|
Methyl Eugenol
Methyl eugenol (allylveratrol) is a natural chemical compound classified as a phenylpropene, a type of phenylpropanoid. It is the methyl ether of eugenol and is important to insect behavior and pollination. It is found in various essential oils. Methyl eugenol is found in a number of plants (over 450 species from 80 families including both angiosperm and gymnosperm families) and has a role in attracting pollinators. About 350 plant species have them as a component of floral fragrance. Their ability to attract insects, particularly ''Bactrocera'' fruit flies (particularly, ''Bactrocera dorsalis'' male flies) was first noticed in 1915 by F. M. Howlett. The compound may have evolved in response to pathogens, as methyl eugenol has some antifungal activity. It also repels many insects. As of October 2018, the US FDA withdrew authorization for the use of methyl eugenol as a synthetic flavoring substance for use in food because petitioners (including the Natural Resources Defense Coun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound. A compound can be transformed into a different substance by a chemical reaction, which may involve interactions with other substances. In this process, bonds between atoms may be broken and/or new bonds formed. There are four major types of compounds, distinguished by how the constituent atoms are bonded together. Molecular compounds are held together by covalent bonds; ionic compounds are held together by ionic bonds; intermetallic compounds are held together by metallic bonds; coordination complexes are held together by coordinate covalent bonds. Non-stoichiometric compounds form a disputed marginal case. A chemical formula specifies the number of atoms of each element in a compound molecule, usi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frank Milburn Howlett
Francis "Frank" Milburn Howlett (5 January 1877 – 20 August 1920) was a British entomologist who served as a Second Imperial Entomologist and as Imperial Pathological Entomologist in India. He specialized in insects (mainly Diptera - sandflies) and parasitic ticks of medical and veterinary importance. A major discovery by him was the attractant methyl eugenol and its effect on flies of the genus ''Bactrocera''. Life and work Howlett was born in Wymondham, Norfolk, the son of Francis John Howlett, a solicitor, and Mary Jane née Milburn. He was educated at Wymondham Grammar School and Bury St Edmunds Grammar School, and then at Christ's College, Cambridge. He was an assistant master at Edinburgh Academy from 1900 to 1903 and at Holt Grammar School before being posted as a professor of natural science (which included the teaching of chemistry) at Muir Central College, Allahabad, from 1905 to 1908, initially in a temporary position (to replace E.G. Hill who was on furlough) wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allyl Compounds
In organic chemistry, an allyl group is a substituent with the structural formula , where R is the rest of the molecule. It consists of a methylene bridge () attached to a vinyl group (). The name is derived from the scientific name for garlic, . In 1844, Theodor Wertheim isolated an allyl derivative from garlic oil and named it "". The term allyl applies to many compounds related to , some of which are of practical or of everyday importance, for example, allyl chloride. Allylation is any chemical reaction that adds an allyl group to a substrate. Nomenclature A site adjacent to the unsaturated carbon atom is called the allylic position or allylic site. A group attached at this site is sometimes described as allylic. Thus, "has an allylic hydroxyl group". Allylic C−H bonds are about 15% weaker than the C−H bonds in ordinary sp3 carbon centers and are thus more reactive. Benzylic and allylic are related in terms of structure, bond strength, and reactivity. Other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
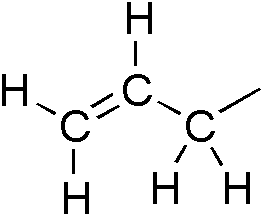
Phenylpropenes
Phenylpropene is the organic compound with the formula C6H5CH2CH=CH2. It is a colorless liquid. The compound consists of a phenyl group attached to allyl. Phenylpropene isomerizes to trans-propenylbenzene. In plant biochemistry, the phenylpropene skeleton is the parent (simplest representation) of the phenylpropanoids. Prominent derivatives include eugenol, safrole Safrole is an organic compound with the formula CH2O2C6H3CH2CH=CH2. It is a colorless oily liquid, although impure samples can appear yellow. A member of the phenylpropanoid family of natural products, it is found in sassafras plants, among oth ..., and many others. References External links * {{Phenylpropene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Isoeugenol
Methyl isoeugenol (isomethyleugenol) is a phenylpropanoid The phenylpropanoids are a diverse family of organic compounds that are synthesized by plants from the amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine. Their name is derived from the six-carbon, aromatic phenyl group and the three-carbon propene tail of ..., the methyl ether of isoeugenol, found in certain essential oils. It can occur as both (''E'')- and (''Z'')-isomers. See also * Methyl eugenol References O-methylated phenylpropanoids Phenylpropenes {{Organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Center For Science In The Public Interest
The Center for Science in the Public Interest (CSPI) is a Washington, D.C.-based non-profit watchdog and consumer advocacy group that advocates for safer and healthier foods. History and funding CSPI is a consumer advocacy organization. Its focus is nutrition and health, food safety, and alcohol policy. CSPI was headed by the microbiologist Michael F. Jacobson, who founded the group in 1971 along with the meteorologist James Sullivan and the chemist Albert Fritsch, two fellow scientists from Ralph Nader's Center for the Study of Responsive Law. In the early days, CSPI focused on various aspects such as nutrition, environmental issues, and nuclear energy. However, after the 1977 departure of Fritsch and Sullivan, CSPI began to focus largely on nutrition and food safety and began publishing nutritional analyses and critiques. CSPI has 501(c)(3) status. Its chief source of income is its ''Nutrition Action Healthletter'', which has about 900,000 subscribers and does not acce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Center For Food Safety
The Center for Food Safety (CFS) is a 501c3, U.S. non-profit advocacy organization, based in Washington, D.C. It maintains an office in San Francisco, California. The executive director is Andrew Kimbrell, an attorney. Its stated mission is to protect human health and the environment, focusing on food production technologies such as genetically modified plants and organisms (GMOs). It was founded in 1997. Program services The largest program services conducted by the Center for Food Safety include: CFS has participated in legal actions against manufacturers of genetically modified crops, such as GE (genetically engineered) alfalfa, wheat, rice, beets, and claims to have successfully stopped the commercialization of at least seven of these in the US. This includes the introduction of controversial Pharming plants (GE plants which produce biopharmaceuticals). The CFS has also been an advocate for GE food labeling at both the state and federal level, pushing for new legis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Resources Defense Council
The Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC) is a United States-based 501(c)(3) non-profit international environmental advocacy group, with its headquarters in New York City and offices in Washington D.C., San Francisco, Los Angeles, Chicago, Bozeman, and Beijing. Founded in 1970, as of 2019, the NRDC had over three million members, with online activities nationwide, and a staff of about 700 lawyers, scientists and other policy experts. History The NRDC was founded in 1970.Robert Gottlieb, ''Forcing the Spring: The Transformation of the American Environmental Movement'' (revised ed.: Island Press, 2005), pp. 193–94. Its establishment was partially an outgrowth of the ''Scenic Hudson Preservation Conference v. Federal Power Commission'', the Storm King case. The case centered on Con Ed's plan to build the world's largest hydroelectric facility at Storm King Mountain. The proposed facility would have pumped vast amounts of water from the Hudson River to a reservoir and relea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, caffeine products, dietary supplements, prescription and over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs (medications), vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices (ERED), cosmetics, animal foods & feed and veterinary products. The FDA's primary focus is enforcement of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C), but the agency also enforces other laws, notably Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act, as well as associated regulations. Much of this regulatory-enforcement work is not directly related to food or drugs, but involves such things as regulating lasers, cellular phones, and condoms, as well as control of disease in contexts v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antifungal
An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as cryptococcal meningitis, and others. Such drugs are usually yes obtained by a doctor's prescription, but a few are available over the counter (OTC). Types of antifungal There are two types of antifungals: local and systemic. Local antifungals are usually administered topically or vaginally, depending on the condition being treated. Systemic antifungals are administered orally or intravenously. Of the clinically employed azole antifungals, only a handful are used systemically. These include ketoconazole, itraconazole, fluconazole, fosfluconazole, voriconazole, posaconazole, and isavuconazole. Examples of non-azole systemic antifungals include griseofulvin and terbinafine. Classes Polyenes A polyene is a molecule with multiple con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bactrocera Dorsalis
''Bactrocera dorsalis'', previously known as ''Dacus dorsalis'' and commonly referred to as the oriental fruit fly, is a species of tephritid fruit fly that is endemic to Southeast Asia. It is one of the major pest species in the genus ''Bactrocera'' with a broad host range of cultivated and wild fruits. Male ''B. dorsalis'' respond strongly to methyl eugenol, which is used to monitor and estimate populations, as well as to annihilate males as a form of pest control. They are also important pollinators and visitors of wild orchids, ''Bulbophyllum cheiri'' and ''Bulbophyllum vinaceum'' in Southeast Asia, which lure the flies using methyl eugenol. The fly is similar to the closely related species '' B. carambolae'' and '' B. occipitalis.'' The species name ''B. dorsalis'' is identical to other synonyms ''B. papayae, B. invadens'' and ''B. philippinensis''. Description ''B. dorsalis'' is a species of tephritid fruit fly. Flies that belong to this family are usually small to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenylpropene
Phenylpropene is the organic compound with the formula C6H5CH2CH=CH2. It is a colorless liquid. The compound consists of a phenyl group attached to allyl. Phenylpropene isomerizes to trans-propenylbenzene. In plant biochemistry, the phenylpropene skeleton is the parent (simplest representation) of the phenylpropanoids. Prominent derivatives include eugenol Eugenol is an allyl chain-substituted guaiacol, a member of the allylbenzene class of chemical compounds. It is a colorless to pale yellow, aromatic oily liquid extracted from certain essential oils especially from clove, nutmeg, cinnamon, ..., safrole, and many others. References External links * {{Phenylpropene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
_(06410590)_(6922916899).jpg)