|
Mobilisation
Mobilization is the act of assembling and readying military troops and supplies for war. The word ''mobilization'' was first used in a military context in the 1850s to describe the preparation of the Prussian Army. Mobilization theories and tactics have continuously changed since then. The opposite of mobilization is demobilization. Mobilization became an issue with the introduction of conscription, and the introduction of the railways in the 19th century. Mobilization institutionalized the mass levy of conscripts that was first introduced during the French Revolution. A number of technological and societal changes promoted the move towards a more organized way of deployment. These included the telegraph to provide rapid communication, the railways to provide rapid movement and concentration of troops, and conscription to provide a trained reserve of soldiers in case of war. History Roman Republic The Roman Republic was able to mobilize at various times between 6% (81 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific Ocean, Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in Genocides in history (World War I through World War II), genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the Spanish flu, 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising French Third Republic, France, Russia, and British Empire, Britain) and the Triple A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schlieffen Plan
The Schlieffen Plan (german: Schlieffen-Plan, ) is a name given after the First World War to German war plans, due to the influence of Field Marshal Alfred von Schlieffen and his thinking on an invasion of France and Belgium, which began on 4 August 1914. Schlieffen was Chief of the General Staff of the German Army from 1891 to 1906. In 1905 and 1906, Schlieffen devised an army deployment plan for a decisive (war-winning) offensive against the French Third Republic. German forces were to invade France through the Netherlands and Belgium rather than across the common border. After losing the First World War, German official historians of the and other writers described the plan as a blueprint for victory. (Colonel-General) Helmuth von Moltke the Younger succeeded Schlieffen as Chief of the German General Staff in 1906 and was dismissed after the First Battle of the Marne (5–12 September 1914). German historians claimed that Moltke had ruined the plan by meddling with it, ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conscription
Conscription (also called the draft in the United States) is the state-mandated enlistment of people in a national service, mainly a military service. Conscription dates back to antiquity and it continues in some countries to the present day under various names. The modern system of near-universal national conscription for young men dates to the French Revolution in the 1790s, where it became the basis of a very large and powerful military. Most European nations later copied the system in peacetime, so that men at a certain age would serve 1–8 years on active duty and then transfer to the reserve force. Conscription is controversial for a range of reasons, including conscientious objection to military engagements on religious or philosophical grounds; political objection, for example to service for a disliked government or unpopular war; sexism, in that historically men have been subject to the draft in the most cases; and ideological objection, for example, to a perceived vio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demobilization
Demobilization or demobilisation (see spelling differences) is the process of standing down a nation's armed forces from combat-ready status. This may be as a result of victory in war, or because a crisis has been peacefully resolved and military force will not be necessary. The opposite of demobilization is mobilization. Forceful demobilization of a defeated enemy is called demilitarization. The United Nations defined demobilization as "a multifaceted process that officially certifies an individual's change of status from being a member of a military grouping of some kind to being a civilian". Persons undergoing demobilization are removed from the command and control of their armed force and group and the transformation from a military mindset to that of a civilian begins. Although combatants become civilians when they acquire their official discharge documents the mental connection and formal ties to their military command structure still exist. To prevent soldiers from r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considered fundamental principles of liberal democracy, while phrases like '' liberté, égalité, fraternité'' reappeared in other revolts, such as the 1917 Russian Revolution, and inspired campaigns for the abolition of slavery and universal suffrage. The values and institutions it created dominate French politics to this day. Its causes are generally agreed to be a combination of social, political and economic factors, which the ''Ancien Régime'' proved unable to manage. In May 1789, widespread social distress led to the convocation of the Estates General, which was converted into a National Assembly in June. Continuing unrest culminated in the Storming of the Bastille on 14 July, which led to a series of radical measures by the Assemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
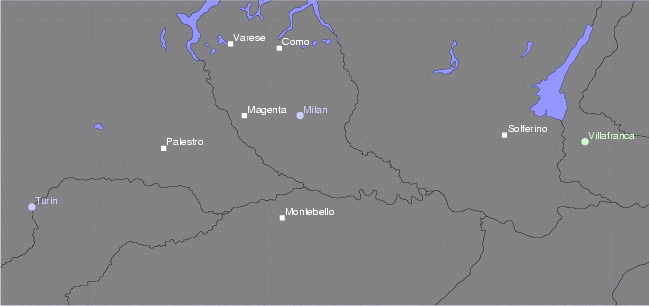
Second Italian War Of Independence
The Second Italian War of Independence, also called the Franco-Austrian War, the Austro-Sardinian War or Italian War of 1859 ( it, Seconda guerra d'indipendenza italiana; french: Campagne d'Italie), was fought by the Second French Empire and the Savoyard Kingdom of Sardinia against the Austrian Empire in 1859 and played a crucial part in the process of Italian Unification. A year prior to the war, in the Plombières Agreement, France agreed to support Sardinia's efforts to expel Austria from Italy in return for territorial compensation in the form of the Duchy of Savoy and the County of Nice. The two states signed a military alliance in January 1859. Sardinia mobilised its army on 9 March 1859, and Austria mobilized on 9 April. On 23 April, Austria delivered an ultimatum to Sardinia demanding its demobilization. Upon Sardinia's refusal, the war began on 26 April. Austria invaded Sardinia three days later, and France declared war on Austria on 3 May. The Austrian invasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom Of Great Britain And Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was a sovereign state in the British Isles that existed between 1801 and 1922, when it included all of Ireland. It was established by the Acts of Union 1800, which merged the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland into a unified state. The establishment of the Irish Free State in 1922 led to the remainder later being renamed the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland in 1927. The United Kingdom, having financed the European coalition that defeated France during the Napoleonic Wars, developed a large Royal Navy that enabled the British Empire to become the foremost world power for the next century. For nearly a century from the final defeat of Napoleon following the Battle of Waterloo to the outbreak of World War I, Britain was almost continuously at peace with Great Powers. The most notable exception was the Crimean War with the Russian Empire, in which actual hostilities were relatively ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Militia
A militia () is generally an army or some other fighting organization of non- professional soldiers, citizens of a country, or subjects of a state, who may perform military service during a time of need, as opposed to a professional force of regular, full-time military personnel; or, historically, to members of a warrior-nobility class (e.g. knights or samurai). Generally unable to hold ground against regular forces, militias commonly support regular troops by skirmishing, holding fortifications, or conducting irregular warfare, instead of undertaking offensive campaigns by themselves. Local civilian laws often limit militias to serve only in their home region, and to serve only for a limited time; this further reduces their use in long military campaigns. Beginning in the late 20th century, some militias (in particular officially recognized and sanctioned militias of a government) act as professional forces, while still being "part-time" or "on-call" organizations. For ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic language, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, mainly inhabiting Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe, and the Balkans to the west; and Siberia to the east. A large Slavic minority is also scattered across the Baltic states and Central Asia, while a substantial Slavic diaspora is found throughout the Americas, as a result of immigration. Present-day Slavs are classified into East Slavs (chiefly Belarusians, Russians, Rusyns, and Ukrainians), West Slavs (chiefly Czechs, Kashubians, Poles, Slovaks and Sorbs) and South Slavs (chiefly Bosniaks, Bulgarians, Croats, Macedonians (ethnic group), Macedonians, Montenegrins, Serbs and Slovenes). The vast majority of Slavs are traditionally Christians. However, modern Slavic nations and ethnic groups are considerably dive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
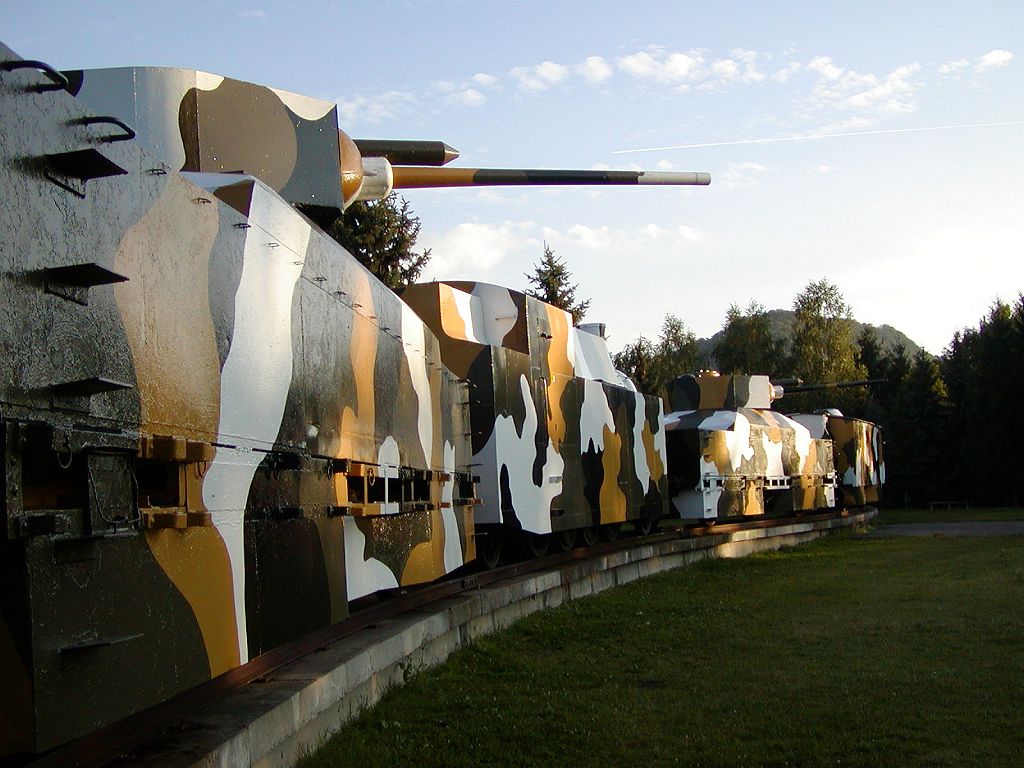
Military Railways
The military use of railways derives from their ability to move troops or materiel rapidly and, less usually, on their use as a platform for military systems, like very large railroad guns and armoured trains, in their own right. Railways have been employed for military purposes in wartime since the Revolutions of 1848. Improvements in other forms of transport have rendered railways less important to the military since the end of World War II and the Cold War, although they are still employed for the transport of armoured vehicles to and from exercises or the mass transport of vehicles to a theatre of operations. The US Air Force developed the Peacekeeper Rail Garrison mobile ICBM in the 1980s, but it never reached operational status. Due to the expense and time required to build specifically military railway networks, military use of railways is usually based on a pre-existing civilian railway network rather than a military-owned one. However, specialized military types of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piedmont
it, Piemontese , population_note = , population_blank1_title = , population_blank1 = , demographics_type1 = , demographics1_footnotes = , demographics1_title1 = , demographics1_info1 = , demographics1_title2 = , demographics1_info2 = , demographics1_title3 = , demographics1_info3 = , timezone1 = CET , utc_offset1 = +1 , timezone1_DST = CEST , utc_offset1_DST = +2 , postal_code_type = , postal_code = , area_code_type = ISO 3166 code , area_code = IT-21 , blank_name_sec1 = GDP (nominal) , blank_info_sec1 = €137 billion (2018) , blank1_name_sec1 = GDP per capita , blank1_info_sec1 = €31,500 (2018) , blank2_name_sec1 = HDI (2019) , blank2_info_sec1 = 0.898 · 10th of 21 , blank_name_sec2 = NUTS Region , blank_info_sec2 = ITC1 , website www.regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |