|
Mixed Strategies
In game theory, a move, action, or play is any one of the options which a player can choose in a setting where the optimal outcome depends ''not only'' on their own actions ''but'' on the actions of others. The discipline mainly concerns the action of a player in a game affecting the behavior or actions of other players. Some examples of "games" include chess, bridge, poker, monopoly, diplomacy or battleship. The term strategy is typically used to mean a complete algorithm for playing a game, telling a player what to do for every possible situation. A player's strategy determines the action the player will take at any stage of the game. However, the idea of a strategy is often confused or conflated with that of a move or action, because of the correspondence between moves and pure strategies in most games: for any move ''X'', "always play move ''X''" is an example of a valid strategy, and as a result every move can also be considered to be a strategy. Other authors treat strateg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Game Theory
Game theory is the study of mathematical models of strategic interactions. It has applications in many fields of social science, and is used extensively in economics, logic, systems science and computer science. Initially, game theory addressed two-person zero-sum games, in which a participant's gains or losses are exactly balanced by the losses and gains of the other participant. In the 1950s, it was extended to the study of non zero-sum games, and was eventually applied to a wide range of Human behavior, behavioral relations. It is now an umbrella term for the science of rational Decision-making, decision making in humans, animals, and computers. Modern game theory began with the idea of mixed-strategy equilibria in two-person zero-sum games and its proof by John von Neumann. Von Neumann's original proof used the Brouwer fixed-point theorem on continuous mappings into compact convex sets, which became a standard method in game theory and mathematical economics. His paper was f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
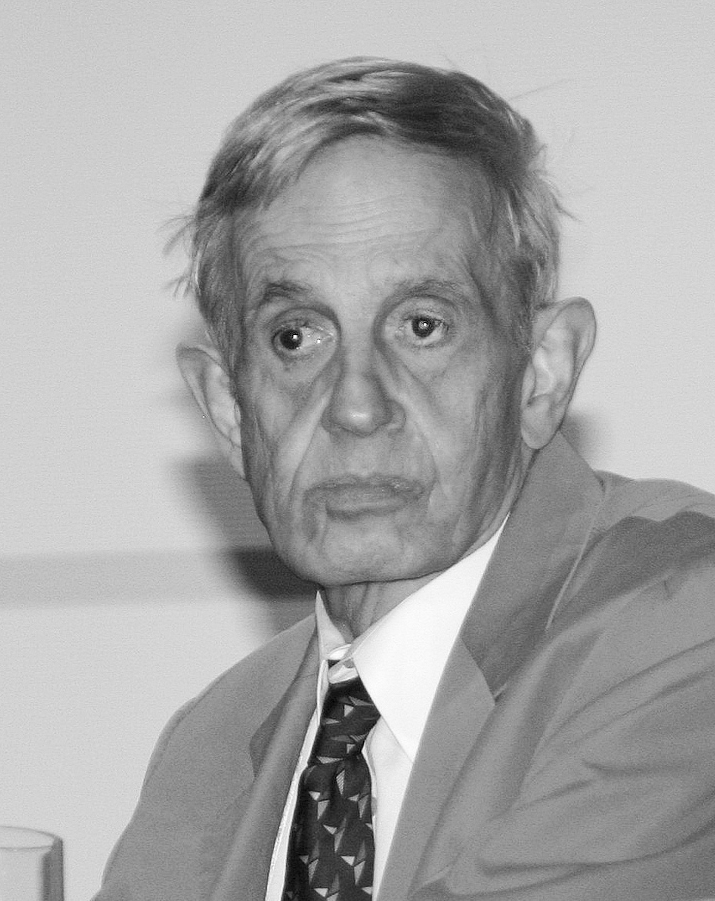
John Forbes Nash
John Forbes Nash Jr. (June 13, 1928 – May 23, 2015), known and published as John Nash, was an American mathematician who made fundamental contributions to game theory, real algebraic geometry, differential geometry, and partial differential equations. Nash and fellow game theorists John Harsanyi and Reinhard Selten were awarded the 1994 Nobel Prize in Economics. In 2015, Louis Nirenberg and he were awarded the Abel Prize for their contributions to the field of partial differential equations. As a graduate student in the Princeton University Department of Mathematics, Nash introduced a number of concepts (including Nash equilibrium and the Nash bargaining solution), which are now considered central to game theory and its applications in various sciences. In the 1950s, Nash discovered and proved the Nash embedding theorems by solving a system of nonlinear partial differential equations arising in Riemannian geometry. This work, also introducing a preliminary form o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haven (graph Theory)
In graph theory, a haven is a certain type of function on sets of vertices in an undirected graph. If a haven exists, it can be used by an evader to win a pursuit–evasion game on the graph, by consulting the function at each step of the game to determine a safe set of vertices to move into. Havens were first introduced by as a tool for characterizing the treewidth of graphs. Their other applications include proving the existence of small separators on minor-closed families of graphs, and characterizing the ends and clique minors of infinite graphs... Definition If is an undirected graph, and is a set of vertices, then an -flap is a nonempty connected component of the subgraph of formed by deleting . A haven of order in is a function that assigns an -flap to every set of fewer than vertices. This function must also satisfy additional constraints which are given differently by different authors. The number is called the ''order'' of the haven.. In the original ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuhn's Theorem
In game theory Game theory is the study of mathematical models of strategic interactions. It has applications in many fields of social science, and is used extensively in economics, logic, systems science and computer science. Initially, game theory addressed ..., Kuhn's theorem is a foundational result in the analysis of extensive-form games, first formalized by American mathematician Harold W. Kuhn in 1953. The theorem establishes a formal equivalence between two types of strategies in extensive-form games with perfect recall: mixed strategies and behavior strategies. A mixed strategy assigns probabilities to complete plans of action (also called pure strategies), while a behavior strategy assigns probabilities to individual actions at each decision point. Kuhn's theorem shows that in any finite extensive-form game where players have perfect recall (the ability to remember all of their previous moves and information), every mixed strategy has an equivalent behavior st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Game Tree
In the context of combinatorial game theory, a game tree is a graph representing all possible game states within a sequential game that has perfect information. Such games include chess, checkers, Go, and tic-tac-toe. A game tree can be used to measure the complexity of a game, as it represents all the possible ways that the game can pan out. Due to the large game trees of complex games such as chess, algorithms that are designed to play this class of games will use partial game trees, which makes computation feasible on modern computers. Various methods exist to solve game trees. If a complete game tree can be generated, a deterministic algorithm, such as backward induction or retrograde analysis can be used. Randomized algorithms and minmax algorithms such as MCTS can be used in cases where a complete game tree is not feasible. Understanding the game tree To better understand the game tree, it can be thought of as a technique for analyzing adversarial games, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Set (game Theory)
In game theory, an information set is the basis for decision making in a game, which includes the actions available to players and the potential outcomes of each action. It consists of a collection of decision nodes that a player cannot distinguish between when making a move, due to incomplete information about previous actions or the current state of the game. In other words, when a player's turn comes, they may be uncertain about which exact node in the game tree they are currently at, and the information set represents all the possibilities they must consider. Information sets are a fundamental concept particularly important in games with imperfect information. In games with perfect information (such as chess or Go (game), Go), every information set contains exactly one decision node, as each player can observe all previous moves and knows the exact game state. However, in games with imperfect information—such as most Card game, card games like poker or Bridge (card game), bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purification Theorem
In game theory, the purification theorem was contributed by Nobel laureate John Harsanyi in 1973. The theorem justifies a puzzling aspect of mixed strategy Nash equilibria In game theory, the Nash equilibrium is the most commonly used solution concept for non-cooperative games. A Nash equilibrium is a situation where no player could gain by changing their own strategy (holding all other players' strategies fixed) ...: each player is wholly indifferent between each of the actions he puts non-zero weight on, yet he mixes them so as to make every other player also indifferent. The purification theorem shows how such mixed strategy equilibria can emerge even if each players plays a pure strategy, so long as players have incomplete information about the payoffs of their opponents. Such strategies arise as the limit of a series of pure strategy equilibria for a disturbed game of incomplete information, in which the payoffs of each player are known to themselves but not their oppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ariel Rubinstein
Ariel Rubinstein (Hebrew: אריאל רובינשטיין; born April 13, 1951) is an Israeli economist who works in economic theory, game theory and bounded rationality. Biography Ariel Rubinstein is a professor of economics at the School of Economics at Tel Aviv University and the Department of Economics at New York University. He studied mathematics and economics at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, 1972–1979 (B.Sc. Mathematics, Economics and Statistics, 1974; M.A. Economics, 1975; M.Sc Mathematics, 1976; Ph.D. Economics, 1979). In 1982, he published "Perfect equilibrium in a bargaining model", an important contribution to the theory of bargaining. The model is known also as a Rubinstein bargaining model. It describes two-person bargaining as an extensive game with perfect information in which the players alternate offers. A key assumption is that the players are impatient. The main result gives conditions under which the game has a unique subgame perfect equilibrium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Econometrica
''Econometrica'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal of economics, publishing articles in many areas of economics, especially econometrics. It is published by Wiley-Blackwell on behalf of the Econometric Society. The current editor-in-chief is Guido Imbens. History ''Econometrica'' was established in 1933. Its first editor was Ragnar Frisch, recipient of the first Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1969, who served as an editor from 1933 to 1954. Although ''Econometrica'' is currently published entirely in English, the first few issues also contained scientific articles written in French. Indexing and abstracting ''Econometrica'' is abstracted and indexed in: * Scopus * EconLit * Social Sciences Citation Index According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stag Hunt
In game theory, the stag hunt, sometimes referred to as the assurance game, trust dilemma or common interest game, describes a conflict between safety and social cooperation. The stag hunt problem originated with philosopher Jean-Jacques Rousseau in his '' Discourse on Inequality''. In the most common account of this dilemma, which is quite different from Rousseau's, two hunters must decide separately, and without the other knowing, whether to hunt a stag or a hare. However, both hunters know the only way to successfully hunt a stag is with the other's help. One hunter can catch a hare alone with less effort and less time, but it is worth far less than a stag and has much less meat. But both hunters would be better off if both choose the more ambitious and more rewarding goal of getting the stag, giving up some autonomy in exchange for the other hunter's cooperation and added might. This situation is often seen as a useful analogy for many kinds of social cooperation, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prisoner's Dilemma
The prisoner's dilemma is a game theory thought experiment involving two rational agents, each of whom can either cooperate for mutual benefit or betray their partner ("defect") for individual gain. The dilemma arises from the fact that while defecting is rational for each agent, cooperation yields a higher payoff for each. The puzzle was designed by Merrill Flood and Melvin Dresher in 1950 during their work at the RAND Corporation. They invited economist Armen Alchian and mathematician John Williams to play a hundred rounds of the game, observing that Alchian and Williams often chose to cooperate. When asked about the results, John_Forbes_Nash_Jr., John Nash remarked that rational behavior in the Prisoner's dilemma#The_iterated_prisoner's_dilemma, iterated version of the game can differ from that in a single-round version. This insight anticipated a Folk_theorem_(game_theory), key result in game theory: cooperation can emerge in repeated interactions, even in situations where it i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
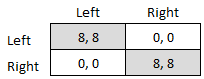
Coordination Game
A coordination game is a type of simultaneous game found in game theory. It describes the situation where a player will earn a higher payoff when they select the same course of action as another player. The game is not one of pure conflict, which results in multiple pure strategy Nash equilibrium, Nash equilibria in which players choose matching strategies. Figure 1 shows a 2-player example. Both (Up, Left) and (Down, Right) are Nash equilibria. If the players expect (Up, Left) to be played, then player 1 thinks their payoff would fall from 2 to 1 if they deviated to Down, and player 2 thinks their payoff would fall from 4 to 3 if they chose Right. If the players expect (Down, Right), player 1 thinks their payoff would fall from 2 to 1 if they deviated to Up, and player 2 thinks their payoff would fall from 4 to 3 if they chose Left. A player's optimal move depends on what they expect the other player to do, and they both do better if they coordinate than if they played an off-e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |