|
Melton (cloth)
Melton cloth is traditionally made of wool and is woven in a twill form. It is thick, due to having been well fulled, which gives it a felt-like smooth surface. It is napped and very closely sheared. Meltons are similar to Mackinaw cloth. It is a very solid cloth in which the twill weave pattern is completely concealed due to the finishing processes. Because of its dense, quasi-felted texture it frays minimally or not at all. It is hard wearing and wind and weather resistant. Its main use is for heavy outer garments and coats and for blankets. In lighter weights melton cloth is traditionally used for lining the underside of jacket collars. It was developed in the Leicestershire town of Melton Mowbray, from which it derives its name. This town is the traditional centre of English fox-hunting, and black and scarlet hunting coats are traditionally made from melton cloth, due to its weatherproof qualities. In England not only is melton used for the scarlet hunting coat, an iconic symbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mackinaw Cloth
Mackinaw cloth is a heavy and dense water-repellent woolen cloth, similar to Melton cloth but using a tartan pattern, often " buffalo plaid". It was used to make a short coat of the same name, sometimes with a doubled shoulder. These jackets have their origins on the Canadian frontier and were later made famous by Canadian and American loggers in the upper Midwest as workwear during the mid-19th century logging boom. Mackinaw blankets are referenced by Josiah A. Gregg in his 1844 book ''Commerce of the Prairies'' about trade on the Santa Fe Trail. He notes that these were contraband, subject to confiscation by customs officers, but that they could be concealed between the double layers of Osnaburg sheet fabrics which formed the roof of covered cargo wagons. Origin of the Mackinaw jacket The Mackinac or Mackinaw region in present-day Michigan was an important trade artery during the 18th and 19th centuries; it was named after the Straits of Mackinac, which connect Lake Michig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wool
Wool is the textile fibre obtained from sheep and other mammals, especially goats, rabbits, and camelids. The term may also refer to inorganic materials, such as mineral wool and glass wool, that have properties similar to animal wool. As an animal fibre, wool consists of protein together with a small percentage of lipids. This makes it chemically quite distinct from cotton and other plant fibres, which are mainly cellulose. Characteristics Wool is produced by follicles which are small cells located in the skin. These follicles are located in the upper layer of the skin called the epidermis and push down into the second skin layer called the dermis as the wool fibers grow. Follicles can be classed as either primary or secondary follicles. Primary follicles produce three types of fiber: kemp, medullated fibers, and true wool fibers. Secondary follicles only produce true wool fibers. Medullated fibers share nearly identical characteristics to hair and are long but lack c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twill
Twill is a type of textile weave with a pattern of diagonal parallel ribs. It is one of three fundamental types of textile weaves along with plain weave and satin. It is made by passing the weft thread over one or more warp threads then under two or more warp threads and so on, with a "step," or offset, between rows to create the characteristic diagonal pattern. Because of this structure, twill generally drapes well. Classification Twill weaves can be classified from four points of view: # According to the stepping: #* ''Warp-way'': 3/1 warp way twill, etc. #* ''Weft-way'': 2/3 weft way twill, etc. # According to the direction of twill lines on the face of the fabric: #* ''S-twill'', or ''left-hand twill weave'': 2/1 S, etc. #* ''Z-twill'', or ''right-hand twill weave'': 3/2 Z, etc. # According to the face yarn (warp or weft): #* ''Warp face twill weave'': 4/2 S, etc. #* ''Weft face twill weave'': 1/3 Z, etc. #* ''Double face'' twill weave'': 3/3 Z, etc. # According to the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fulling
Fulling, also known as felting, tucking or walking ( Scots: ''waukin'', hence often spelled waulking in Scottish English), is a step in woollen clothmaking which involves the cleansing of woven or knitted cloth (particularly wool) to eliminate (lanoline) oils, dirt, and other impurities, and to make it shrink by friction and pressure. The work delivers a smooth, tightly finished fabric that is isolating and water repellent. Well known example are duffel cloth, first produced in Flanders in the 14th century and loden, produced in Austria from the 16th century on. The practice to do this by hand or feet died out with the introduction of machines during the industrial revolution. Process Fulling involves two processes: scouring and milling (thickening). Originally, fulling was carried out by the pounding of the woollen cloth with a club, or the fuller's feet or hands. In Scottish Gaelic tradition, this process was accompanied by waulking songs, which women sang to set the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felt
Felt is a textile material that is produced by matting, condensing and pressing fibers together. Felt can be made of natural fibers such as wool or animal fur, or from synthetic fibers such as petroleum-based acrylic or acrylonitrile or wood pulp–based rayon. Blended fibers are also common. Natural fibre felt has special properties that allow it to be used for a wide variety of purposes. "It is fire-retardant and self-extinguishing; it dampens vibration and absorbs sound; and it can hold large amounts of fluid without feeling wet..." History Felt from wool is one of the oldest known textiles. Many cultures have legends as to the origins of felt making. Sumerian legend claims that the secret of feltmaking was discovered by Urnamman of Lagash. The story of Saint Clement and Saint Christopher relates that the men packed their sandals with wool to prevent blisters while fleeing from persecution. At the end of their journey, the movement and sweat had turned the wool into f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nap (textile)
Primarily, nap is the raised (fuzzy) surface on certain kinds of cloth, such as velvet or moleskin. Nap can refer additionally to other surfaces that look like the surface of a napped cloth, such as the surface of a felt or beaver hat. Starting around the 14th century, the word referred originally to the roughness of weaving, woven cloth before it was Shearing (textiles), sheared."nap". ''The Oxford English Dictionary''. 2nd ed. 1989. When cloth, especially woollen cloth, is woven, the surface of the cloth is not smooth, and this roughness is the nap. Generally the cloth is then "sheared" to create an even surface, and the nap is thus removed. A person who trimmed the surface of cloth with shears to remove any excess nap was known as a shearman. Piled nap Since the 15th century, the term ''nap'' has generally referred to a special pile (textile), pile given to the cloth. The term ''pile'' refers to raised fibres that are there on purpose, rather than as a by-product of producing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blanket
A blanket is a swath of soft cloth large enough either to cover or to enfold most of the user's body and thick enough to keep the body warm by trapping radiant body heat that otherwise would be lost through convection. Etymology The term arose from the generalization of a specific fabric called ''Blanket fabric'', a heavily napped woolen weave pioneered by Thomas Blanket (Blanquette), a Flemish weaver who lived in Bristol, England, in the 14th century. Earlier usage of the term is possible through its derivation from the French word for white: . According to the Oxford English Dictionary, the word was used a noun as long ago as the 14th century. William Shakespeare is recognised as the first person to use the verb ''blanket'', meaning to 'cover with or as with a blanket'. In the play ''King Lear'', published in 1608, the character Edgar says: "My face ile grime with filth, Blanket my loynes, else all my haire with knots." History An ancient form of blanket is recor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melton Mowbray
Melton Mowbray () is a town in Leicestershire, England, north-east of Leicester, and south-east of Nottingham. It lies on the River Eye, known below Melton as the Wreake. The town had a population 27,670 in 2019. The town is sometimes promoted as Britain's "Rural Capital of Food", it is the home of the Melton Mowbray pork pie and is the location of one of six licensed makers of Stilton cheese. History Toponymy The name comes from the early English word Medeltone – meaning "Middletown surrounded by small hamlets" (as do Milton and Middleton). Mowbray is the Norman family name of early Lords of the Manor – namely Robert de Mowbray. Early history In and around Melton, there are 28 scheduled ancient monuments, some 705 buildings of special architectural or historical interest, 16 sites of special scientific interest, and several deserted village sites. Its industrial archaeology includes the Grantham Canal and remains of the Melton Mowbray Navigation. Windmill sites and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fox-hunting
Fox hunting is an activity involving the tracking, chase and, if caught, the killing of a fox, traditionally a red fox, by trained foxhounds or other scent hounds. A group of unarmed followers, led by a "master of foxhounds" (or "master of hounds"), follow the hounds on foot or on horseback. In Australia, the term also refers to the hunting of foxes with firearms, similar to deer hunting. Fox hunting with hounds, as a formalised activity, originated in England in the sixteenth century, in a form very similar to that practised until February 2005, when a law banning the activity in England and Wales came into force. A ban on hunting in Scotland had been passed in 2002, but it continues to be within the law in Northern Ireland and several other areas, including Australia, Canada, France, the Republic of Ireland and the United States. The sport is controversial, particularly in the United Kingdom. Proponents of fox hunting view it as an important part of rural culture, and usef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donkey Jacket
A donkey jacket is a medium-length workwear jacket, typically made of unlined black or dark blue thick Melton woollen fabric, with the shoulders back and front reinforced and protected from rain with leather or PVC panels. Originating in the United Kingdom, the garment is untailored at the waist such that it hangs down straight from the shoulders. The front vertical edges fall straight and are squared-off at the bottom edge which is also straight horizontally with no vent at the back. In length it reaches below the crotch area. It has no lapels and is closed by four to five buttons at the front that fasten tightly up to the neck with a broad and stiff turn-up collar, allowing the wearer to protect the neck from wind, cold and wet weather. It is thus well suited to outdoors work in demanding conditions. Origins In 1888 George Key opened up his own shop above his father John Key's first-floor draper shop on Lower Brook Street in Rugeley, Staffordshire, England. That same ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
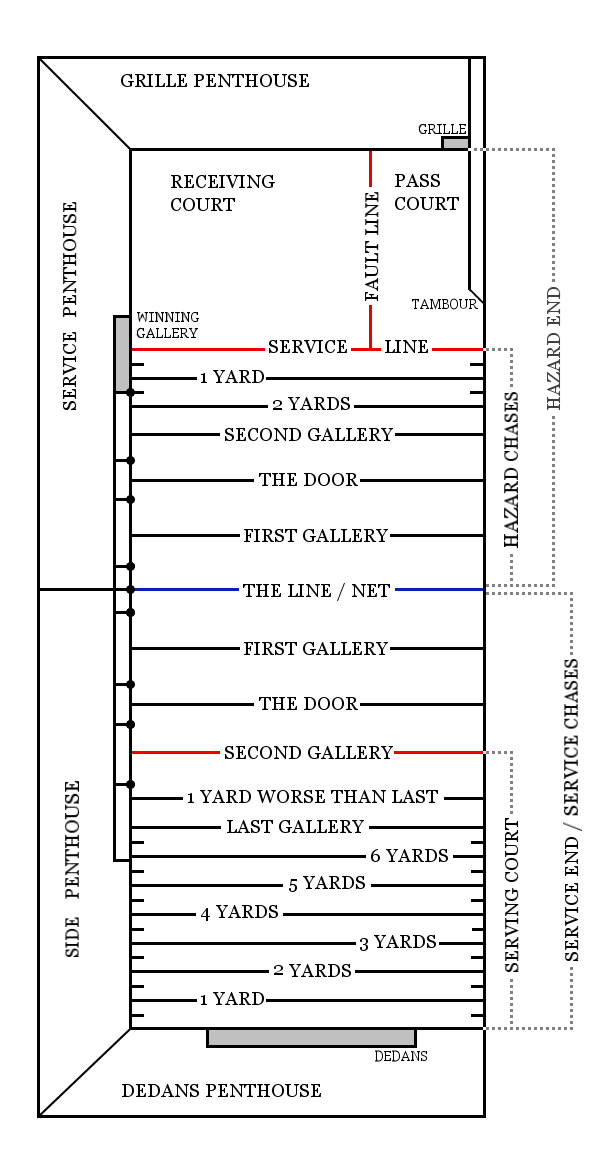
Real Tennis
Real tennis – one of several games sometimes called "the sport of kings" – is the original racquet sport from which the modern game of tennis (also called "lawn tennis") is derived. It is also known as court tennis in the United States, formerly royal tennis in England and Australia, and ''courte-paume'' in France (to distinguish it from longue-paume, and in reference to the older, racquetless game of ''jeu de paume'', the ancestor of modern handball and racquet games). Many French real tennis courts are at ''jeu de paume'' clubs. The term ''real'' was first used by journalists in the early 20th century as a retronym to distinguish the ancient game from modern ''lawn'' tennis (even though, at present, the latter sport is seldom contested on lawns outside the few social-club-managed estates such as Wimbledon). There are more than 50 active real tennis courts in the world, located in the United Kingdom, Australia, the United States and France. Other countries have c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 216 days was longer than that of List of monarchs in Britain by length of reign, any previous British monarch and is known as the Victorian era. It was a period of industrial, political, scientific, and military change within the United Kingdom, and was marked by a great expansion of the British Empire. In 1876, the British Parliament voted to grant her the additional title of Empress of India. Victoria was the daughter of Prince Edward, Duke of Kent and Strathearn (the fourth son of King George III), and Princess Victoria of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld. After the deaths of her father and grandfather in 1820, she was Kensington System, raised under close supervision by her mother and her comptroller, John Conroy. She inherited the throne aged 18 af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |