|
Massacre Of The Acqui Division
The massacre of the Acqui Division, also known as the Cephalonia massacre, was the mass execution of the soldiers of the Italian 33rd Infantry Division "Acqui" by German soldiers on the island of Cephalonia, Greece, in September 1943, following the Italian armistice during the Second World War. About 5,000 soldiers were executed, and around 3,000 more drowned. Following the decision of the Italian government to negotiate a surrender to the Allies in 1943, the German Army tried to disarm the Italians during Operation Achse. On 13 September the Italians of the Acqui resisted, and fought the Germans on the island of Cephalonia. By 22 September the last of the Italian resistance surrendered after running out of ammunition. A total of 1,315 Italians were killed in the battle, 5,155 were executed by 26 September, and 3,000 drowned when the German ships taking the survivors to concentration camps were sunk by the Allies. It was one of the largest prisoner of war massacres of the war, al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalonia
Kefalonia or Cephalonia ( el, Κεφαλονιά), formerly also known as Kefallinia or Kephallenia (), is the largest of the Ionian Islands in western Greece and the 6th largest island in Greece after Crete, Euboea, Lesbos, Rhodes and Chios. It is also a separate regional units of Greece, regional unit of the Ionian Islands (region), Ionian Islands region. It was a former Latin Catholic diocese Roman Catholic Diocese of Cephalonia and Zakynthos, Kefalonia–Zakynthos (Cefalonia–Zante) and short-lived titular see as just Kefalonia. The capital city of Cephalonia is Argostoli. History Antiquity Legend An ''Aitiology, aition'' explaining the name of Cephallenia and reinforcing its cultural connections with Athens associates the island with the mythological figure of Cephalus, who helped Amphitryon of Mycenae in a war against the Taphians and Teleboans. He was rewarded with the island of Same (ancient Greece), Same, which thereafter came to be known as Kefallinia, Cephallenia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Achse
Operation Achse (german: Fall Achse, lit=Case Axis), originally called Operation Alaric (), was the codename for the German operation to forcibly disarm the Italian armed forces after Italy's armistice with the Allies on 3 September 1943. Several German divisions had entered Italy after the fall of Benito Mussolini in July 1943, while Italy was officially still an ally of Germany, despite the protests of the new Italian government under Pietro Badoglio. The armistice was made public on 8 September. German forces moved rapidly to take over the Italian zones of occupation in the Balkans and southern France, and to disarm Italian forces in Italy. Some Italian troops, with no orders from superiors, and hampered by many desertions, resisted the Germans. Most notably on the Greek island of Cephalonia, where 1,315 Italian soldiers were killed in action against the Germans and over 5,100 prisoners of war of the 33rd Infantry Division "Acqui" were summarily executed by the German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
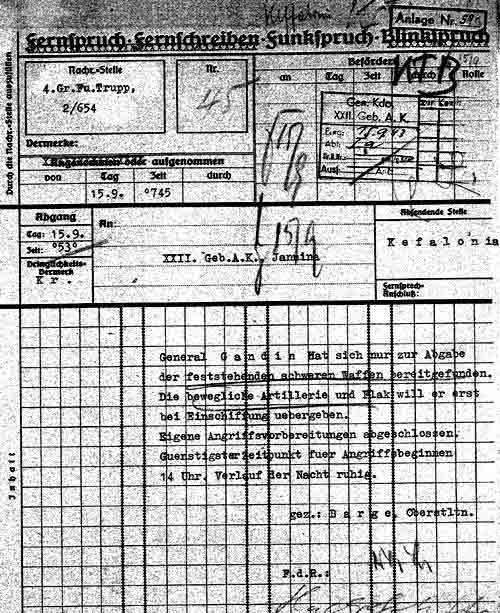
Telegram
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas pigeon post is not. Ancient signalling systems, although sometimes quite extensive and sophisticated as in China, were generally not capable of transmitting arbitrary text messages. Possible messages were fixed and predetermined and such systems are thus not true telegraphs. The earliest true telegraph put into widespread use was the optical telegraph of Claude Chappe, invented in the late 18th century. The system was used extensively in France, and European nations occupied by France, during the Napoleonic era. The electric telegraph started to replace the optical telegraph in the mid-19th century. It was first taken up in Britain in the form of the Cooke and Wheatstone telegraph, initially used mostly as an aid to railway signalling. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eleventh Army (Italy)
The 11th Army ( it, 11ª Armata) was a World War II field army of the Royal Italian Army. It was formed in November 1940 for service in the Greco-Italian War, and after the German invasion of Greece and the capitulation of that country in April 1941, assumed occupation duties in the Greek mainland. It remained on station in Greece until the Armistice of Cassibile on 8 September 1943, when it was forcibly disbanded by the Germans. History It was formed on 9 November 1940 out of the 11th Army Corps, then based in Italian-occupied Albania and engaged in operations against Greece alongside the 9th Army. Its engagement against the Greeks lasted until the fall of Greece in April 1941. Occupation of Greece Thereafter, the Eleventh Army assumed duties of occupation in Greece, headquartered in Athens. Its command also doubled as the Higher Armed Forces Command Greece (''Comando Superiore Forze Armate Grecia'', abbrev. ''C.S. FF. AA. Grecia''), with responsibility over mainland Greece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlo Vecchiarelli
Carlo Vecchiarelli (10 January 1884 – 13 December 1948) was an Italian general. He was a veteran combatant of the First World War. Between the two world wars he held the positions of Military Attaché at the Italian Embassy in Prague, Honorary Field Assistant to King Vittorio Emanuele III, Military Attaché at the Italian Embassy in Vienna, commander of the 7th Alpini Regiment, of the I Alpini Brigade, of the 47th Infantry Division "Bari", of the 132nd Armored Division "Ariete", and of the V Army Corps of Trieste. During the Second World War he was commander of the I and XX Army Corps, and of the 11th Army stationed in Greece, with headquarters in Athens. After the proclamation of the Armistice of Cassibile of 8 September 1943, after receiving ambiguous instructions from the Supreme Command, on the morning of 9 September 1943 he gave the order to surrender all heavy weapons to the Germans, in exchange for the latter's commitment to repatriate the Army. The Germans, howe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armistice Between Italy And Allied Armed Forces
The Armistice of Cassibile was an armistice signed on 3 September 1943 and made public on 8 September between the Kingdom of Italy and the Allies during World War II. It was signed by Major General Walter Bedell Smith for the Allies and Brigade General Giuseppe Castellano for Italy at a conference of generals from both sides in an Allied military camp at Cassibile, in Sicily, which had recently been occupied by the Allies. The armistice was approved by both the Italian King Victor Emmanuel III and Marshal Badoglio, the Prime Minister of Italy at the time. Germany moved rapidly by freeing Benito Mussolini (12 September) and attacking Italian forces in Italy (8–19 September), southern France and the Balkans. The Italian forces were quickly defeated, and most of Italy was occupied by German troops, who established a puppet state, the Italian Social Republic. The king, the Italian government, and most of the navy escaped to territories occupied by the Allies. Background Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunisia Campaign
The Tunisian campaign (also known as the Battle of Tunisia) was a series of battles that took place in Tunisia during the North African campaign of the World War II, Second World War, between Axis powers, Axis and Allies of World War II, Allied forces from 17 November 1942 to 13 May 1943. The Allies consisted of British Empire, British Imperial Forces, including a Sacred Band (World War II), Greek contingent, with United States, American and Military history of France during World War II, French corps. The battle opened with initial success by the Nazi Germany, German and Fascist Italy (1922–1943), Italian forces but the massive supply interdiction efforts led to the decisive defeat of the Axis. Over 250,000 Wehrmacht, German and Royal Italian Army during World War II, Italian troops were taken as Prisoner of war, prisoners of war, including most of the Afrika Korps. Background Western Desert The first two years of the North African campaign, war in North Africa were charact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Cross
The Iron Cross (german: link=no, Eisernes Kreuz, , abbreviated EK) was a military decoration in the Kingdom of Prussia, and later in the German Empire (1871–1918) and Nazi Germany (1933–1945). King Frederick William III of Prussia established it on 17 March 1813 during the Napoleonic Wars (EK 1813). The award was backdated to the birthday (10 March) of his late wife, Queen Louise. Louise was the first person to receive this decoration (posthumously). Recommissioned Iron Cross was also awarded during the Franco-Prussian War (EK 1870), World War I (EK 1914), and World War II (EK 1939). During the 1930s and World War II, the Nazi regime superimposed a swastika on the traditional medal. The Iron Cross was usually a military decoration only, though there were instances awarded to civilians for performing military functions, including Hanna Reitsch, who received the Iron Cross, 2nd class, and Iron Cross, 1st Class, and Melitta Schenk Gräfin von Stauffenberg, who received ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Front (World War II)
The Eastern Front of World War II was a Theater (warfare), theatre of conflict between the European Axis powers against the Soviet Union (USSR), Polish Armed Forces in the East, Poland and other Allies of World War II, Allies, which encompassed Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Northern Europe, Northeast Europe (Baltic states, Baltics), and Southeast Europe (Balkans) from 22 June 1941 to 9 May 1945. It was known as the Great Patriotic War (term), Great Patriotic War in the Soviet Union – and still is in some of its successor states, while almost everywhere else it has been called the ''Eastern Front''. In present-day German and Ukrainian historiography the name German-Soviet War is typically used. The battles on the Eastern Front of the Second World War constituted the largest military confrontation in history. They were characterised by unprecedented ferocity and brutality, wholesale destruction, mass deportations, and immense loss of life due to combat, starvation, expos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corfu
Corfu (, ) or Kerkyra ( el, Κέρκυρα, Kérkyra, , ; ; la, Corcyra.) is a Greek island in the Ionian Sea, of the Ionian Islands, and, including its small satellite islands, forms the margin of the northwestern frontier of Greece. The island is part of the Corfu regional unit, and is administered by three municipalities with the islands of Othonoi, Ereikoussa, and Mathraki.https://corfutvnews.gr/diaspasi-deite-tin-tropologia/ The principal city of the island (pop. 32,095) is also named Corfu. Corfu is home to the Ionian University. The island is bound up with the history of Greece from the beginnings of Greek mythology, and is marked by numerous battles and conquests. Ancient Korkyra took part in the Battle of Sybota which was a catalyst for the Peloponnesian War, and, according to Thucydides, the largest naval battle between Greek city states until that time. Thucydides also reports that Korkyra was one of the three great naval powers of fifth century BC Greece, alo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
33 Infantry Division Acqui
33 may refer to: *33 (number) 33 (thirty-three) is the natural number following 32 and preceding 34. In mathematics 33 is: * the largest positive integer that cannot be expressed as a sum of different triangular numbers. * the smallest odd repdigit that is not a prime n ... *33 BC *AD 33 *1933 *2033 Music *33 (Luis Miguel album), ''33'' (Luis Miguel album) (2003) *33 (Southpacific album), ''33'' (Southpacific album) (1998) *33 (Wanessa album), ''33'' (Wanessa album) (2016) *"33 'GOD'", a 2016 song by Bon Iver *Thirty-Three (song), "Thirty-Three" (song), a 1995 song by the Smashing Pumpkins *"Thirty Three", a song by Karma to Burn from the album ''Almost Heathen'', 2001 *"33", a 2002 song by Coheed and Cambria *"33" a 2020 song by Polo G Television *El 33, a Catalan television channel *33 (Battlestar Galactica), "33" (''Battlestar Galactica''), an episode of ''Battlestar Galactica'' Other uses *Los 33, the miners involved in the 2010 Copiapó mining accident **''The 33'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
