|
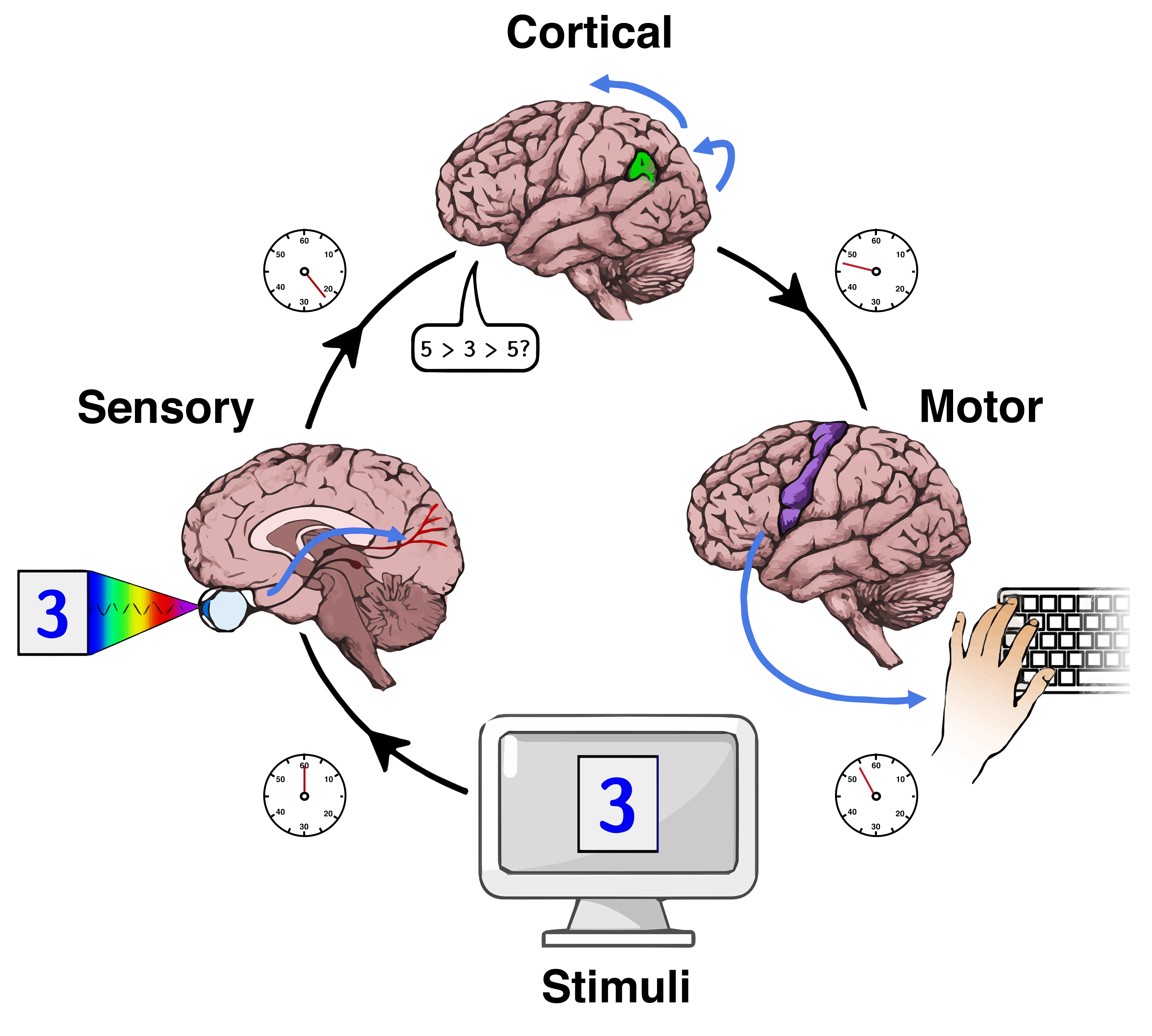
Mental Speed
Mental chronometry is the scientific study of processing speed or reaction time on cognitive tasks to infer the content, duration, and temporal sequencing of mental operations. Reaction time (RT; sometimes referred to as "response time") is measured by the elapsed time between stimulus onset and an individual's response on elementary cognitive tasks (ETCs), which are relatively simple perceptual-motor tasks typically administered in a laboratory setting. Mental chronometry is one of the core methodological paradigms of human experimental, cognitive, and differential psychology, but is also commonly analyzed in psychophysiology, cognitive neuroscience, and behavioral neuroscience to help elucidate the biological mechanisms underlying perception, attention, and decision-making in humans and other species. Mental chronometry uses measurements of elapsed time between sensory stimulus onsets and subsequent behavioral responses to study the time course of information processing in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reaction Time Stages
Reaction may refer to a process or to a response (other), response to an action, event, or exposure: Physics and chemistry *Chemical reaction *Nuclear reaction *Reaction (physics), as defined by Newton's third law *Chain reaction (other). Biology and medicine *Adverse drug reaction *Allergy, Allergic reaction *Reflex, neural reaction *Hypersensitivity, immune reaction *Intolerance (other) *Light reaction (other). Psychology *Emotional, reaction *Reactivity (behaviour) *Proactivity, opposite of reactive behaviour *Reactive attachment disorder. Politics and culture *Reactionary, a political tendency *Reaction video *Commentary (other). Proper names and titles *Reaction (album), ''Reaction'' (album), a 1986 album by American R&B singer Rebbie Jackson **Reaction (song), "Reaction" (song), the title song from the Rebbie Jackson album *"Reaction", a single by Dead Letter Circus *ReAction GUI, a GUI toolkit used on AmigaOS *Reaction.life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Pearson
Karl Pearson (; born Carl Pearson; 27 March 1857 – 27 April 1936) was an English mathematician and biostatistician. He has been credited with establishing the discipline of mathematical statistics. He founded the world's first university statistics department at University College, London in 1911, and contributed significantly to the field of biometrics and meteorology. Pearson was also a proponent of social Darwinism, eugenics and scientific racism. Pearson was a protégé and biographer of Sir Francis Galton. He edited and completed both William Kingdon Clifford's ''Common Sense of the Exact Sciences'' (1885) and Isaac Todhunter's ''History of the Theory of Elasticity'', Vol. 1 (1886–1893) and Vol. 2 (1893), following their deaths. Biography Pearson was born in Islington, London into a Quaker family. His father was William Pearson QC of the Inner Temple, and his mother Fanny (née Smith), and he had two siblings, Arthur and Amy. Pearson attended University College Scho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millisecond
A millisecond (from '' milli-'' and second; symbol: ms) is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one thousandth (0.001 or 10−3 or 1/1000) of a second and to 1000 microseconds. A unit of 10 milliseconds may be called a centisecond, and one of 100 milliseconds a decisecond, but these names are rarely used. To help compare orders of magnitude of different times, this page lists times between 10−3 seconds and 100 seconds (1 millisecond and one second). ''See also'' times of other orders of magnitude. Examples The Apollo Guidance Computer used metric units internally, with centiseconds used for time calculation and measurement. *1 millisecond (1 ms) – cycle time for frequency 1 kHz; duration of light for typical photo flash strobe; time taken for sound wave to travel about 34 cm; repetition interval of GPS C/A PN code *1 millisecond - time taken for light to travel 204.19 km in a single mode fiber optic cable for a wavelength o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oswald Külpe
Oswald Külpe (; 3 August 1862 – 30 December 1915) was a German structural psychologist of the late 19th and early 20th century. Külpe, who is lesser known than his German mentor, Wilhelm Wundt, revolutionized experimental psychology at his time. In his obituary, Aloys Fischer wrote that, “undoubtedly Külpe was the second founder of experimental psychology on German soil; for with every change of base he made it a requirement that an experimental laboratory should be provided.” Külpe studied as a doctoral student and assistant to Wundt at the University of Leipzig, though his ideas differed from Wundt as he developed his own research (Boring, 1961). Külpe made significant contributions to the field of psychology, some of which are still relevant to this day, including the systematic experimental introspection, imageless thoughts, mental sets, and abstraction. Biography In August 1862, Oswald Külpe was born in Kandau, Courland, one of the Baltic providences of Russia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structuralism (psychology)
Structuralism in psychology (also structural psychology) is a theory of consciousness developed by Wilhelm Wundt and his student Edward Bradford Titchener. This theory was challenged in the 20th century. Structuralism as a school of psychology seeks to analyze the adult mind (the total sum of experience from birth to the present) in terms of the simplest definable components and then to find how these components fit together to form more complex experiences as well as how they correlate to physical events. To do this, psychologists employ introspection, self-reports of sensations, views, feelings, and emotions. Titchener Edward B. Titchener, along with Wilhelm Wundt, is credited for the theory of structuralism. It is considered to be the first "school" of psychology. Because he was a student of Wilhelm Wundt at the University of Leipzig, Titchener's ideas on how the mind worked were heavily influenced by Wundt's theory of voluntarism and his ideas of association and appercep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franciscus Donders
Franciscus (Franz) Cornelius Donders FRS FRSE (27 May 1818 – 24 March 1889) was a Dutch ophthalmologist. During his career, he was a professor of physiology in Utrecht, and was internationally regarded as an authority on eye diseases, directing the Netherlands Hospital for Eye Patients. Along with Graefe and Helmholtz, he was one of the primary founders of scientific ophthalmology. Life He was born in Tilburg, the son of Jan Franz Donders and Agnes Elizabeth Hegh. He was educated at Duizel School and seminaries in both Tilburg and Boxmeer. By the age of seventeen, Franciscus Donders had started studying medicine in the School of Military in Utrecht. It was here that he discovered his passion for experimental study, specifically in the field of chemistry. By the age of twenty-two he entered the junior military in order to become a surgeon For several years, the young Donders studied at the Royal Dutch Hospital for Military Medicine in Utrecht, then earning his M.D. in 1840 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptation (eye)
In visual physiology, adaptation is the ability of the retina of the eye to adjust to various levels of light. Natural night vision, or scotopic vision, is the ability to see under low-light conditions. In humans, rod cells are exclusively responsible for night vision as cone cells are only able to function at higher illumination levels. Night vision is of lower quality than day vision because it is limited in resolution and colors cannot be discerned; only shades of gray are seen. In order for humans to transition from day to night vision they must undergo a dark adaptation period of up to two hours in which each eye adjusts from a high to a low luminescence "setting", increasing sensitivity hugely, by many orders of magnitude. This adaptation period is different between rod and cone cells and results from the regeneration of photopigments to increase retinal sensitivity. Light adaptation, in contrast, works very quickly, within seconds. Efficiency The human eye can functio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Hovland
Carl Iver Hovland (June 12, 1912 – April 16, 1961) was a psychologist working primarily at Yale University and for the US Army during World War II who studied attitude change and persuasion. He first reported the sleeper effect after studying the effects of the Frank Capra's propaganda film ''Why We Fight'' on soldiers in the Army. In later studies on this subject, Hovland collaborated with Irving Janis who would later become famous for his theory of groupthink. Hovland also developed social judgment theory of attitude Attitude may refer to: Philosophy and psychology * Attitude (psychology), an individual's predisposed state of mind regarding a value * Metaphysics of presence * Propositional attitude, a relational mental state connecting a person to a pro ... change. Carl Hovland thought that the ability of someone to resist persuasion by a certain group depended on your degree of belonging to the group. Biography Carl Iver Hovland was born in Chicago on June 12, 1912. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henri Piéron
Louis Charles Henri Piéron (18 July 1881 – 6 November 1964) was a French psychologist. He was one of the founders of scientific psychology in France. He developed the Toulouse-Piéron Cancellation Test (TP) with Édouard Toulouse. Biography Henri Piéron was Professor of Physiology of Sensation at the Collège de France from 1923 to 1951. He took part in the first Davos University Course (a project to start an international university based in Davos) in 1928, along with many other prominent academics such as Albert Einstein and Hans Driesch. The same year, he created the ''Institut national d'orientation professionnelle'' (INOP), which became the ''Institut national d'étude du travail et d'orientation professionnelle''Inetop in 1942, and is now supported by the Conservatoire National des Arts et Métiers. After founding the first institute for "careers", he took charge of training guidance counsellors and conducted research into the field of counselling psychology. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. More generally, it can be described as the ability to perceive or infer information, and to retain it as knowledge to be applied towards adaptive behaviors within an environment or context. Intelligence is most often studied in humans but has also been observed in both non-human animals and in plants despite controversy as to whether some of these forms of life exhibit intelligence. Intelligence in computers or other machines is called artificial intelligence. Etymology The word ''intelligence'' derives from the Latin nouns '' intelligentia'' or '' intellēctus'', which in turn stem from the verb '' intelligere'', to comprehend or perceive. In the Middle Ages, the word ''intellectus'' became the scholarly technical term for understanding, and a translation f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Galton
Sir Francis Galton, FRS FRAI (; 16 February 1822 – 17 January 1911), was an English Victorian era polymath: a statistician, sociologist, psychologist, anthropologist, tropical explorer, geographer, inventor, meteorologist, proto-geneticist, psychometrician and a proponent of social Darwinism, eugenics, and scientific racism. He was knighted in 1909. Galton produced over 340 papers and books. He also created the statistical concept of correlation and widely promoted regression toward the mean. He was the first to apply statistical methods to the study of human differences and inheritance of intelligence, and introduced the use of questionnaires and surveys for collecting data on human communities, which he needed for genealogical and biographical works and for his anthropometric studies. He was a pioneer of eugenics, coining the term itself in 1883, and also coined the phrase " nature versus nurture". His book ''Hereditary Genius'' (1869) was the first social sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kymograph
A kymograph (from Greek κῦμα, swell or wave + γραφή, writing; also called a kymographion) is an analog device that draws a graphical representation of spatial position over time in which a spatial axis represents time. It basically consists of a revolving drum wrapped with a sheet of paper on which a stylus moves back and forth recording perceived changes of phenomena such as motion or pressure. The kymograph was initially a mechanical and hydraulic device, invented by German physiologist Carl Ludwig in the 1840s, and found its first use as a means to monitor blood pressure. The blood pressure was conveyed by hydraulics and levers to move a stylus that scratched a white trace into soot-covered paper on the revolving drum. Time is represented by the drum's rotation rate, and was recorded by a further stylus driven by a clock or tuning fork. The kymograph almost immediately became the central instrument in physiology and physiology education. Throughout the nineteenth and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |