|
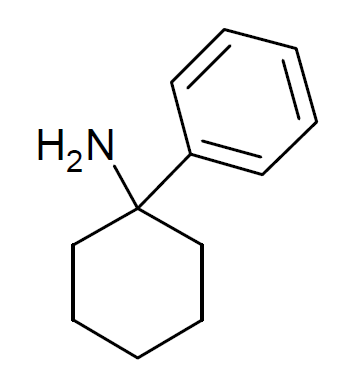
Methoxyketamine
Methoxyketamine or 2-MeO-2-deschloroketamine is a designer drug of the arylcyclohexylamine class first reported in 1963. It is an analog of ketamine in which the chlorine atom has been replaced with a methoxy group. Its synthesis by rearrangement of an amino ketone has been reported. As an arylcyclohexylamine, methoxyketamine most likely functions as an NMDA receptor antagonist. It produces sedative, hallucinogenic, and (at high doses) anesthetic effects, but with a lower potency than ketamine itself. See also * 2-Fluorodeschloroketamine * Bromoketamine * Methoxmetamine * Trifluoromethyldeschloroketamine Trifluoromethyldeschloroketamine (TFMDCK) is a designer drug from the arylcyclohexylamine family, which is presumed to have similar properties to ketamine, a dissociative anesthetic drug with hallucinogenic and sedative effects. It has been sold ... References Arylcyclohexylamines Designer drugs Dissociative drugs Ketones Phenol ethers {{organic-compound-stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arylcyclohexylamine
Arylcyclohexylamines, also known as arylcyclohexamines or arylcyclohexanamines, are a chemical class of pharmaceutical, designer, and experimental drugs. History Phencyclidine (PCP) is believed to be the first arylcyclohexylamine with recognized anesthetic properties, but several arylcyclohexylamines were described before PCP in the scientific literature, beginning with PCA (1-phenylcyclohexan-1-amine) the synthesis of which was first published in 1907. PCE was reported in 1953 and PCMo (4-(1-phenyl-cyclohexyl)-morpholine see chart below for figure) in 1954, with PCMo described as a potent sedative. Arylcyclohexylamine anesthetics were intensively investigated at Parke-Davis, beginning with the 1956 synthesis of phencyclidine and later the related compound ketamine. The 1970s saw the debut of these compounds, especially PCP and its analogues, as illicitly used recreational drugs due to their dissociative hallucinogenic and euphoriant effects. Since that time, the class has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arylcyclohexylamines
Arylcyclohexylamines, also known as arylcyclohexamines or arylcyclohexanamines, are a chemical class of pharmaceutical, designer, and experimental drugs. History Phencyclidine (PCP) is believed to be the first arylcyclohexylamine with recognized anesthetic properties, but several arylcyclohexylamines were described before PCP in the scientific literature, beginning with PCA (1-phenylcyclohexan-1-amine) the synthesis of which was first published in 1907. PCE was reported in 1953 and PCMo (4-(1-phenyl-cyclohexyl)-morpholine see chart below for figure) in 1954, with PCMo described as a potent sedative. Arylcyclohexylamine anesthetics were intensively investigated at Parke-Davis, beginning with the 1956 synthesis of phencyclidine and later the related compound ketamine. The 1970s saw the debut of these compounds, especially PCP and its analogues, as illicitly used recreational drugs due to their dissociative hallucinogenic and euphoriant effects. Since that time, the class has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-Fluorodeschloroketamine
2-Fluorodeschloroketamine (also known as 2'-Fl-2-Oxo-PCM, Fluoroketamine and 2-FDCK) is a dissociative anesthetic related to ketamine. Its sale and use as a designer drug has been reported in various countries. It is an analogue of ketamine where the chlorine group has been replaced by fluorine. Due to its recent emergence, the pharmacological specifics of the compound are mostly unclear. Effects are still ketamine like but with more euphoria and analgesic properties. History The synthesis of 2-FDCK was first described in a 2013 paper as part of a larger effort to synthesize and evaluate new anesthetic drugs based on ketamine and its analogues. Ketamine itself was first introduced in 1964 and was approved for clinical use in 1970. Since then it has become one of the most important and applicable general anesthetics as well as a popular recreational drug. The use of 2-FDCK as a research chemical has been reported in various countries.European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromoketamine
2-Bromodeschloroketamine (also known as 2-Br-2'-Oxo-PCM and Bromoketamine) is a chemical compound of the arylcyclohexylamine class, which is an analog of the dissociative anesthetic drug ketamine in which the chlorine atom has been replaced with a bromine atom. It is used in scientific research as a comparison or control compound in studies into the metabolism of ketamine and norketamine, and has also been sold online alongside arylcyclohexylamine designer drugs, though it is unclear whether bromoketamine has similar pharmacological activity. See also * 2-Fluorodeschloroketamine * 3-Fluorodeschloroketamine * Deschloroketamine * Methoxyketamine * Trifluoromethyldeschloroketamine Trifluoromethyldeschloroketamine (TFMDCK) is a designer drug from the arylcyclohexylamine family, which is presumed to have similar properties to ketamine, a dissociative anesthetic drug with hallucinogenic and sedative effects. It has been sold o ... References Arylcyclohexylamines Designer dru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trifluoromethyldeschloroketamine
Trifluoromethyldeschloroketamine (TFMDCK) is a designer drug from the arylcyclohexylamine family, which is presumed to have similar properties to ketamine, a dissociative anesthetic drug with hallucinogenic and sedative effects. It has been sold over the internet since around 2016, though genuine samples appear to be rare. The ''o''-trifluoromethyl analogue of hydroxynorketamine has also been researched as an antidepressant. See also * Bromoketamine * Deschloroketamine * Methoxyketamine * Methoxmetamine Methoxmetamine (also known as 3-MeO-2'-Oxo-PCM, MXM and MMXE) is a dissociative anesthetic of the arylcyclohexylamine class that is closely related to methoxetamine and methoxyketamine, and has been sold online as a designer drug A designer drug ... References Arylcyclohexylamines Designer drugs Dissociative drugs Trifluoromethyl compounds {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrochloride
In chemistry, a hydrochloride is an acid salt resulting, or regarded as resulting, from the reaction of hydrochloric acid with an organic base (e.g. an amine). An alternative name is chlorhydrate, which comes from French. An archaic alternative name is muriate, derived from hydrochloric acid's ancient name: muriatic acid. Uses Converting amines into their hydrochlorides is a common way to improve their water solubility, which can be desirable for substances used in medications. The European Pharmacopoeia lists more than 200 hydrochlorides as active ingredients in medications. These hydrochlorides, compared to free bases, may more readily dissolve in the gastrointestinal tract and be absorbed into the bloodstream more quickly. Additionally, many hydrochlorides of amines have a longer shelf-life than their respective free bases. Amine hydrochlorides represent latent forms of a more reactive free base. In this regard, formation of an amine hydrochloride confers protection. This eff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Designer Drug
A designer drug is a structural or functional analog of a controlled substance that has been designed to mimic the pharmacological effects of the original drug, while avoiding classification as illegal and/or detection in standard drug tests. Designer drugs include psychoactive substances that have been designated by the European Union as new psychoactive substances (NPS) as well as analogs of performance-enhancing drugs such as designer steroids. Some of these were originally synthesized by academic or industrial researchers in an effort to discover more potent derivatives with fewer side effects, and shorter duration (and possibly also because it is easier to apply for patents for new molecules) and were later co-opted for recreational use. Other designer drugs were prepared for the first time in clandestine laboratories. Because the efficacy and safety of these substances have not been thoroughly evaluated in animal and human trials, the use of some of these drugs may result i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog (chemistry)
A structural analog (analogue in modern traditional English; Commonwealth English), also known as a chemical analog or simply an analog, is a compound having a structure similar to that of another compound, but differing from it in respect to a certain component. It can differ in one or more atoms, functional groups, or substructures, which are replaced with other atoms, groups, or substructures. A structural analog can be imagined to be formed, at least theoretically, from the other compound. Structural analogs are often isoelectronic. Despite a high chemical similarity, structural analogs are not necessarily functional analogs and can have very different physical, chemical, biochemical, or pharmacological properties. In drug discovery, either a large series of structural analogs of an initial lead compound are created and tested as part of a structure–activity relationship study or a database is screened for structural analogs of a lead compound. Chemical analogues of il ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketamine
Ketamine is a dissociative anesthetic used medically for induction and maintenance of anesthesia. It is also used as a recreational drug. It is one of the safest anesthetics, as, in contrast with opiates, ether, and propofol, it suppresses neither respiration nor heart rate. Ketamine is also simple to administer and highly tolerable compared to drugs with similar effects which are flammable, irritating, or even explosive. Ketamine is a novel compound, derived from PCP, created in pursuit of a safer anesthetic with similar characteristics. Ketamine is also used for acute pain management. At anesthetic doses, ketamine induces a state of "dissociative anesthesia", a trance-like state providing pain relief, sedation, and amnesia. The distinguishing features of ketamine anesthesia are preserved breathing and airway reflexes, stimulated heart function with increased blood pressure, and moderate bronchodilation. At lower, sub-anesthetic doses, ketamine is a promising agent for pain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methoxy Group
In organic chemistry, a methoxy group is the functional group consisting of a methyl group bound to oxygen. This alkoxy group has the formula . On a benzene ring, the Hammett equation classifies a methoxy substituent at the ''para'' position as an electron-donating group, but as an electron-withdrawing group if at the ''meta'' position. At the ''ortho'' position, steric effects are likely to cause a significant alteration in the Hammett equation prediction which otherwise follows the same trend as that of the ''para'' position. Occurrence The simplest of methoxy compounds are methanol and dimethyl ether. Other methoxy ethers include anisole and vanillin. Many alkoxides contain methoxy groups, e.g. tetramethyl orthosilicate and titanium methoxide. Such compounds are often classified as methoxides. Esters with a methoxy group can be referred to as methyl esters, and the —COOCH3 substituent is called a methoxycarbonyl. Biosynthesis In nature, methoxy groups are found on nucleosi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NMDA Receptor Antagonist
NMDA receptor antagonists are a class of drugs that work to antagonize, or inhibit the action of, the ''N''-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR). They are commonly used as anesthetics for animals and humans; the state of anesthesia they induce is referred to as dissociative anesthesia. Several synthetic opioids function additionally as NMDAR-antagonists, such as pethidine, levorphanol, methadone, dextropropoxyphene, tramadol and ketobemidone. Some NMDA receptor antagonists, such as ketamine, dextromethorphan (DXM), phencyclidine (PCP), methoxetamine (MXE), and nitrous oxide (N2O), are sometimes used as recreational drugs, for their dissociative, hallucinogenic, and euphoriant properties. When used recreationally, they are classified as dissociative drugs. Uses and effects NMDA receptor antagonists induce a state called dissociative anesthesia, marked by catalepsy, amnesia, and analgesia. Ketamine is a favored anesthetic for emergency patients with unknown medical history and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methoxmetamine
Methoxmetamine (also known as 3-MeO-2'-Oxo-PCM, MXM and MMXE) is a dissociative anesthetic of the arylcyclohexylamine class that is closely related to methoxetamine and methoxyketamine, and has been sold online as a designer drug. References Arylcyclohexylamines Designer drugs Dissociative drugs O-methylated phenols Secondary amines {{hallucinogen-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |