|
Menit
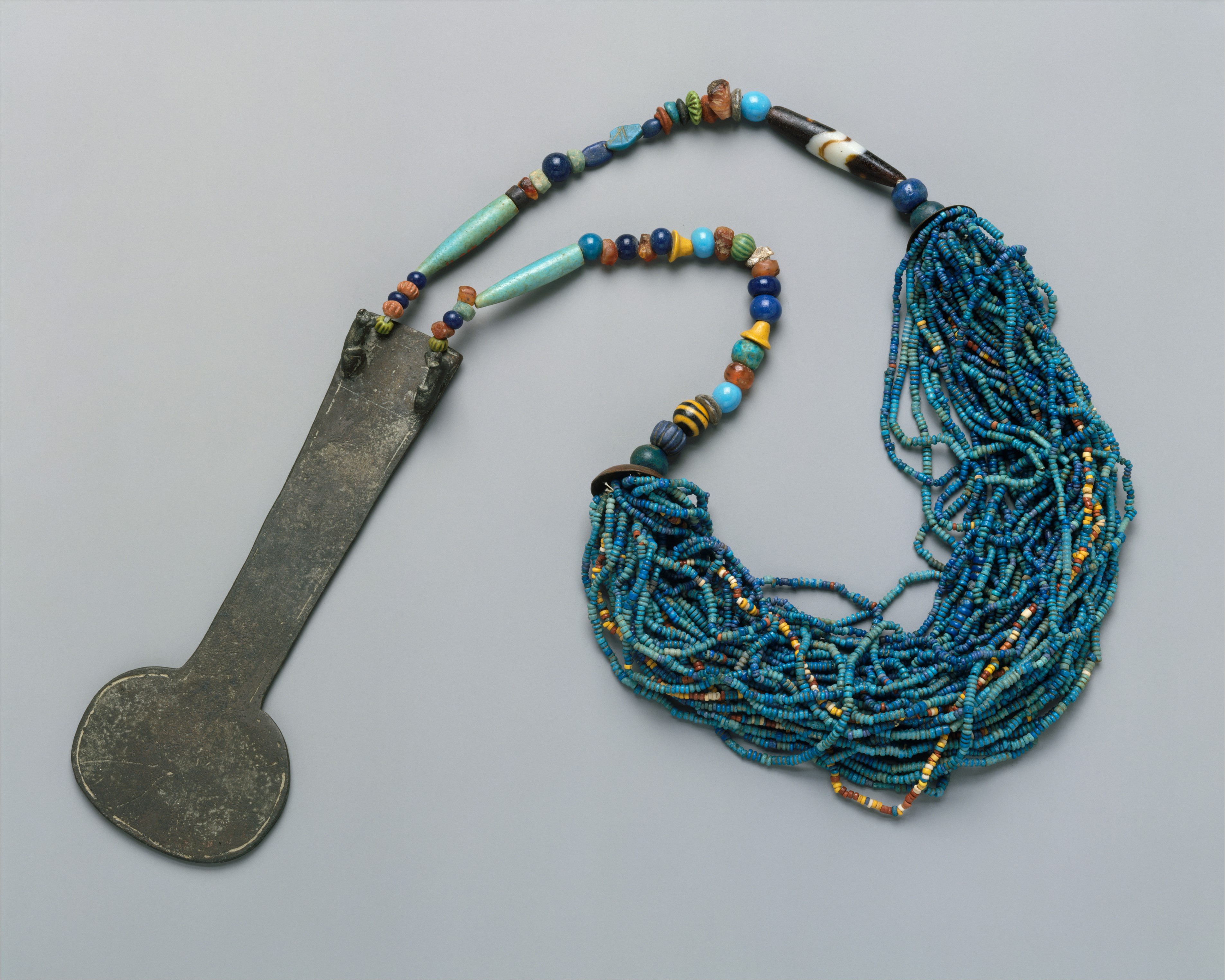
In ancient Egyptian religion, a menat ( egy, mnj.t, ar, منات) was a type of artefact closely associated with the goddess Hathor. Operation The menat was held in the hand by its counterpoise and used as a rattle by Hathor's priestesses. It was also worn as a protective amulet, particularly by Apis bulls. Parts The menat typically included an aegis attached to beaded strings. The other ends of the strings were tied to a counterweight that dangled on the wearer's back. The aegis was often made of faience, but other materials such as leather and bronze were also used. It was often inscribed or bore depictions of deities associated with Hathor. Purpose The necklace was meant to ensure good luck and fortune and to protect against evil spirits. It was also worn for protection in the afterlife and is often found buried with the dead, given as a grave gift since Ramesside times . It was expected to foster fruitfulness and good health for women, and for men it signified virili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menat Necklace From Malqata MET DT234778
In ancient Egyptian religion, a menat ( egy, mnj.t, ar, منات) was a type of artefact closely associated with the goddess Hathor. Operation The menat was held in the hand by its counterpoise and used as a rattle by Hathor's priestesses. It was also worn as a protective amulet, particularly by Apis bulls. Parts The menat typically included an aegis attached to beaded strings. The other ends of the strings were tied to a counterweight that dangled on the wearer's back. The aegis was often made of faience, but other materials such as leather and bronze were also used. It was often inscribed or bore depictions of deities associated with Hathor. Purpose The necklace was meant to ensure good luck and fortune and to protect against evil spirits. It was also worn for protection in the afterlife and is often found buried with the dead, given as a grave gift since Ramesside times . It was expected to foster fruitfulness and good health for women, and for men it signified virility.Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egyptian Faience
Egyptian faience is a sintered-quartz ceramic material from Ancient Egypt. The sintering process "covered he materialwith a true vitreous coating" as the quartz underwent vitrification, creating a bright lustre of various colours "usually in a transparent blue or green isotropic glass". Its name in the Ancient Egyptian language was , and modern archeological terms for it include sintered quartz, glazed frit, and glazed composition. is distinct from the crystalline pigment Egyptian blue, for which it has sometimes incorrectly been used as a synonym. It is not faience in the usual sense of tin-glazed pottery, and is different from the enormous range of clay-based Ancient Egyptian pottery, from which utilitarian vessels were made. It is similar to later Islamic stonepaste (or "fritware") from the Middle East, although that generally includes more clay. Egyptian faience is considerably more porous than glass proper. It can be cast in molds to create small vessels, jewelry and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pieter Willem Van Der Horst
Pieter Willem van der Horst (born 4 July 1946) is a scholar and university professor emeritus specializing in New Testament studies, Early Christian literature, and the Jewish and Hellenistic context of Early Christianity. Education and career Van der Horst was born in Driebergen, Netherlands. He studied classical philology and received a doctorate in theology in 1978. From 1969 to 2006, he was a research assistant, junior and senior lecturer, and full professor at the Faculty of Theology of Utrecht University. He is an editor of the series Commentaries on Early Jewish Literature, published by Walter de Gruyter. He became a member of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences in 1994.Manfred Gerstenfeld, "Utrecht University: The Myth of Jewish Cannibalism, Censorship, and Fear of Muslim Intimidation," Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs, September 2008online./ref> "Jewish cannibalism" controversy In 2006, van der Horst became embroiled in a controversy over his retiremen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virility
Virility (from the Latin ''virilitas'', manhood or virility, derived from Latin ''vir'', man) refers to any of a wide range of masculine characteristics viewed positively. Virile means "marked by strength or force". Virility is commonly associated with vigour, health, sturdiness, and constitution, especially in the fathering of children. In this last sense, virility is to men as fertility is to women. ''Virile'' has become obsolete in referring to a "nubile" young woman, or "a maid that is Marriageable or ripe for a Husband, or Virill". Historically, masculine attributes such as beard growth have been seen as signs of virility and leadership (for example in ancient Egypt and Greece). Male virility Evidence shows that increased male age is associated with a decline in semen volume, sperm motility, and sperm morphology. In studies that controlled for female age, comparisons between men under 30 and men over 50 found relative decreases in pregnancy rates between 23% and 38%. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramesside Period
The Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XX, alternatively 20th Dynasty or Dynasty 20) is the third and last dynasty of the Ancient Egyptian New Kingdom period, lasting from 1189 BC to 1077 BC. The 19th and 20th Dynasties furthermore together constitute an era known as the ''Ramesside period''. This dynasty is generally considered to be the start of the decline of Ancient Egypt. History Background Upon the death of the last pharaoh of the 19th Dynasty, Queen Twosret, Egypt descended into a period of civil war, as attested by the Elephantine stela built by Setnakhte. The circumstances of Twosret's demise are uncertain, as she may have died peacefully during her reign or been overthrown by Setnakhte, who was likely already middle aged at the time. 20th Dynasty A consistent theme of this dynasty was the loss of pharaonic power to the High Priests of Amun. Horemheb, a pharaoh of the 18th Dynasty, had restored the traditional Ancient Egyptian religion and the priesthood of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
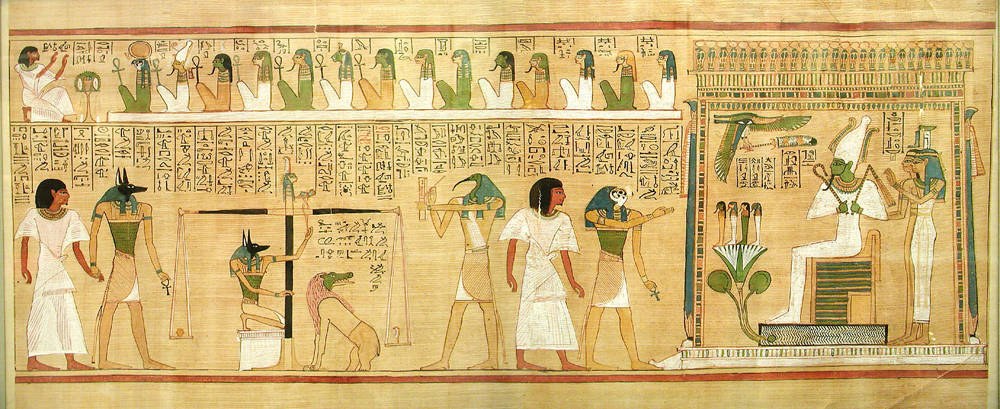
Afterlife
The afterlife (also referred to as life after death) is a purported existence in which the essential part of an individual's identity or their stream of consciousness continues to live after the death of their physical body. The surviving essential aspect varies between belief systems; it may be some partial element, or the entire soul or spirit of an individual, which carries with it and may confer personal identity or, on the contrary, nirvana. Belief in an afterlife is in contrast to the belief in oblivion after death. In some views, this continued existence takes place in a spiritual realm, while in others, the individual may be reborn into this world and begin the life cycle over again, likely with no memory of what they have done in the past. In this latter view, such rebirths and deaths may take place over and over again continuously until the individual gains entry to a spiritual realm or otherworld. Major views on the afterlife derive from religion, esotericism an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such as arsenic or silicon. These additions produce a range of alloys that may be harder than copper alone, or have other useful properties, such as ultimate tensile strength, strength, ductility, or machinability. The three-age system, archaeological period in which bronze was the hardest metal in widespread use is known as the Bronze Age. The beginning of the Bronze Age in western Eurasia and India is conventionally dated to the mid-4th millennium BCE (~3500 BCE), and to the early 2nd millennium BCE in China; elsewhere it gradually spread across regions. The Bronze Age was followed by the Iron Age starting from about 1300 BCE and reaching most of Eurasia by about 500 BCE, although bronze continued to be much more widely used than it is in mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
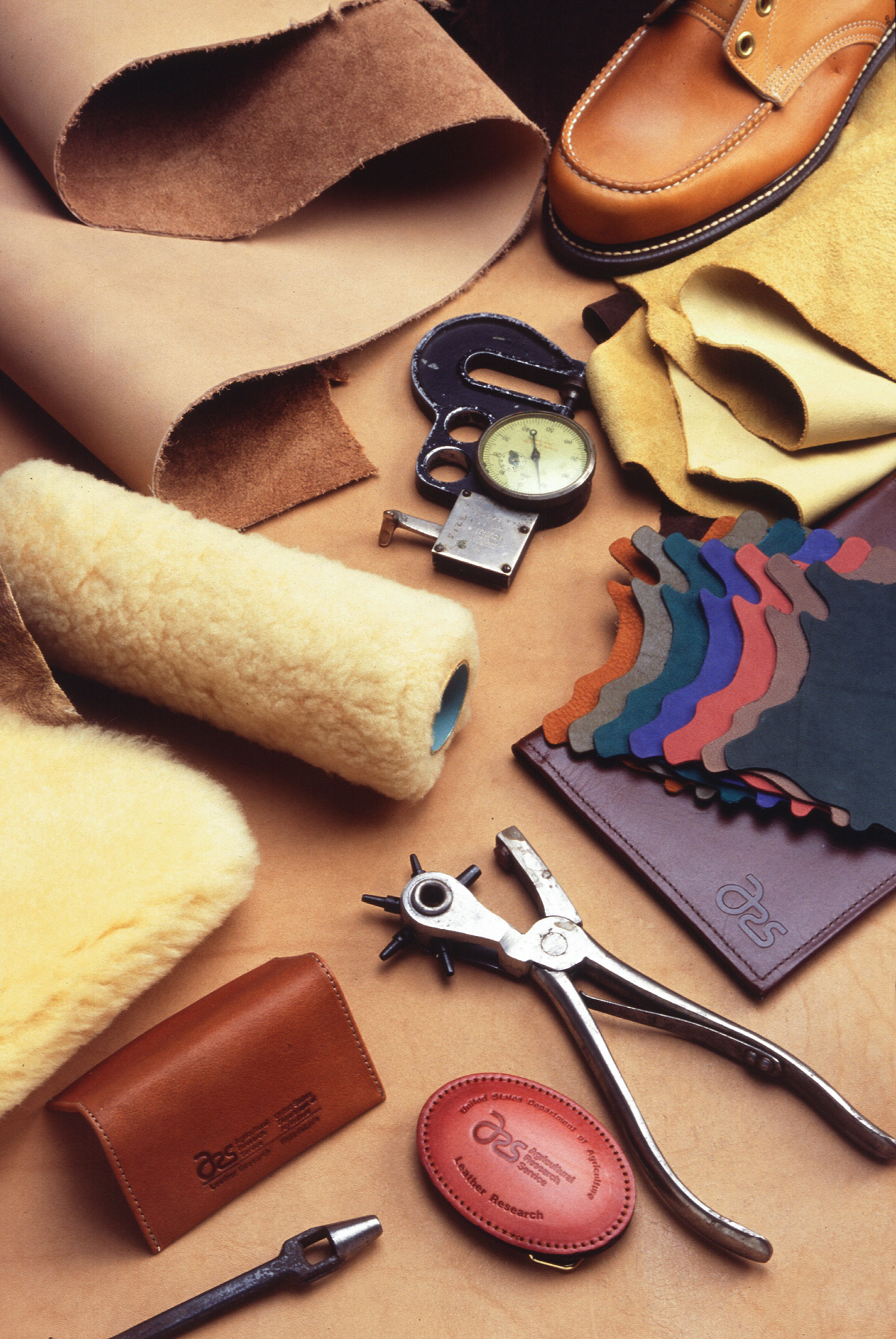
Leather
Leather is a strong, flexible and durable material obtained from the tanning, or chemical treatment, of animal skins and hides to prevent decay. The most common leathers come from cattle, sheep, goats, equine animals, buffalo, pigs and hogs, and aquatic animals such as seals and alligators. Leather can be used to make a variety of items, including clothing, footwear, handbags, furniture, tools and sports equipment, and lasts for decades. Leather making has been practiced for more than 7,000 years and the leading producers of leather today are China and India. Animal rights groups claim that modern commercial leather making and the consumption of its products is unethically killing animals. According to the life-cycle assessment (LCA) report for the United Nations Industrial Development Organization, 99% of the raw hides and skins used in the production of leather derive from animals raised for meat and/or dairy production. Critics of tanneries claim that they engage in uns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counterweight
A counterweight is a weight that, by applying an opposite force, provides balance and stability of a mechanical system. The purpose of a counterweight is to make lifting the load faster and more efficient, which saves energy and causes less wear and tear on the lifting machine. Counterweights are often used in traction lifts (elevators), cranes and funfair rides. In these applications, the expected load multiplied by the distance that load will be spaced from the central support (called the "tipping point") must be equal to the counterweight's mass times its distance from the tipping point in order to prevent over-balancing either side. This distance times mass is called the load moment. A counterbalance is a weight or force that balances or offsets another as when two objects of equal weight, power, or influence are acting in opposition to each other. The objects are then said to be in counterbalance. Counterweights in action Trebuchet: There are five major components of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendera Krypta 12
Dendera ( ar, دَنْدَرة ''Dandarah''; grc, Τεντυρις or Τεντυρα; Bohairic cop, ⲛⲓⲧⲉⲛⲧⲱⲣⲓ, translit=Nitentōri; Sahidic cop, ⲛⲓⲧⲛⲧⲱⲣⲉ, translit=Nitntōre), also spelled ''Denderah'', ancient Iunet 𓉺𓈖𓏏𓊖 “jwn.t”, Tentyris or Tentyra is a small town and former bishopric in Egypt situated on the west bank of the Nile, about south of Qena, on the opposite side of the river. It is located approximately north of Luxor and remains a Latin Catholic titular see. It contains the Dendera Temple complex, one of the best-preserved temple sites from ancient Upper Egypt. Etymology The original name of the town is , the etymology of which is unknown. It was later complemented by the name of the chief goddess Hathor and became Egyptian which is the source of cop, ⲛⲓⲧⲉⲛⲧⲱⲣⲓ, translit=Nitentōri or just "of the goddess", which is the source of grc-x-koine, Τεντυρις. The modern Arabic name of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aegis
The aegis ( ; grc, αἰγίς ''aigís''), as stated in the ''Iliad'', is a device carried by Athena and Zeus, variously interpreted as an animal skin or a shield and sometimes featuring the head of a Gorgon. There may be a connection with a deity named Aex or Aix, a daughter of Helios and a nurse of Zeus or alternatively a mistress of Zeus (Hyginus, ''Astronomica'' 2. 13). The modern concept of doing something "under someone's ''aegis'' means doing something under the protection of a powerful, knowledgeable, or benevolent source. The word ''aegis'' is identified with protection by a strong force with its roots in Greek mythology and adopted by the Romans; there are parallels in Norse mythology and in Egyptian mythology as well, where the Greek word ''aegis'' is applied by extension. Etymology The Greek ''aigis'', has many meanings including: # "violent windstorm", from the verb ''aïssō'' (word stem ''aïg-'') = "I rush or move violently". Akin to ''kataigis'', "thund ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apis (deity)
In ancient Egyptian religion, Apis or Hapis ( egy, ḥjpw, reconstructed as Old Egyptian with unknown final vowel > Medio-Late Egyptian , cop, ϩⲁⲡⲉ ''ḥapə''), alternatively spelled Hapi-ankh, was a sacred bull worshiped in the Memphis region, identified as the son of Hathor, a primary deity in the pantheon of ancient Egypt. Initially, he was assigned a significant role in her worship, being sacrificed and reborn. Later, Apis also served as an intermediary between humans and other powerful deities (originally Ptah, later Osiris, then Atum). The Apis bull was an important sacred animal to the ancient Egyptians. As with the other sacred beasts, Apis' importance increased over the centuries. During colonization of the conquered Egypt, Greek and Roman authors had much to say about Apis, the markings by which the black calf was recognized, the manner of his conception by a ray from heaven, his house at Memphis (with a court for his deportment), the mode of prognosti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |









.jpg)