|
Microlithic Culture
A microlith is a small stone tool usually made of flint or chert and typically a centimetre or so in length and half a centimetre wide. They were made by humans from around 35,000 to 3,000 years ago, across Europe, Africa, Asia and Australia. The microliths were used in spear points and arrowheads. Microliths are produced from either a small blade ( microblade) or a larger blade-like piece of flint by abrupt or truncated retouching, which leaves a very typical piece of waste, called a microburin. The microliths themselves are sufficiently worked so as to be distinguishable from workshop waste or accidents. Two families of microliths are usually defined: laminar and geometric. An assemblage of microliths can be used to date an archeological site. Laminar microliths are slightly larger, and are associated with the end of the Upper Paleolithic and the beginning of the Epipaleolithic era; geometric microliths are characteristic of the Mesolithic and the Neolithic. Geometric micro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
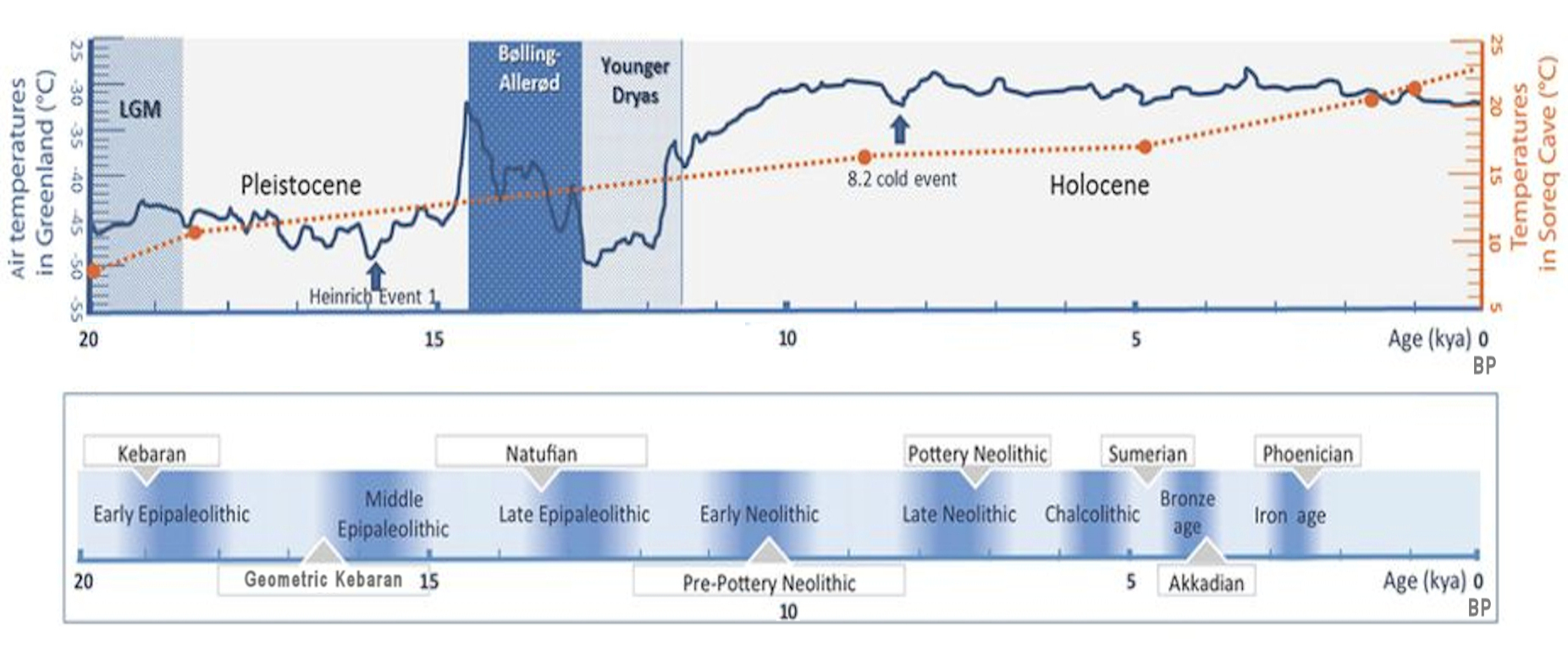
Kebaran Culture
The Kebaran culture, also known as the Early Near East Epipalaeolithic, was an archaeological culture in the Eastern Mediterranean area (c. 23,000 to 15,000 BP), named after its type site, Kebara Cave south of Haifa. The Kebaran were a highly mobile nomadic population, composed of hunters and gatherers in the Levant and Sinai areas who used microlithic tools. Overview The Kebaran is the last Upper Paleolithic phase of the Levant. Kebaran stone tool assemblages are characterized by small, geometric microliths, and are thought to have lacked the specialized grinders and pounders found in later Near Eastern cultures. Small stone tools called microliths and retouched bladelets can be found for the first time. The microliths of this culture period differ greatly from the Aurignacian artifacts. The Kebaran is preceded by the Athlitian phase of the Upper Paleolithic Levantine Aurignacian (formerly called Antelian) and followed by the proto-agrarian Natufian culture of the Epipalaeolit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement. It began about 12,000 years ago when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East, and later in other parts of the world. The Neolithic lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BC), marked by the development of metallurgy, leading up to the Bronze Age and Iron Age. In other places the Neolithic followed the Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) and then lasted until later. In Ancient Egypt, the Neolithic lasted until the Protodynastic period, 3150 BC.Karin Sowada and Peter Grave. Egypt in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tardenoisian
The Tardenoisian (or Beuronian) is an archaeological culture of the Mesolithic/Epipaleolithic period from northern France and Belgium. Similar cultures are known further east in central Europe, parts of Britain. and west across Spain. It is named after the type site at Fère-en-Tardenois in the Tardenois region in France, where E. Taté first discovered its characteristic artifacts in 1885. Characteristic artifacts differ from earlier industries by the presence of geometric microliths, microburin, scalene triangles, trapezoids and chisel-ended arrowheads and small flint blades made by the pressure-technique. The term is also used for several microlithic industries and sites in northern Italy and Eastern Europe and to distinguish the northern French Tardenoisian sites from the Sauveterrian industry in southern France. The Tardenoisian followed the Ahrensburgian, with which it was paralleled, and lasted from about 9.000 BC until 6.000 in the Neolithic The Neolithic period, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibero-Maurusian
The Iberomaurusian is a backed Blade (archaeology), bladelet lithic technology, lithic industry found near the coasts of Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia. It is also known from a single major site in Libya, the Haua Fteah, where the industry is locally known as the Eastern Oranian.The "Western Oranian" would refer to the Iberomaurusian in Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia, but this expression is seldom used. The Iberomaurusian seems to have appeared around the time of the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), somewhere between c. 25,000 and 23,000 radiocarbon calibration, cal BP. It would have lasted until the early Holocene c. 11,000 cal BP. The name of the Iberomaurusian means "of Iberia and Mauretania (Roman province), Mauretania", the latter being a Latin name for Northwest Africa. Pallary (1909) coined this termPallary, P., 1909. Instructions pour la recherche préhistorique dans le Nord-Ouest de l'Afrique, Algiers. to describe assemblages from the site of La Mouillah in the belief that the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
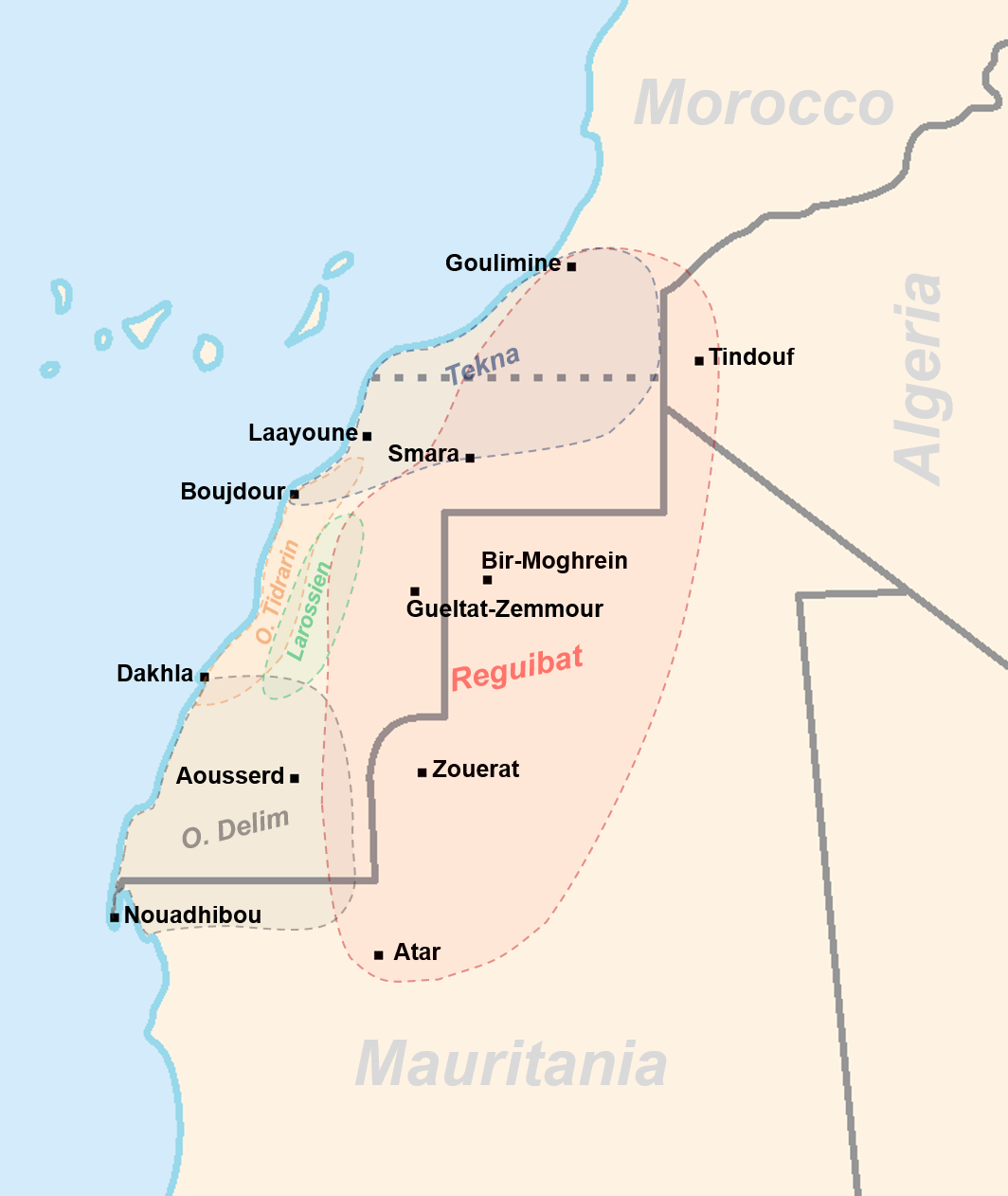
Sahrawi People
The Sahrawi, or Saharawi people ( ar, صحراويون '; es, Saharaui), are an ethnic group and nation native to the western part of the Sahara desert, which includes the Western Sahara, southern Morocco, much of Mauritania, and along the southwestern border of Algeria. They are of mixed Berber, Arab and Black African descent. As with most peoples living in the Sahara, the Sahrawi culture is a mix of Arab and indigenous African elements. The modern Sahrawi culture consists of a Berber core and considerable Arab influences. Sahrawis are composed of many tribes and are largely speakers of the Hassaniya dialect of Arabic. Etymology The Arabic word ' literally means "Inhabitant of the Desert". The word Sahrawi is derived from the Arabic word ' (), meaning desert. A man is called a "Sahrawi", and a woman is called a "Sahrawiya". In other languages it is pronounced in similar or different ways: * Berber: ''Aseḥrawi'' or ''Aneẓrofan'' * English: ''Sahrawi'' or ''Sahar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurignacian
The Aurignacian () is an archaeological industry of the Upper Paleolithic associated with European early modern humans (EEMH) lasting from 43,000 to 26,000 years ago. The Upper Paleolithic developed in Europe some time after the Levant, where the Emiran period and the Ahmarian period form the first periods of the Upper Paleolithic, corresponding to the first stages of the expansion of ''Homo sapiens'' out of Africa. They then migrated to Europe and created the first European culture of modern humans, the Aurignacian. An Early Aurignacian or Proto-Aurignacian stage is dated between about 43,000 and 37,000 years ago. The Aurignacian proper lasts from about 37,000 to 33,000 years ago. A Late Aurignacian phase transitional with the Gravettian dates to about 33,000 to 26,000 years ago. The type site is the Cave of Aurignac, Haute-Garonne, south-west France. The main preceding period is the Mousterian of the ''Neanderthals''. One of the oldest examples of figurative art, the Venus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universidad De Salamanca
The University of Salamanca ( es, Universidad de Salamanca) is a Spanish higher education institution, located in the city of Salamanca, in the autonomous community of Castile and León. It was founded in 1218 by King Alfonso IX. It is the oldest university in the Hispanic world and one of the oldest in the world in continuous operation. It has over 30,000 students from 50 different nationalities. History Prior to the foundation of the university, Salamanca was home to a cathedral school, known to have been in existence by 1130. The university was founded as a ''studium generale'' by the Leonese King Alfonso IX in 1218 as the ''scholas Salamanticae'', with the actual creation of the university (or the transformation of the existing school into the university) occurring between August 1218 and the following winter. A further royal charter from King Alfonso X, dated 8 May 1254, established rules for the organisation and financial endowment of the university, and referre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magdalenian
The Magdalenian cultures (also Madelenian; French: ''Magdalénien'') are later cultures of the Upper Paleolithic and Mesolithic in western Europe. They date from around 17,000 to 12,000 years ago. It is named after the type site of La Madeleine, a rock shelter located in the Vézère valley, commune of Tursac, in France's Dordogne department. Édouard Lartet and Henry Christy originally termed the period ''L'âge du renne'' (the Age of the Reindeer). They conducted the first systematic excavations of the type site, publishing in 1875. The Magdalenian epoch is associated with reindeer hunters, although Magdalenian sites contain extensive evidence for the hunting of red deer, horses, and other large mammals present in Europe toward the end of the last glacial period. The culture was geographically widespread, and later Magdalenian sites stretched from Portugal in the west to Poland in the east, and as far north as France, the Channel Islands, England, and Wales. It is the th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
"Noailles" Burin
Burin from the Upper Paleolithic (Gravettian) (ca. 29,000–22,000 BP) In the field of lithic reduction, a burin (from the French ''burin'', meaning "cold chisel" or modern engraving burin) is a type of handheld lithic flake with a chisel-like edge which prehistoric humans used for engraving or for carving wood or bone. In archaeology, burin use is often associated with "burin spalls", which are a form of debitage created when toolmakers strike a small flake obliquely from the edge of the burin flake in order to form the graving edge. Documented use left, 180px, Carinated "burin"/microblade core with multiple facets Standardized burin usage is typical of the Middle Paleolithic and Upper Palaeolithic cultures in Europe, but archaeologists have also identified them in North American cultural assemblages, and in his book ''Early Man in China'', Jia Lanpo of Beijing University lists dihedral burins and burins for truncation among artifacts uncovered along the banks of the Liy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravettian
The Gravettian was an archaeological industry of the European Upper Paleolithic that succeeded the Aurignacian circa 33,000 years BP. It is archaeologically the last European culture many consider unified, and had mostly disappeared by 22,000 BP, close to the Last Glacial Maximum, although some elements lasted until 17,000 BP. In Spain and France, it was succeeded by the Solutrean, and developed into or continued as the Epigravettian in Italy, the Balkans, Ukraine and Russia. The Gravettian culture is known for Venus figurines, which were typically carved from either ivory or limestone. The culture was first identified at the site of La Gravette in the southwestern French department of Dordogne.Kipfer, Barbara Ann. "Encyclopedic Dictionary of Archaeology". Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, 2000. P. 216. Gravettian culture The Gravettians were hunter-gatherers who lived in a bitterly cold period of European prehistory, and the Gravettian lifestyle was shaped by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
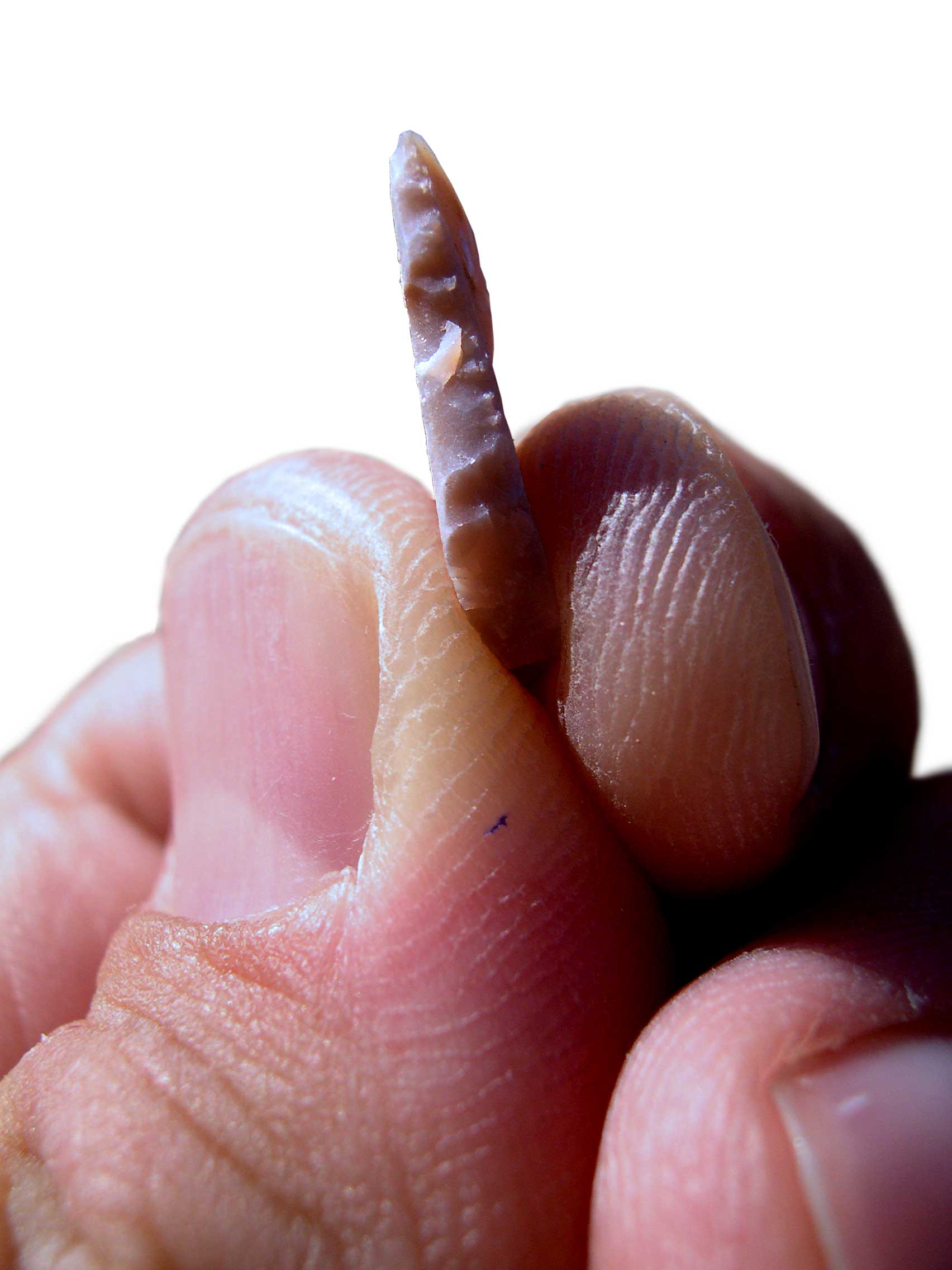
Microlith In Hand
A microlith is a small stone tool usually made of flint or chert and typically a centimetre or so in length and half a centimetre wide. They were made by humans from around 35,000 to 3,000 years ago, across Europe, Africa, Asia and Australia. The microliths were used in spear points and arrowheads. Microliths are produced from either a small blade ( microblade) or a larger blade-like piece of flint by abrupt or truncated retouching, which leaves a very typical piece of waste, called a microburin. The microliths themselves are sufficiently worked so as to be distinguishable from workshop waste or accidents. Two families of microliths are usually defined: laminar and geometric. An assemblage of microliths can be used to date an archeological site. Laminar microliths are slightly larger, and are associated with the end of the Upper Paleolithic and the beginning of the Epipaleolithic era; geometric microliths are characteristic of the Mesolithic and the Neolithic. Geometric microlit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrow (weapon)
An arrow is a fin-stabilized projectile launched by a bow. A typical arrow usually consists of a long, stiff, straight shaft with a weighty (and usually sharp and pointed) arrowhead attached to the front end, multiple fin-like stabilizers called fletchings mounted near the rear, and a slot at the rear end called a nock for engaging the bowstring. A container or bag carrying additional arrows for convenient reloading is called a quiver. The use of bows and arrows by humans predates recorded history and is common to most cultures. A craftsman who makes arrows is a fletcher, and one that makes arrowheads is an arrowsmith.Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 56 History The oldest evidence of likely arrowheads, dating to c. 64,000 years ago, were found in Sibudu Cave, current South Africa.Backwell L, d'Errico F, Wadley L.(2008). Middle Stone Age bone tools from the Howiesons Poort layers, Sibudu Cave, South Africa. Journal of Archaeological Science, 35:1566–1580. Backwell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)




