|
Mid-range
In statistics, the mid-range or mid-extreme is a measure of central tendency of a sample defined as the arithmetic mean of the maximum and minimum values of the data set: :M=\frac. The mid-range is closely related to the range, a measure of statistical dispersion defined as the difference between maximum and minimum values. The two measures are complementary in sense that if one knows the mid-range and the range, one can find the sample maximum and minimum values. The mid-range is rarely used in practical statistical analysis, as it lacks efficiency as an estimator for most distributions of interest, because it ignores all intermediate points, and lacks robustness, as outliers change it significantly. Indeed, for many distributions it is one of the least efficient and least robust statistics. However, it finds some use in special cases: it is the maximally efficient estimator for the center of a uniform distribution, trimmed mid-ranges address robustness, and as an L-estima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L-estimator
In statistics, an L-estimator (or L-statistic) is an estimator which is a linear combination of order statistics of the measurements. This can be as little as a single point, as in the median (of an odd number of values), or as many as all points, as in the mean. The main benefits of L-estimators are that they are often extremely simple, and often robust statistics: assuming sorted data, they are very easy to calculate and interpret, and are often resistant to outliers. They thus are useful in robust statistics, as descriptive statistics, in statistics education, and when computation is difficult. However, they are inefficient, and in modern times robust statistics M-estimators are preferred, although these are much more difficult computationally. In many circumstances L-estimators are reasonably efficient, and thus adequate for initial estimation. Examples A basic example is the median. Given ''n'' values x_1, \ldots, x_n, if n=2k+1 is odd, the median equals x_, the (n+1)/2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sample Maximum
In statistics, the sample maximum and sample minimum, also called the largest observation and smallest observation, are the values of the greatest and least elements of a sample. They are basic summary statistics, used in descriptive statistics such as the five-number summary and Bowley's seven-figure summary and the associated box plot. The minimum and the maximum value are the first and last order statistics (often denoted ''X''(1) and ''X''(''n'') respectively, for a sample size of ''n''). If the sample has outliers, they necessarily include the sample maximum or sample minimum, or both, depending on whether they are extremely high or low. However, the sample maximum and minimum need not be outliers, if they are not unusually far from other observations. Robustness The sample maximum and minimum are the ''least'' robust statistics: they are maximally sensitive to outliers. This can either be an advantage or a drawback: if extreme values are real (not measurement errors), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median
The median of a set of numbers is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a Sample (statistics), data sample, a statistical population, population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as the “middle" value. The basic feature of the median in describing data compared to the Arithmetic mean, mean (often simply described as the "average") is that it is not Skewness, skewed by a small proportion of extremely large or small values, and therefore provides a better representation of the center. Median income, for example, may be a better way to describe the center of the income distribution because increases in the largest incomes alone have no effect on the median. For this reason, the median is of central importance in robust statistics. Median is a 2-quantile; it is the value that partitions a set into two equal parts. Finite set of numbers The median of a finite list of numbers is the "middle" number, when those numbers are liste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimmed Estimator
In statistics, a trimmed estimator is an estimator derived from another estimator by excluding some of the extreme values, a process called truncation. This is generally done to obtain a more robust statistic, and the extreme values are considered outliers. Trimmed estimators also often have higher efficiency for mixture distributions, and heavy-tailed distributions than the corresponding untrimmed estimator, at the cost of lower efficiency for other distributions, such as the normal distribution. Given an estimator, the x% trimmed version is obtained by discarding the x% lowest or highest observations or on both end: it is a statistic on the ''middle'' of the data. For instance, the 5% trimmed mean is obtained by taking the mean of the 5% to 95% range. In some cases a trimmed estimator discards a fixed number of points (such as maximum and minimum) instead of a percentage. Examples The median is the most trimmed statistic (nominally 50%), as it discards all but the most centra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimum-variance Unbiased Estimator
In statistics a minimum-variance unbiased estimator (MVUE) or uniformly minimum-variance unbiased estimator (UMVUE) is an unbiased estimator that has lower variance than any other unbiased estimator for all possible values of the parameter. For practical statistics problems, it is important to determine the MVUE if one exists, since less-than-optimal procedures would naturally be avoided, other things being equal. This has led to substantial development of statistical theory related to the problem of optimal estimation. While combining the constraint of unbiasedness with the desirability metric of least variance leads to good results in most practical settings—making MVUE a natural starting point for a broad range of analyses—a targeted specification may perform better for a given problem; thus, MVUE is not always the best stopping point. Definition Consider estimation of g(\theta) based on data X_1, X_2, \ldots, X_n i.i.d. from some member of a family of densities p_\theta, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midhinge
In statistics, the midhinge () is the average of the first and third quartiles and is thus a measure of location. Equivalently, it is the 25% trimmed mid-range or 25% midsummary; it is an L-estimator. The midhinge is defined as \begin \operatorname(X) &= \overline \\ &= \frac \\ &= \frac \\ &= M_(X). \end The midhinge is related to the interquartile range (), the difference of the third and first quartiles (i.e. ), which is a measure of statistical dispersion. The two are complementary in sense that if one knows the midhinge and the , one can find the first and third quartiles. The use of the term ''hinge'' for the lower or upper quartiles derives from John Tukey's work on exploratory data analysis in the late 1970s,Tukey, J. W. (1977) ''Exploratory Data Analysis'', Addison-Wesley. and ''midhinge'' is a fairly modern term dating from around that time. The midhinge is slightly simpler to calculate than the trimean (), which originated in the same context and equals the avera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuous Uniform Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the continuous uniform distributions or rectangular distributions are a family of symmetric probability distributions. Such a distribution describes an experiment where there is an arbitrary outcome that lies between certain bounds. The bounds are defined by the parameters, a and b, which are the minimum and maximum values. The interval can either be closed (i.e. ,b/math>) or open (i.e. (a,b)). Therefore, the distribution is often abbreviated U(a,b), where U stands for uniform distribution. The difference between the bounds defines the interval length; all intervals of the same length on the distribution's support are equally probable. It is the maximum entropy probability distribution for a random variable X under no constraint other than that it is contained in the distribution's support. Definitions Probability density function The probability density function of the continuous uniform distribution is f(x) = \begin \dfrac & ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesokurtic
In probability theory and statistics, kurtosis (from , ''kyrtos'' or ''kurtos'', meaning "curved, arching") refers to the degree of “tailedness” in the probability distribution of a real-valued random variable. Similar to skewness, kurtosis provides insight into specific characteristics of a distribution. Various methods exist for quantifying kurtosis in theoretical distributions, and corresponding techniques allow estimation based on sample data from a population. It’s important to note that different measures of kurtosis can yield varying #Interpretation, interpretations. The standard measure of a distribution's kurtosis, originating with Karl Pearson, is a scaled version of the fourth moment (mathematics), moment of the distribution. This number is related to the tails of the distribution, not its peak; hence, the sometimes-seen characterization of kurtosis as "peakedness" is incorrect. For this measure, higher kurtosis corresponds to greater extremity of Deviation (stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of statistical survey, surveys and experimental design, experiments. When census data (comprising every member of the target population) cannot be collected, statisticians collect data by developing specific experiment designs and survey sample (statistics), samples. Representative sampling assures that inferences and conclusions can reasonably extend from the sample ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
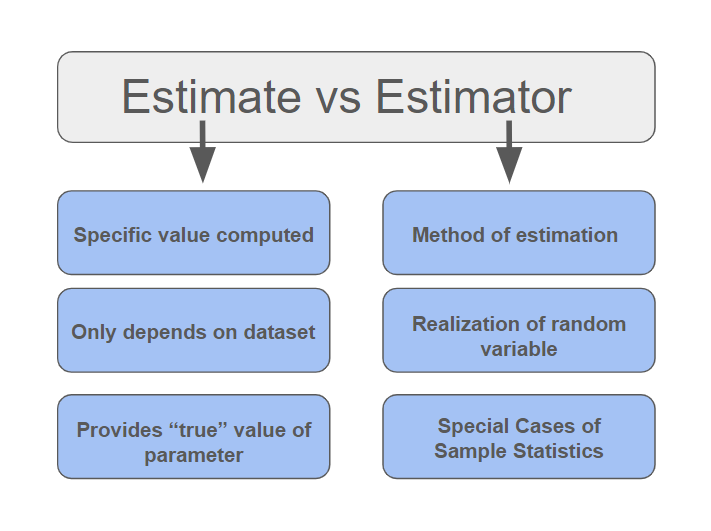
Estimator
In statistics, an estimator is a rule for calculating an estimate of a given quantity based on Sample (statistics), observed data: thus the rule (the estimator), the quantity of interest (the estimand) and its result (the estimate) are distinguished. For example, the sample mean is a commonly used estimator of the population mean. There are point estimator, point and interval estimators. The point estimators yield single-valued results. This is in contrast to an interval estimator, where the result would be a range of plausible values. "Single value" does not necessarily mean "single number", but includes vector valued or function valued estimators. ''Estimation theory'' is concerned with the properties of estimators; that is, with defining properties that can be used to compare different estimators (different rules for creating estimates) for the same quantity, based on the same data. Such properties can be used to determine the best rules to use under given circumstances. Howeve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Tank Problem
German(s) may refer to: * Germany, the country of the Germans and German things **Germania (Roman era) * Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language ** For citizenship in Germany, see also German nationality law **Germanic peoples (Roman era) * German diaspora * German language * German cuisine, traditional foods of Germany People * German (given name) * German (surname) * Germán, a Spanish name Places * German (parish), Isle of Man * German, Albania, or Gërmej * German, Bulgaria * German, Iran * German, North Macedonia * German, New York, U.S. * Agios Germanos, Greece Other uses * German (mythology), a South Slavic mythological being * Germans (band), a Canadian rock band * "German" (song), a 2019 song by No Money Enterprise * ''The German'', a 2008 short film * "The Germans", an episode of ''Fawlty Towers'' * ''The German'', a nickname for Congolese rebel André Kisase Ngandu See also * Germanic (di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimean
In statistics the trimean (TM), or Tukey's trimean, is a measure of a probability distribution's location defined as a weighted average of the distribution's median and its two quartiles: : TM= \frac This is equivalent to the arithmetic mean of the median and the midhinge: : TM= \frac\left(Q_2 + \frac\right) The foundations of the trimean were part of Arthur Bowley's teachings, and later popularized by statistician John Tukey in his 1977 book which has given its name to a set of techniques called exploratory data analysis. Like the median and the midhinge, but unlike the sample mean, it is a statistically resistant L-estimator with a breakdown point of 25%. This beneficial property has been described as follows: Efficiency Despite its simplicity, the trimean is a remarkably efficient estimator of population mean. More precisely, for a large data set (over 100 points) from a symmetric population, the average of the 18th, 50th, and 82nd percentile is the most efficient 3-p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |