|
Muroid Molar
Rodents of the superfamily Muroidea, which includes mice, rats, voles, hamsters, bamboo rats, and many other species, generally have three molars in each quadrant of the jaws. A few of the oldest species retain the fourth upper premolar, and some living species have lost the third and even the second molars. Features of the molar crown are often used in muroid taxonomy, and many different systems have been proposed to name these features. Description Muroids are most closely related to the Dipodidae, a smaller group of rodents that includes the jerboas, birch mice, and jumping mice.Carleton and Musser, 2005, p. 749 Jerboas have a dental formula of , including incisors in the upper and lower jaws, three molars in the upper and lower jaw, and in most species a small premolar (the fourth upper premolar, P4) in the upper jaw only.Ellerman, 1940, p. 561 In contrast, all muroids lack the P4,Carleton and Musser, 1984, p. 292 but some species of '' Pappocricetodon'' from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megalomys Desmarestii
''Megalomys desmarestii'', also known as the Martinique muskrat,Watts, 1990, p. 528 Desmarest's pilorie,Musser and Carleton, 2005 or the Martinique giant rice rat, is an extinct rice rat from Martinique in the Caribbean. Description It was among the largest species of West Indian rice rat, as big as a cat, and was one of the first Caribbean mammals to become extinct during the 20th century. It may have been aquatic, as it was known to escape into the sea when pursued by predators, but it never swam away from the island. Extinction It was common on Martinique until the end of the 19th century, when attempts were made to exterminate it because it was considered to be a pest in the island's coconut plantations. It was also hunted for food; however, due to a strong musky odor, cooking required people to singe off its hair, air out the body overnight and boil it in two batches of water. On 8 May 1902, the volcano Mount Pelée erupted, completely destroying the island's principal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Formula
Dentition pertains to the development of teeth and their arrangement in the mouth. In particular, it is the characteristic arrangement, kind, and number of teeth in a given species at a given age. That is, the number, type, and morpho-physiology (that is, the relationship between the shape and form of the tooth in question and its inferred function) of the teeth of an animal. Animals whose teeth are all of the same type, such as most non-mammalian vertebrates, are said to have '' homodont'' dentition, whereas those whose teeth differ morphologically are said to have '' heterodont'' dentition. The dentition of animals with two successions of teeth (deciduous, permanent) is referred to as '' diphyodont'', while the dentition of animals with only one set of teeth throughout life is ''monophyodont''. The dentition of animals in which the teeth are continuously discarded and replaced throughout life is termed ''polyphyodont''. The dentition of animals in which the teeth are set in s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ontogeny
Ontogeny (also ontogenesis) is the origination and development of an organism (both physical and psychological, e.g., moral development), usually from the time of fertilization of the egg to adult. The term can also be used to refer to the study of the entirety of an organism's lifespan. Ontogeny is the developmental history of an organism within its own lifetime, as distinct from phylogeny, which refers to the evolutionary history of a species. Another way to think of ontogeny is that it is the process of an organism going through all of the developmental stages over its lifetime. The developmental history includes all the developmental events that occur during the existence of an organism, beginning with the changes in the egg at the time of fertilization and events from the time of birth or hatching and afterward (i.e., growth, remolding of body shape, development of secondary sexual characteristics, etc.). While developmental (i.e., ontogenetic) processes can influence sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudohydromys
''Pseudohydromys'' is a genus of rodent in the family Muridae endemic to New Guinea. It contains the following species: * Bishop's moss mouse (''Pseudohydromys berniceae'') * Huon small-toothed moss mouse (''Pseudohydromys carlae'') * Laurie's moss mouse (''Pseudohydromys eleanorae'') * One-toothed shrew mouse (''Pseudohydromys ellermani'') * Mottled-tailed shrew mouse (''Pseudohydromys fuscus'') * German's one-toothed moss mouse (''Pseudohydromys germani'') * Eastern shrew mouse (''Pseudohydromys murinus'') * Musser's shrew mouse (''Pseudohydromys musseri'') * Western shrew mouse The western shrew mouse (''Pseudohydromys occidentalis'') is a species of rodent in the family Muridae. It is found in West Papua (region), West Papua, Indonesia and Papua New Guinea. References * Pseudohydromys Rodents of Papua New Gui ... (''Pseudohydromys occidentalis'') * Woolley's moss mouse (''Pseudohydromys patriciae'') * Southern small-toothed moss mouse (''Pseudohydromys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murinae
The Old World rats and mice, part of the subfamily Murinae in the family Muridae, comprise at least 519 species. Members of this subfamily are called murines. In terms of species richness, this subfamily is larger than all mammal families except the Cricetidae and Muridae, and is larger than all mammal orders except the bats and the remainder of the rodents. Description The Murinae are native to Africa, Europe, Asia, and Australia. They are terrestrial placental mammals. They have also been introduced to all continents except Antarctica, and are serious pest animals. This is particularly true in island communities where they have contributed to the endangerment and extinction of many native animals. Two prominent murine species have become vital laboratory animals: the brown rat and house mouse are both used as medical subjects. The murines have a distinctive molar pattern that involves three rows of cusps instead of two, the primitive pattern seen most frequently in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', "dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope Carbon-13, 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope Carbon-12, 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Popigai impact structure, Siberia and in what is now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incisor
Incisors (from Latin ''incidere'', "to cut") are the front teeth present in most mammals. They are located in the premaxilla above and on the mandible below. Humans have a total of eight (two on each side, top and bottom). Opossums have 18, whereas armadillos have none. Structure Adult humans normally have eight incisors, two of each type. The types of incisor are: * maxillary central incisor (upper jaw, closest to the center of the lips) * maxillary lateral incisor (upper jaw, beside the maxillary central incisor) * mandibular central incisor (lower jaw, closest to the center of the lips) * mandibular lateral incisor (lower jaw, beside the mandibular central incisor) Children with a full set of deciduous teeth (primary teeth) also have eight incisors, named the same way as in permanent teeth. Young children may have from zero to eight incisors depending on the stage of their tooth eruption and tooth development. Typically, the mandibular central incisors erupt first, followed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jumping Mouse
Zapodidae, the jumping mice, is a family of mouse-like rodents in North America and China. Although mouse-like in general appearance, these rodents are distinguished by their elongated hind limbs, and, typically, by the presence of four pairs of cheek-teeth in each jaw. There are five toes to all the feet, but the first in the fore-feet is rudimentary, and furnished with a flat nail. The tail makes up about 60% of its body length and is used to gain balance while jumping. The cheeks have pouches. The Sichuan jumping "yeti" mouse (''Eozapus setchuanus'') from China can be identified by the ‘Y’ marking on its belly. Jumping mice live in wooded areas, grassy fields and alpine meadows. When disturbed, they start, in enormous bounds of eight or ten feet in length, which soon diminish to three or four, and in leaping the feet scarcely seem to touch the ground. They are nocturnal and generally live alone. The nest is placed in clefts of rocks, among timber, or in hollow trees, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are native to all major land masses except for New Zealand, Antarctica, and several oceanic islands, though they have subsequently been introduced to most of these land masses by human activity. Rodents are extremely diverse in their ecology and lifestyles and can be found in almost every terrestrial habitat, including human-made environments. Species can be arboreal, fossorial (burrowing), saltatorial/richochetal (leaping on their hind legs), or semiaquatic. However, all rodents share several morphological features, including having only a single upper and lower pair of ever-growing incisors. Well-known rodents include mice, rats, squirrels, prairie dogs, porcupines, beavers, guinea pigs, and hamsters. Rabbits, hares, and pikas, whose i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birch Mouse
Birch mice (genus ''Sicista'') are small jumping rodents that resemble mice with long, tufted tails and very long hind legs, allowing for remarkable leaps. They are the only extant members of the family Sminthidae. They are native to Eurasian forests and steppes. All variants possess a long tail of of length and weigh about . Head and body length of and hind foot length of . The animal's skin color is light brown or dark-brown to brownish yellow on the upper side and paler on the underside, but generally brownish. Birch mice have a vast geographic distribution in that they inhabit a wide variety of habitats, from semiarid areas to subalpine meadows. Species Nineteen species are listed by the American Society of Mammalogists as of 2021: * Armenian birch mouse, '' Sicista armenica'' * Northern birch mouse, '' Sicista betulina'' * Caucasian birch mouse, '' Sicista caucasica'' * Long-tailed birch mouse, '' Sicista caudata'' * Tsimlyansk birch mouse, '' Sicista cimlanica'' * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
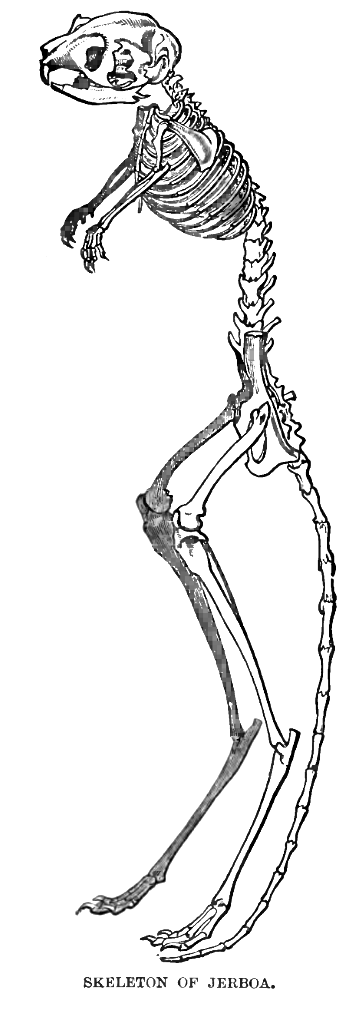
Jerboa
Jerboas (from ar, جربوع ') are hopping desert rodents found throughout North Africa and Asia, and are members of the family Dipodidae. They tend to live in hot deserts. When chased, jerboas can run at up to . Some species are preyed on by little owls (''Athene noctua'') in central Asia. Most species of jerboas have excellent hearing that they use to avoid becoming the prey of nocturnal predators. The typical lifespan of a jerboa is around 6 years. Taxonomy Jerboas, as previously defined, were thought to be paraphyletic, with the jumping mice (Zapodidae) and birch mice (Sminthidae) also classified in the family Dipodidae. However, phylogenetic analysis split all three as distinct families, leaving just the jerboas in Dipodidae and revealing them to be a monophyletic group. Anatomy and body features Jerboas look somewhat like miniature kangaroos, and have some external similarities. Both have long hind legs, short forelegs, and long tails. Jerboas move around in a similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |