|
Mouthwashes
Mouthwash, mouth rinse, oral rinse, or mouth bath is a liquid which is held in the mouth passively or swilled around the mouth by contraction of the perioral muscles and/or movement of the head, and may be gargled, where the head is tilted back and the liquid bubbled at the back of the mouth. Usually mouthwashes are antiseptic solutions intended to reduce the microbial load in the mouth, although other mouthwashes might be given for other reasons such as for their analgesic, anti-inflammatory or anti-fungal action. Additionally, some rinses act as saliva substitutes to neutralize acid and keep the mouth moist in xerostomia (dry mouth). Cosmetic mouthrinses temporarily control or reduce bad breath and leave the mouth with a pleasant taste. Rinsing with water or mouthwash after brushing with a fluoride toothpaste can reduce the availability of salivary fluoride. This can lower the anti-cavity re-mineralization and antibacterial effects of fluoride. Fluoridated mouthwash may mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bad Breath
Bad breath, also known as halitosis, is a symptom in which a noticeably unpleasant breath odour is present. It can result in anxiety among those affected. It is also associated with depression and symptoms of obsessive compulsive disorder. The concerns of bad breath may be divided into genuine and non-genuine cases. Of those who have genuine bad breath, about 85% of cases come from inside the mouth. The remaining cases are believed to be due to disorders in the nose, sinuses, throat, lungs, esophagus, or stomach. Rarely, bad breath can be due to an underlying medical condition such as liver failure or ketoacidosis. Non-genuine cases occur when someone complains of having bad breath but other people cannot detect it. This is estimated to make up between 5% and 72% of cases. The treatment depends on the underlying cause. Initial efforts may include tongue cleaning, mouthwash, and flossing. Tentative evidence supports the use of mouthwash containing chlorhexidine or cetylpyridin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Listerine Products
Listerine is an American brand of antiseptic mouthwash that is promoted with the slogan "Kills germs that cause bad breath", Named after Joseph Lister, who pioneered antiseptic surgery at the Glasgow Royal Infirmary in Scotland, Listerine was developed in 1879 by Joseph Lawrence, a chemist in St. Louis, Missouri. Originally marketed by the Lambert Pharmacal Company (which later became Warner–Lambert), Listerine has been manufactured and distributed by Johnson & Johnson since that company's acquisition of Pfizer's consumer healthcare division on December 20, 2006. The Listerine brand name is also used in toothpaste, chewable tablets, and self-dissolving teeth-whitening strips. History Inspired by Louis Pasteur's ideas on microbial infection, the English doctor Joseph Lister demonstrated in 1865 that use of carbolic acid on surgical dressings would significantly reduce rates of post-surgical infection. Lister's work in turn inspired St. Louis-based doctor Joseph Lawrence to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiseptic
An antiseptic (from Greek ἀντί ''anti'', "against" and σηπτικός ''sēptikos'', "putrefactive") is an antimicrobial substance or compound that is applied to living tissue/skin to reduce the possibility of infection, sepsis, or putrefaction. Antiseptics are generally distinguished from ''antibiotics'' by the latter's ability to safely destroy bacteria within the body, and from ''disinfectants'', which destroy microorganisms found on non-living objects. Antibacterials include antiseptics that have the proven ability to act against bacteria. Microbicides which destroy virus particles are called viricides or antivirals. Antifungals, also known as antimycotics, are pharmaceutical fungicides used to treat and prevent mycosis (fungal infection). Surgery The widespread introduction of antiseptic surgical methods was initiated by the publishing of the paper ''Antiseptic Principle of the Practice of Surgery'' in 1867 by Joseph Lister, which was inspired by Louis Pasteur's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
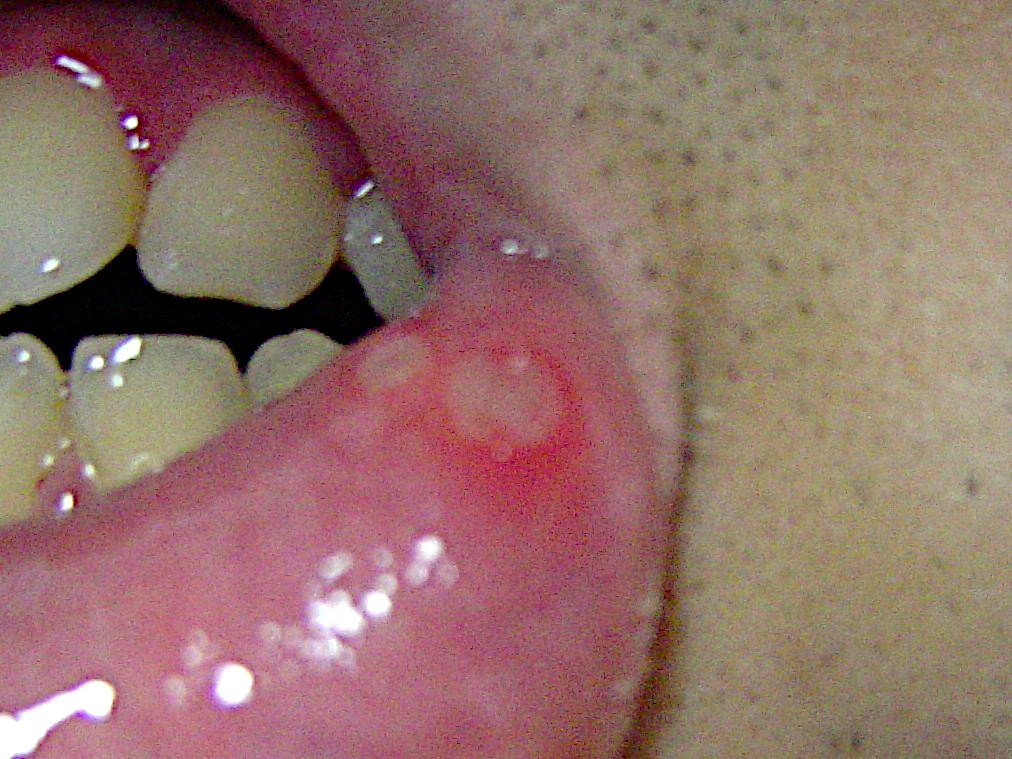
Aphthous Ulcer
Aphthous stomatitis, or recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS), is a common condition characterized by the repeated formation of benign and non-contagious mouth ulcers (aphthae) in otherwise healthy individuals. The informal term ''canker sore'' is also used, mainly in North America, although it may also refer to other types of mouth ulcers. The cause is not completely understood but involves a T cell-mediated immune response triggered by a variety of factors which may include nutritional deficiencies, local trauma, stress, hormonal influences, allergies, genetic predisposition, certain foods, dehydration, some food additives, or some hygienic chemical additives like SDS (common in toothpaste). These ulcers occur periodically and heal completely between attacks. In the majority of cases, the individual ulcers last about 7–10 days, and ulceration episodes occur 3–6 times per year. Most appear on the non-keratinizing epithelial surfaces in the mouth – i.e. anywhere excep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xerostomia
Xerostomia, also known as dry mouth, is dryness in the mouth, which may be associated with a change in the composition of saliva, or reduced salivary flow, or have no identifiable cause. This symptom is very common and is often seen as a side effect of many types of medication. It is more common in older people (mostly because this group tend to take several medications) and in persons who breathe through their mouths. Dehydration, radiotherapy involving the salivary glands, chemotherapy and several diseases can cause reduced salivation (hyposalivation), or a change in saliva consistency and hence a complaint of xerostomia. Sometimes there is no identifiable cause, and there may sometimes be a psychogenic reason for the complaint. Definition Xerostomia is the subjective sensation of dry mouth, which is often (but not always) associated with hypofunction of the salivary glands. The term is derived from the Greek words ξηρός (''xeros'') meaning "dry" and στόμα (''stoma' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toothpaste
Toothpaste is a paste or gel dentifrice used with a toothbrush to clean and maintain the aesthetics and health of teeth. Toothpaste is used to promote oral hygiene: it is an abrasive that aids in removing dental plaque and food from the teeth, assists in suppressing halitosis, and delivers active ingredients (most commonly fluoride) to help prevent tooth decay (dental caries) and gum disease (gingivitis).American Dental Association Description of Toothpaste Owing to differences in composition and fluoride content, not all toothpastes are equally effective in maintaining oral health. The decline of tooth decay during the 20th century has been attributed to the introduction and regular use of fluoride-containing toothpastes worldwide. Large amounts of swallowed toothpaste can be toxic. Common colors for toothpaste include white (sometimes with colored stripes or green tint) and blue. Usefulness Toothpastes are generally useful to maintain dental health. Toothpastes containing fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
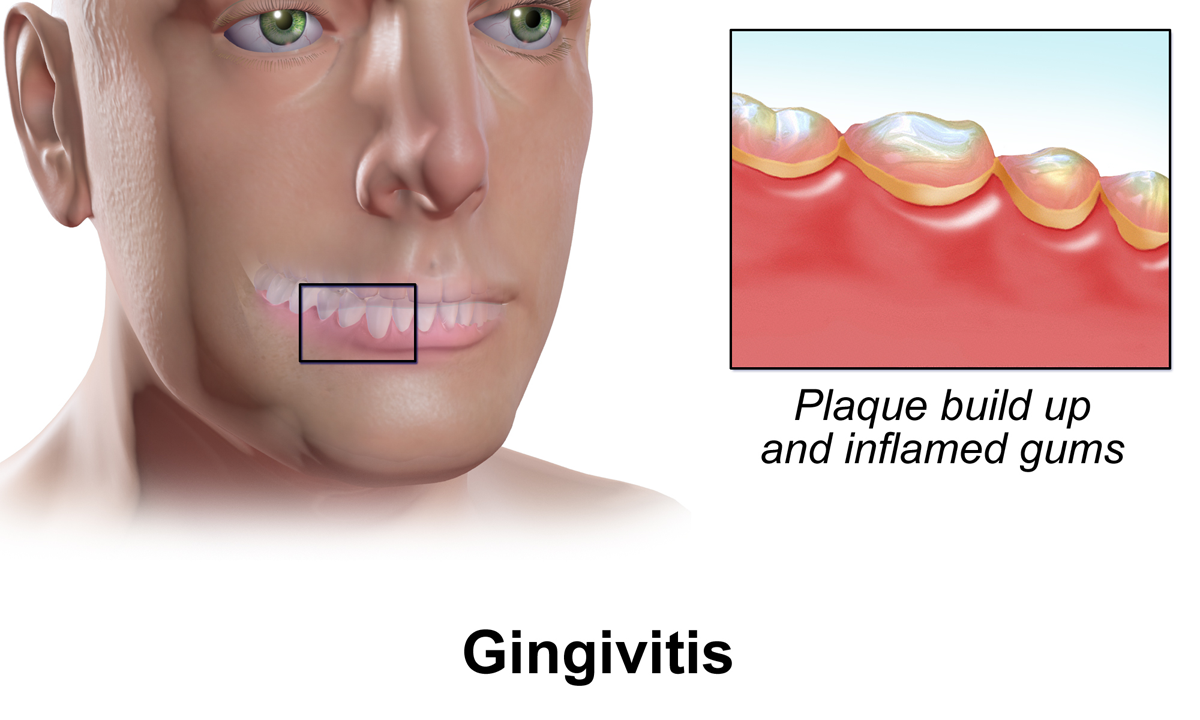
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a non-destructive disease that causes inflammation of the gums. The most common form of gingivitis, and the most common form of periodontal disease overall, is in response to bacterial biofilms (also called plaque) that is attached to tooth surfaces, termed ''plaque-induced gingivitis''. Most forms of gingivitis are plaque-induced. While some cases of gingivitis never progress to periodontitis, periodontitis is always preceded by gingivitis. Gingivitis is reversible with good oral hygiene; however, without treatment, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, in which the inflammation of the gums results in tissue destruction and bone resorption around the teeth. Periodontitis can ultimately lead to tooth loss. Signs and symptoms The symptoms of gingivitis are somewhat non-specific and manifest in the gum tissue as the classic signs of inflammation: *Swollen gums *Bright red gums *Gums that are tender or painful to the touch *Bleeding gums or bleeding after bru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphthous Stomatitis
Aphthous stomatitis, or recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS), is a common condition characterized by the repeated formation of benign and non- contagious mouth ulcers (aphthae) in otherwise healthy individuals. The informal term ''canker sore'' is also used, mainly in North America, although it may also refer to other types of mouth ulcers. The cause is not completely understood but involves a T cell-mediated immune response triggered by a variety of factors which may include nutritional deficiencies, local trauma, stress, hormonal influences, allergies, genetic predisposition, certain foods, dehydration, some food additives, or some hygienic chemical additives like SDS (common in toothpaste). These ulcers occur periodically and heal completely between attacks. In the majority of cases, the individual ulcers last about 7–10 days, and ulceration episodes occur 3–6 times per year. Most appear on the non-keratinizing epithelial surfaces in the mouth – i.e. anywhere exce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Hygiene
Oral hygiene is the practice of keeping one's mouth clean and free of disease and other problems (e.g. bad breath) by regular brushing of the teeth (dental hygiene) and cleaning between the teeth. It is important that oral hygiene be carried out on a regular basis to enable prevention of dental disease and bad breath. The most common types of dental disease are tooth decay (''cavities'', ''dental caries'') and gum diseases, including gingivitis, and periodontitis. General guidelines for adults suggest brushing at least twice a day with a fluoridated toothpaste: brushing last thing at night and at least on one other occasion. Cleaning between the teeth is called interdental cleaning and is as important as tooth brushing. This is because a toothbrush cannot reach between the teeth and therefore only removes about 50% of plaque from the surface of the teeth. There are many tools to clean between the teeth, including floss, tape and interdental brushes; it is up to each individual to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooth Extraction
A dental extraction (also referred to as tooth extraction, exodontia, exodontics, or informally, tooth pulling) is the removal of teeth from the dental alveolus (socket) in the alveolar bone. Extractions are performed for a wide variety of reasons, but most commonly to remove teeth which have become unrestorable through tooth decay, periodontal disease, or dental trauma, especially when they are associated with toothache. Sometimes impacted wisdom teeth (wisdom teeth that are stuck and unable to grow normally into the mouth) cause recurrent infections of the gum (pericoronitis), and may be removed when other conservative treatments have failed (cleaning, antibiotics and operculectomy). In orthodontics, if the teeth are crowded, healthy teeth may be extracted (often bicuspids) to create space so the rest of the teeth can be straightened. Procedure Extractions could be categorized into non-surgical (simple) and surgical, depending on the type of tooth to be removed and other fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs) or it may aim to prolong life or to reduce symptoms ( palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called ''medical oncology''. The term ''chemotherapy'' has come to connote non-specific usage of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or induce DNA damage, which is why inhibition of DNA repair can augment chemotherapy. The connotation of the word chemotherapy excludes more selective agents that block extracellular signals (signal transduction). The development of therapies with specific molecular or genetic targets, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Radiation therapy may be curative in a number of types of cancer if they are localized to one area of the body. It may also be used as part of adjuvant therapy, to prevent tumor recurrence after surgery to remove a primary malignant tumor (for example, early stages of breast cancer). Radiation therapy is synergistic with chemotherapy, and has been used before, during, and after chemotherapy in susceptible cancers. The subspecialty of oncology concerned with radiotherapy is called radiation oncology. A physician who practices in this subspecialty is a radiation oncologist. Radiation therapy is commonly applied to the cancerous tumor because of its ability to control cell growth. Ionizing radiation works by damaging the DNA of cancerous tissue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |