement from the first (''x'' axis) to the second (''y'' axis); the third (''z'' axis) can point along either thumb. Left-hand and right-hand rules arise when dealing with coordinate axes. The rule can be used to find the direction of the magnetic field, rotation, spirals, electromagnetic fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipole
In physics, a dipole () is an electromagnetic phenomenon which occurs in two ways: *An electric dipole deals with the separation of the positive and negative electric charges found in any electromagnetic system. A simple example of this system is a pair of charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign separated by some typically small distance. (A permanent electric dipole is called an electret.) *A magnetic dipole is the closed circulation of an electric current system. A simple example is a single loop of wire with constant current through it. A bar magnet is an example of a magnet with a permanent magnetic dipole moment. Dipoles, whether electric or magnetic, can be characterized by their dipole moment, a vector quantity. For the simple electric dipole, the electric dipole moment points from the negative charge towards the positive charge, and has a magnitude equal to the strength of each charge times the separation between the charges. (To be precise: for the definition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxwell's Equations
Maxwell's equations, or Maxwell–Heaviside equations, are a set of coupled partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electromagnetism, classical optics, and electric circuits. The equations provide a mathematical model for electric, optical, and radio technologies, such as power generation, electric motors, wireless communication, lenses, radar etc. They describe how electric field, electric and magnetic fields are generated by electric charge, charges, electric current, currents, and changes of the fields.''Electric'' and ''magnetic'' fields, according to the theory of relativity, are the components of a single electromagnetic field. The equations are named after the physicist and mathematician James Clerk Maxwell, who, in 1861 and 1862, published an early form of the equations that included the Lorentz force law. Maxwell first used the equations to propose that light is an electromagnetic phenomenon. The modern f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synapse
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target effector cell. Synapses are essential to the transmission of nervous impulses from one neuron to another. Neurons are specialized to pass signals to individual target cells, and synapses are the means by which they do so. At a synapse, the plasma membrane of the signal-passing neuron (the ''presynaptic'' neuron) comes into close apposition with the membrane of the target (''postsynaptic'') cell. Both the presynaptic and postsynaptic sites contain extensive arrays of molecular machinery that link the two membranes together and carry out the signaling process. In many synapses, the presynaptic part is located on an axon and the postsynaptic part is located on a dendrite or soma. Astrocytes also exchange information with the synaptic neurons, responding to synaptic activity and, in turn, regulating neurotransmission. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |