|
Mechanical Counter
Mechanical counters are digital counters built using mechanical components. Long before electronics became common, mechanical devices were used to count events. They typically consist of a series of disks mounted on an axle, with the digits zero through nine marked on their edge. The right most disk moves one increment with each event. Each disk except the left-most has a protrusion that, after the completion of one revolution, moves the next disk to the left one increment. Such counters were used as odometers for bicycles and cars and in tape recorders and fuel dispensers and to control manufacturing processes. One of the largest manufacturers was the Veeder-Root company, and their name was often used for this type of counter.. Mechanical counters can be made into electromechanical counters, that count electrical impulses, by adding a small solenoid. History An odometer for measuring distance was first described by Vitruvius around 27 and 23 BC, although the actual inventor may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the ChuHan contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD) and the Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a golden age in Chinese history, and it has influenced the identity of the Chinese civilization ever since. Modern China's majority ethnic group refers to themselves as the "Han people", the Sinitic language is known as "Han language", and the written Chinese is referred to as "Han characters". The emperor was at the pinnacle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electricity Meter
North American domestic analog electricity meter. Electricity meter with transparent plastic case (Israel) North American domestic electronic electricity meter An electricity meter, electric meter, electrical meter, energy meter, or kilowatt-hour meter is a device that measures the amount of electric energy consumed by a residence, a business, or an electrically powered device. Electric meter or energy meter measures the total power consumed over a time interval. Electric utilities use electric meters installed at customers' premises for billing and monitoring purposes. They are typically calibrated in billing units, the most common one being the kilowatt hour (''kWh''). They are usually read once each billing period. When energy savings during certain periods are desired, some meters may measure demand, the maximum use of power in some interval. "Time of day" metering allows electric rates to be changed during a day, to record usage during peak high-cost periods and of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knitting Counter
A row counter for hand knitting is a tally counter for counting rows or courses worked, for counting stitch pattern repetitions, or for counting increases or decreases of the number of stitches in consecutive rows. The first commercially produced one appeared on the market in the 1920s after the general public started regularly knitting from unfamiliar printed and complex patterns. Design variations include on-needle barrel-shaped counters for straight-needle work, stitch-marker counters for knitting on double-pointed and circular needles, complex counters which attempted to assist with decreases, increases and lacework, stand-alone hand-held counters in imitation of the hand-tally, pendant counters worn round the neck and online software for iPhones. Early tally methods in Europe and the United States Until the early 19th century, in Europe and the United States, groups of localised professional hand knitters specialised in a few well-known patterns in which keeping a tal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tally Counter
A tally counter is a mechanical, electronic, or software device used to incrementally count something, typically fleeting. One of the most common things tally counters are used for is counting people, animals, or things that are coming and going from some location. Description A tally counter is usually cased in metal and is cylindrical in shape. Part of the circle is flattened out and contains a window of plastic or glass. Inside the counter are a number of rings with the numbers from 0 to 9 in descending order going clockwise. Most counters have four such rings, allowing the user to count up to 9999. A metal ring may be attached to aid in holding the counter, and usually half the ring is bent to allow it to fold flush with the counter when not in use. The counter is activated by pressing a button located above the screen. This causes the first ring to advance one number. After the count has reached 0009, then the second ring will advance one click and the first ring will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voting Machine
A voting machine is a machine used to record votes in an election without paper. The first voting machines were mechanical but it is increasingly more common to use ''electronic voting machines''. Traditionally, a voting machine has been defined by its mechanism, and whether the system tallies votes at each voting location, or centrally. Voting machines should not be confused with tabulating machines, which count votes done by paper ballot. Voting machines differ in usability, security, cost, speed, accuracy, and ability of the public to oversee elections. Machines may be more or less accessible to voters with different disabilities. Tallies are simplest in parliamentary systems where just one choice is on the ballot, and these are often tallied manually. In other political systems where many choices are on the same ballot, tallies are often done by machines to give faster results. Historical machines In ancient Athens (5th and 4th centuries BCE) voting was done by different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabulating Machine
The tabulating machine was an electromechanical machine designed to assist in summarizing information stored on punched cards. Invented by Herman Hollerith, the machine was developed to help process data for the 1890 U.S. Census. Later models were widely used for business applications such as accounting and inventory control. It spawned a class of machines, known as unit record equipment, and the data processing industry. The term "Super Computing" was used by the ''New York World'' newspaper in 1931 to refer to a large custom-built tabulator that IBM made for Columbia University. 1890 census The 1880 census had taken eight years to process. Since the U.S. Constitution mandates a census every ten years to apportion both congressional representatives and direct taxes among the states, a combination of larger staff and faster-recording systems was required. In the late 1880s Herman Hollerith, inspired by conductors using holes punched in different positions on a railway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analytical Engine
The Analytical Engine was a proposed mechanical general-purpose computer designed by English mathematician and computer pioneer Charles Babbage. It was first described in 1837 as the successor to Babbage's difference engine, which was a design for a simpler mechanical calculator. The Analytical Engine incorporated an arithmetic logic unit, control flow in the form of conditional branching and loops, and integrated memory, making it the first design for a general-purpose computer that could be described in modern terms as Turing-complete. In other words, the structure of the Analytical Engine was essentially the same as that which has dominated computer design in the electronic era. The Analytical Engine is one of the most successful achievements of Charles Babbage. Babbage was never able to complete construction of any of his machines due to conflicts with his chief engineer and inadequate funding. It was not until 1941 that Konrad Zuse built the first general-purpose com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
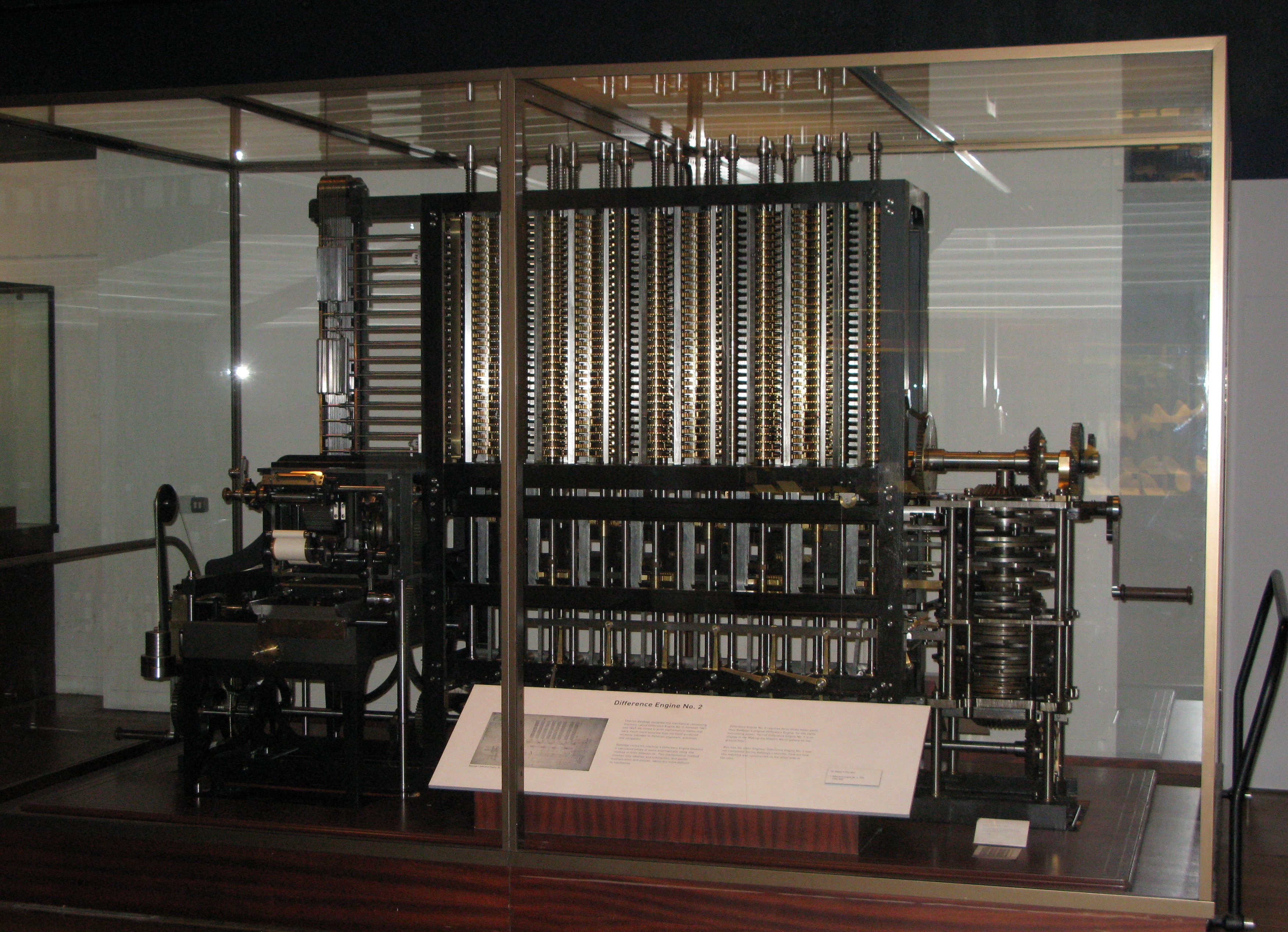
Difference Engine
A difference engine is an automatic mechanical calculator designed to tabulate polynomial, polynomial functions. It was designed in the 1820s, and was first created by Charles Babbage. The name, the difference engine, is derived from the method of divided differences, a way to interpolate or tabulate functions by using a small set of polynomial co-efficients. Some of the most common mathematical functions used in engineering, science and navigation, were, and still are computable with the use of the difference engine's capability of computing logarithmic and trigonometric functions, which can be Taylor series, approximated by polynomials, so a difference engine can compute many useful mathematical table, tables of numbers. History The notion of a mechanical calculator for mathematical functions can be traced back to the Antikythera mechanism of the 2nd century BC, while early modern examples are attributed to Blaise Pascal, Pascal and Gottfried Leibniz, Leibniz in the 17th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arithmometer
The arithmometer (french: arithmomètre) was the first digital mechanical calculator strong enough and reliable enough to be used daily in an office environment. This calculator could add and subtract two numbers directly and could perform long multiplications and divisions effectively by using a movable accumulator for the result. Patented in France by Thomas de Colmar in 1820 and manufactured from 1851 to 1915, it became the first commercially successful mechanical calculator.Chase G.C.: ''History of Mechanical Computing Machinery'', Vol. 2, Number 3, July 1980, page 204, IEEE Annals of the History of Computing https://archive.org/details/ChaseMechanicalComputingMachinery Its sturdy design gave it a strong reputation for reliability and accuracy and made it a key player in the move from to calculating machines that took place during the second half of the 19th century. Its production debut of 1851 launched the mechanical calculator industry which ultimately built million ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
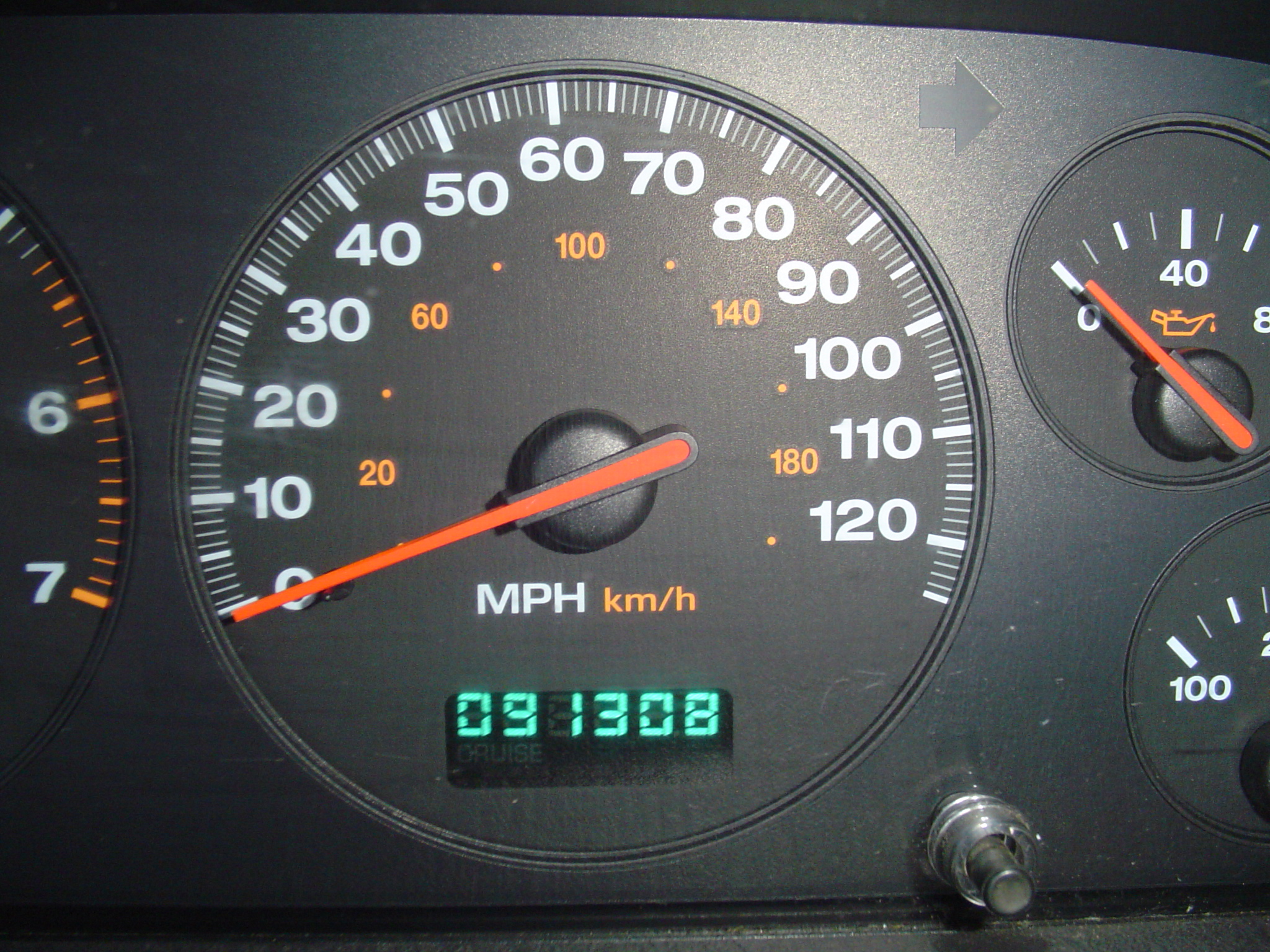
Odometer
An odometer or odograph is an instrument used for measuring the distance traveled by a vehicle, such as a bicycle or car. The device may be electronic, mechanical, or a combination of the two (electromechanical). The noun derives from ancient Greek , ''hodómetron'', from , ''hodós'' ("path" or "gateway") and , ''métron'' ("measure"). Early forms of the odometer existed in the ancient Greco-Roman world as well as in ancient China. In countries using Imperial units or US customary units it is sometimes called a mileometer or milometer, the former name especially being prevalent in the United Kingdom and among members of the Commonwealth. History Classical Era Possibly the first evidence for the use of an odometer can be found in the works of the ancient Roman Pliny (NH 6. 61-62) and the ancient Greek Strabo (11.8.9). Both authors list the distances of routes traveled by Alexander the Great (r. 336-323 BC) as by his bematists Diognetus and Baeton. However, the high ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li (unit)
''Li'' (, ''lǐ'', or , ''shìlǐ''), also known as the Chinese mile, is a traditional Chinese unit of distance. The li has varied considerably over time but was usually about one third of an English mile and now has a standardized length of a half-kilometer (). This is then divided into 1,500 chi or "Chinese feet". The character 里 combines the characters for "field" ( 田, ''tián'') and "earth" ( 土, ''tǔ''), since it was considered to be about the length of a single village. As late as the 1940s, a "li" did not represent a fixed measure but could be longer or shorter depending on the ''effort'' required to cover the distance. There is also another ''li'' (Traditional: 釐, Simplified: 厘, ''lí'') that indicates a unit of length of a ''chi'', but it is used much less commonly. This ''li'' is used in the People's Republic of China as the equivalent of the ''centi-'' prefix in metric units, thus ''limi'' ( 厘米, límǐ) for centimeter. The tonal difference makes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)