|
Macular Hypoplasia
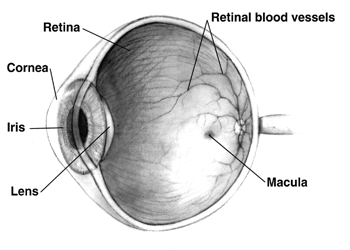
Macular hypoplasia (or foveal hypoplasia) is a rare medical condition involving the underdevelopment of the macula, a small area on the retina (the eye's internal surface) responsible for seeing in detail and sensing light. Macular hypoplasia is often associated with albinism. When the foveal area of the eye is compromised, visual clarity and color perception are reduced. Diagnosing is done by an ophthalmologist. The foveal area of the eye is located in the back of the eyeball. It is placed in front of the optic nerve and is responsible for light sensory and visual perceptiveness. Other diseases with foveal hypoplasia besides albinism include aniridia, retinopathy of prematurity, and Alport syndrome. Causes Macular hypoplasia occurs the most in people that have a diagnosis of albinism. There are four gene mutations that occur in albinism and are linked to macular hypoplasia. The four mutations can occur on the phenotypes of FH, PAX6, SLC38A8, and AHR. The most common gene mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Eye Cross-sectional View Grayscale
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families and kinship networks to political states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus ''Homo'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only extant member. Anatomically mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |