|
Microcystis
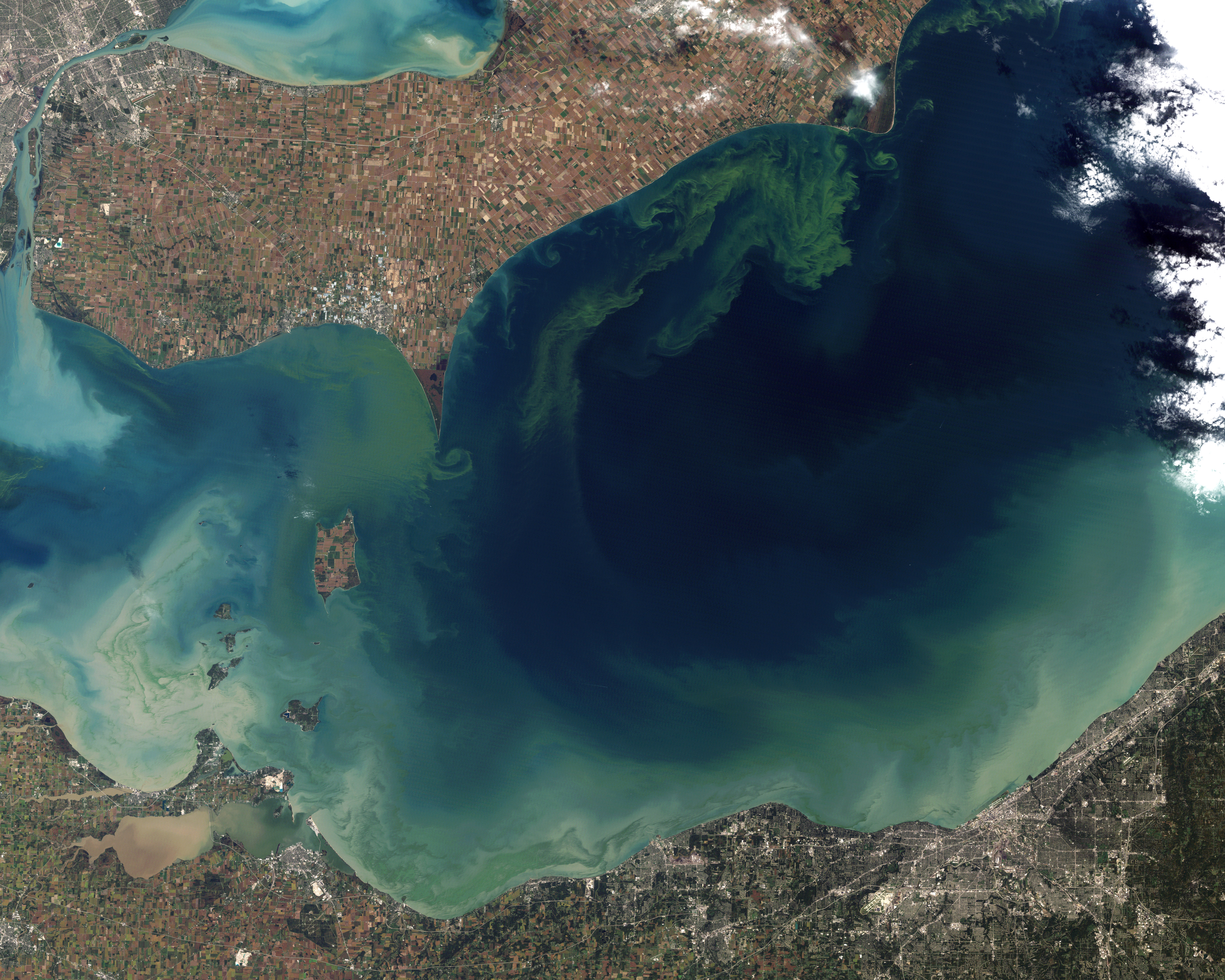
''Microcystis'' is a genus of freshwater cyanobacteria that includes the harmful algal bloom-forming '' Microcystis aeruginosa''. Over the last few decades, cyanobacterial blooms caused by eutrophication have become a major environmental problem in aquatic ecosystems worldwide, and the most representative and harmful cyanobacteria is ''Microcystis''.'''' ''Microcystis'' blooms have increased due to global climate change, spanning six continents and causing increased health risks to wildlife and humans. This article will address the conditions for the growth of ''Microcystis,'' physical characteristics, ecology, geographic distribution'','' and health risks of ''Microcystis.'' Conditions for ''Microcystis'' During the summer in temperate systems, ''Microcystis'' can rise to form blooms on the water surface. These blooms, linked to anthropogenic nutrient loading, occur generally when water temperatures exceed 15 °C. But, as the global climate changes, the intensity and oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcystis 3
''Microcystis'' is a genus of freshwater cyanobacteria that includes the harmful algal bloom-forming ''Microcystis aeruginosa''. Over the last few decades, cyanobacterial blooms caused by eutrophication have become a major environmental problem in aquatic ecosystems worldwide, and the most representative and harmful cyanobacteria is ''Microcystis''.'''' ''Microcystis'' blooms have increased due to global climate change, spanning six continents and causing increased health risks to wildlife and humans. This article will address the conditions for the growth of ''Microcystis,'' physical characteristics, ecology, geographic distribution'','' and health risks of ''Microcystis.'' Conditions for ''Microcystis'' During the summer in temperate systems, ''Microcystis'' can rise to form blooms on the water surface. These blooms, linked to Anthropogenic biome, anthropogenic nutrient loading, occur generally when water temperatures exceed 15 °C. But, as the global climate changes, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
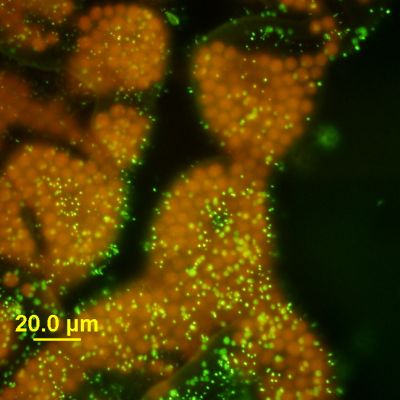
Microcystis Wesenbergii Colony Under Epifluorescence Microscopy
''Microcystis'' is a genus of freshwater cyanobacteria that includes the harmful algal bloom-forming ''Microcystis aeruginosa''. Over the last few decades, cyanobacterial blooms caused by eutrophication have become a major environmental problem in aquatic ecosystems worldwide, and the most representative and harmful cyanobacteria is ''Microcystis''.'''' ''Microcystis'' blooms have increased due to global climate change, spanning six continents and causing increased health risks to wildlife and humans. This article will address the conditions for the growth of ''Microcystis,'' physical characteristics, ecology, geographic distribution'','' and health risks of ''Microcystis.'' Conditions for ''Microcystis'' During the summer in temperate systems, ''Microcystis'' can rise to form blooms on the water surface. These blooms, linked to anthropogenic nutrient loading, occur generally when water temperatures exceed 15 °C. But, as the global climate changes, the intensity and occ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcystis Aeruginosa
''Microcystis aeruginosa'' is a species of freshwater cyanobacteria that can form harmful algal blooms of economic and ecological importance. They are the most common toxic cyanobacterial bloom in eutrophic fresh water. Cyanobacteria produce neurotoxins and peptide hepatotoxins, such as microcystin and cyanopeptolin. ''Microcystis aeruginosa'' produces numerous congeners of microcystin, with microcystin-LR being the most common. Microcystis blooms have been reported in at least 108 countries, with the production of microcystin noted in at least 79. Characteristics As the etymological derivation implies, ''Microcystis'' is characterized by small cells (of only a few micrometers diameter), which lack individual sheaths. Cells usually are organized into colonies (large colonies of which may be viewed with the naked eye) that begin in a spherical shape, but lose their coherence to become perforated or irregularly shaped over time in culture. Recent evidence suggests one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria ( ) are a group of autotrophic gram-negative bacteria that can obtain biological energy via oxygenic photosynthesis. The name "cyanobacteria" () refers to their bluish green (cyan) color, which forms the basis of cyanobacteria's informal common name, blue-green algae. Cyanobacteria are probably the most numerous taxon to have ever existed on Earth and the first organisms known to have produced oxygen, having appeared in the middle Archean eon and apparently originated in a freshwater or terrestrial environment. Their photopigments can absorb the red- and blue-spectrum frequencies of sunlight (thus reflecting a greenish color) to split water molecules into hydrogen ions and oxygen. The hydrogen ions are used to react with carbon dioxide to produce complex organic compounds such as carbohydrates (a process known as carbon fixation), and the oxygen is released as a byproduct. By continuously producing and releasing oxygen over billions of years, cyanobacte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmful Algal Bloom
A harmful algal bloom (HAB), or excessive algae growth, sometimes called a red tide in marine environments, is an algal bloom that causes negative impacts to other organisms by production of natural algae-produced toxins, water deoxygenation, mechanical damage to other organisms, or by other means. HABs are sometimes defined as only those algal blooms that produce toxins, and sometimes as any algal bloom that can result in severely lower oxygen levels in natural waters, killing organisms in marine or fresh waters. Blooms can last from a few days to many months. After the bloom dies, the microbes that decompose the dead algae use up more of the oxygen, generating a " dead zone" which can cause fish die-offs. When these zones cover a large area for an extended period of time, neither fish nor plants are able to survive. It is sometimes unclear what causes specific HABs as their occurrence in some locations appears to be entirely natural, while in others they appear to be a re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanobacterial Blooms
Cyanotoxins are toxins produced by cyanobacteria (also known as blue-green algae). Cyanobacteria are found almost everywhere, but particularly in lakes and in the ocean where, under high concentration of phosphorus conditions, they reproduce exponentially to form blooms. Blooming cyanobacteria can produce cyanotoxins in such concentrations that they can poison and even kill animals and humans. Cyanotoxins can also accumulate in other animals such as fish and shellfish, and cause poisonings such as shellfish poisoning. Some of the most powerful natural poisons known are cyanotoxins. They include potent neurotoxins, hepatotoxins, cytotoxins, and endotoxins. The ''cyano'' in the term cyanobacteria refers to its colour, not to its relation to cyanides, though cyanobacteria can catabolize hydrogen cyanide during nitrogen fixation. Exposure to cyanobacteria can result in gastro-intestinal and hayfever symptoms or pruritic skin rashes. Exposure to the cyanobacteria neurotoxin BMA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hartbeespoort Dam
Hartbeespoort Dam (also known as ''Harties'') is an arch type dam situated in the North West Province of South Africa. It lies in a valley to the south of the Magaliesberg mountain range and north of the Witwatersberg mountain range, about 35 kilometres north west of Johannesburg and 20 kilometres west of Pretoria. The name of the dam means "dam at the gorge of the hartebeest" (a species of antelope) in Afrikaans. This "poort" in the Magaliesberg was a popular spot for hunters, where they cornered and shot the hartebeest. The dam was originally designed for irrigation, which is currently its primary use, as well as for domestic and industrial use. The dam is considered to be in a hypereutrophic state since the early 1970s. Mismanagement of waste water treatment from urban zones within the Hartbeespoort Dam catchment area is largely to blame, having distorted the food web with over 280 tons of phosphate and nitrate deposits. The town of Hartbeespoort is situated close to the dam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P Ratio
P, or p, is the sixteenth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''pee'' (pronounced ), plural ''pees''. History The Semitic Pê (mouth), as well as the Greek Π or π ( Pi), and the Etruscan and Latin letters that developed from the former alphabet all symbolized , a voiceless bilabial plosive. Use in writing systems English In English orthography, represents the sound . A common digraph in English is , which represents the sound , and can be used to transliterate ''phi'' in loanwords from Greek. In German, the digraph is common, representing a labial affricate . Most English words beginning with are of foreign origin, primarily French, Latin and Greek; these languages preserve the Proto-Indo-European initial *p. Native English cognates of such words often start with , since English is a Germanic language and thus has undergone Grimm's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphate
Phosphates are the naturally occurring form of the element phosphorus. In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid, phosphoric acid . The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosphoric acid by the removal of three protons . Removal of one proton gives the dihydrogen phosphate ion while removal of two protons gives the hydrogen phosphate ion . These names are also used for salts of those anions, such as ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and trisodium phosphate. File:3-phosphoric-acid-3D-balls.png, Phosphoricacid File:2-dihydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png, Dihydrogenphosphate File:1-hydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png, Hydrogenphosphate File:0-phosphate-3D-balls.png, Phosphate or orthophosphate In organic chemistry, phosphate or orthophosphate is an organophosphate, an ester of orthophosphoric acid of the form where one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater Aquatic ecosystem, ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek language, Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'. Phytoplankton obtain their energy through photosynthesis, as trees and other plants do on land. This means phytoplankton must have light from the sun, so they live in the well-lit surface layers (euphotic zone) of oceans and lakes. In comparison with terrestrial plants, phytoplankton are distributed over a larger surface area, are exposed to less seasonal variation and have markedly faster turnover rates than trees (days versus decades). As a result, phytoplankton respond rapidly on a global scale to climate variations. Phytoplankton form the base of marine and freshwater food webs and are key players in the global carbon cycle. They account for about half of global photosynthetic activity and at least half o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhamnose
Rhamnose (Rha, Rham) is a naturally occurring deoxy sugar. It can be classified as either a methyl- pentose or a 6-deoxy- hexose. Rhamnose predominantly occurs in nature in its L-form as L-rhamnose (6-deoxy-L- mannose). This is unusual, since most of the naturally occurring sugars are in D-form. Exceptions are the methyl pentoses L- fucose and L-rhamnose and the pentose L- arabinose. However, examples of naturally-occurring D-rhamnose are found in some species of bacteria, such as '' Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' and '' Helicobacter pylori''. Rhamnose can be isolated from buckthorn (''Rhamnus''), poison sumac, and plants in the genus ''Uncaria''. Rhamnose is also produced by microalgae belonging to class Bacillariophyceae (diatoms). Rhamnose is commonly bound to other sugars in nature. It is a common glycone component of glycosides from many plants. Rhamnose is also a component of the outer cell membrane of acid-fast bacteria in the ''Mycobacterium'' genus, which includes the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photic Zone
The photic zone (or euphotic zone, epipelagic zone, or sunlight zone) is the uppermost layer of a body of water that receives sunlight, allowing phytoplankton to perform photosynthesis. It undergoes a series of physical, chemical, and biological processes that supply nutrients into the upper water column. The photic zone is home to the majority of Aquatic ecosystem, aquatic life due to the activity (Marine primary production, primary production) of the phytoplankton. The thicknesses of the photic and euphotic zones vary with the intensity of sunlight as a function of season and latitude and with the degree of water turbidity. The bottommost, or aphotic, zone is the region of perpetual darkness that lies beneath the photic zone and includes most of the ocean waters. Photosynthesis in photic zone In the photic zone, the photosynthesis rate exceeds the respiration rate. This is due to the abundant solar energy which is used as an energy source for photosynthesis by primary produce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |