|
Mass Deacidification
Mass deacidification is a term used in library and information science as one possible measure against the degradation of paper in old books, the so-called "slow fires". The goal of the process is to increase the pH of acidic paper. Although acid-free paper has become more common, a large body of acidic paper still exists in books made after the 1850s; this is because of its cheaper and simpler production methods. Acidic paper, especially when exposed to light, air pollution, or high relative humidity, yellows and becomes brittle over time. During mass deacidification an alkaline agent is deposited in the paper to neutralize existing acid and prevent further decay. Mass deacidification is intended for objects on acidic paper that will be lost if no action is performed. History of research and process development Mass deacidification — along with microfilm and lamination — was developed during the early and mid-20th century as a response to the chemical process of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Library And Information Science
Library and information science(s) or studies (LIS) is an interdisciplinary field of study that deals generally with organization, access, collection, and protection/regulation of information, whether in physical (e.g. art, legal proceedings, etc.) or digital forms. In spite of various trends to merge the two fields, some consider the two original disciplines, library science and information science, to be separate. However, it is common today to use the terms synonymously or to drop the term "library" and to speak about ''information departments'' or ''I-schools''. There have also been attempts to revive the concept of documentation and to speak of Library, information and documentation studies (or science). History By the late 1960s, mainly due to the meteoric rise of human computing power and the new academic disciplines formed therefrom, academic institutions began to add the term "information science" to their names. The first school to do this was at the University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholson Baker
Nicholson Baker (born January 7, 1957) is an American novelist and essayist. His fiction generally de-emphasizes narrative in favor of careful description and characterization. His early novels such as ''The Mezzanine'' and ''Room Temperature'' were distinguished by their minute inspection of his characters' and narrators' stream of consciousness. Out of a total of ten novels, three are erotica: '' Vox'', '' The Fermata'' and '' House of Holes''. Baker also writes non-fiction books. '' U and I: A True Story'', about his relationship with John Updike, was published in 1991. He then wrote about the American library system in his 2001 book '' Double Fold: Libraries and the Assault on Paper'', for which he received a National Book Critics Circle Award and the Calw Hermann Hesse Prize for the German translation. A pacifist, he wrote '' Human Smoke'' (2008) about the buildup to World War II. Baker has published articles in ''Harper's Magazine'', the ''London Review of Books'' and ''Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preservation Survey
Preservation survey (also known as condition survey, conservation needs survey or preservation assessment) is the process of collecting and analyzing data about the physical condition of library materials. Preservation surveys are used by libraries to determine the condition of their collections and identify necessary actions for preserving, conserving or repairing materials. They are most often conducted at research and university libraries. Preservation surveys are often the first step when planning and implementing a preservation program in a library. By collecting data and compiling statistics about a collection’s condition, library staff can determine environmental threats and preservation needs. It is also possible to use the resulting data to predict future deterioration. Since preservation needs usually well exceed an institution’s resources, the data acquired in an assessment can aid libraries in establishing priorities in regard to deteriorating materials. As Ross ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulp (paper)
Pulp is a lignocellulosic fibrous material prepared by chemically or mechanically separating cellulose fibers from wood, fiber crops, waste paper, or rags. Mixed with water and other chemical or plant-based additives, pulp is the major raw material used in papermaking and the industrial production of other paper products. History Before the widely acknowledged invention of papermaking by Cai Lun in China around 105 AD, paper-like writing materials such as papyrus and amate were produced by ancient civilizations using plant materials which were largely unprocessed. Strips of bark or bast material were woven together, beaten into rough sheets, dried, and polished by hand. Pulp used in modern and traditional papermaking is distinguished by the process which produces a finer, more regular slurry of cellulose fibers which are pulled out of solution by a screen and dried to form sheets or rolls. The earliest paper produced in China consisted of bast fibers from the paper mulberr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paper
Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, rags, grasses or other vegetable sources in water, draining the water through fine mesh leaving the fibre evenly distributed on the surface, followed by pressing and drying. Although paper was originally made in single sheets by hand, almost all is now made on large machines—some making reels 10 metres wide, running at 2,000 metres per minute and up to 600,000 tonnes a year. It is a versatile material with many uses, including printing, painting, graphics, signage, design, packaging, decorating, writing, and cleaning. It may also be used as filter paper, wallpaper, book endpaper, conservation paper, laminated worktops, toilet tissue, or currency and security paper, or in a number of industrial and construction processes. The papermaking process developed in east Asia, probably China, at least as early as 105 CE, by the Han court eunuch Cai Lun, although the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preservation (library And Archival Science)
In Library science, library and archival science, preservation is a set of preventive conservation activities aimed at prolonging the life of a record, book, or object while making as few changes as possible. Preservation activities vary widely and may include monitoring the condition of items, maintaining the temperature and humidity in collection storage areas, writing a plan in case of emergencies, digitizing items, writing relevant metadata, and increasing accessibility. Preservation, in this definition, is practiced in a library or an archive by a librarian, archivist, or other professional when they perceive a record is in need of maintenance. Preservation should be distinguished from interventive Conservation and restoration of books, manuscripts, documents and ephemera, conservation and restoration, which refers to the treatment and repair of individual items to slow the process of decay, or restore them to a usable state. Preventive conservation is occasionally used int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harry Ransom Humanities Research Center
The Harry Ransom Center (until 1983 the Humanities Research Center) is an archive, library and museum at the University of Texas at Austin, specializing in the collection of literary and cultural artifacts from the Americas and Europe for the purpose of advancing the study of the arts and humanities. The Ransom Center houses 36 million literary manuscripts, one million rare books, five million photographs, and more than 100,000 works of art. The center has a reading room for scholars and galleries which display rotating exhibitions of works and objects from the collections. In the 2015–16 academic year, the center hosted nearly 6,000 research visits resulting in the publication of over 145 books. History Harry Ransom founded the Humanities Research Center in 1957 with the ambition of expanding the rare books and manuscript holdings of the University of Texas. He acquired the Edward Alexander Parsons Collection, the T. Edward Hanley Collection, and the Norman Bel Geddes Collect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Archives And Records Administration
The National Archives and Records Administration (NARA) is an " independent federal agency of the United States government within the executive branch", charged with the preservation and documentation of government and historical records. It is also tasked with increasing public access to those documents which make up the National Archive. NARA is officially responsible for maintaining and publishing the legally authentic and authoritative copies of acts of Congress, presidential directives, and federal regulations. NARA also transmits votes of the Electoral College to Congress. It also examines Electoral College and Constitutional amendment ratification documents for prima facie legal sufficiency and an authenticating signature. The National Archives, and its publicly exhibited Charters of Freedom, which include the original United States Declaration of Independence, United States Constitution, United States Bill of Rights, and many other historical documents, is headquarte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesium Oxide
Magnesium oxide ( Mg O), or magnesia, is a white hygroscopic solid mineral that occurs naturally as periclase and is a source of magnesium (see also oxide). It has an empirical formula of MgO and consists of a lattice of Mg2+ ions and O2− ions held together by ionic bonding. Magnesium hydroxide forms in the presence of water (MgO + H2O → Mg(OH)2), but it can be reversed by heating it to remove moisture. Magnesium oxide was historically known as magnesia alba (literally, the white mineral from Magnesia), to differentiate it from ''magnesia negra'', a black mineral containing what is now known as manganese. Related oxides While "magnesium oxide" normally refers to MgO, the compound magnesium peroxide MgO2 is also known. According to evolutionary crystal structure prediction, MgO2 is thermodynamically stable at pressures above 116 GPa (gigapascals), and a semiconducting suboxide Mg3O2 is thermodynamically stable above 500 GPa. Because of its stability, MgO is used as a model sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aqueous Solution
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, or sodium chloride (NaCl), in water would be represented as . The word ''aqueous'' (which comes from ''aqua'') means pertaining to, related to, similar to, or dissolved in, water. As water is an excellent solvent and is also naturally abundant, it is a ubiquitous solvent in chemistry. Since water is frequently used as the solvent in experiments, the word solution refers to an aqueous solution, unless the solvent is specified. A ''non-aqueous solution'' is a solution in which the solvent is a liquid, but is not water. (See also Solvent and Inorganic nonaqueous solvent.) Characteristics Substances that are ''hydrophobic'' ('water-fearing') do not dissolve well in water, whereas those that are ''hydrophilic'' ('water-friendly') do. An example of a hydrophilic substance is sodium chlo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
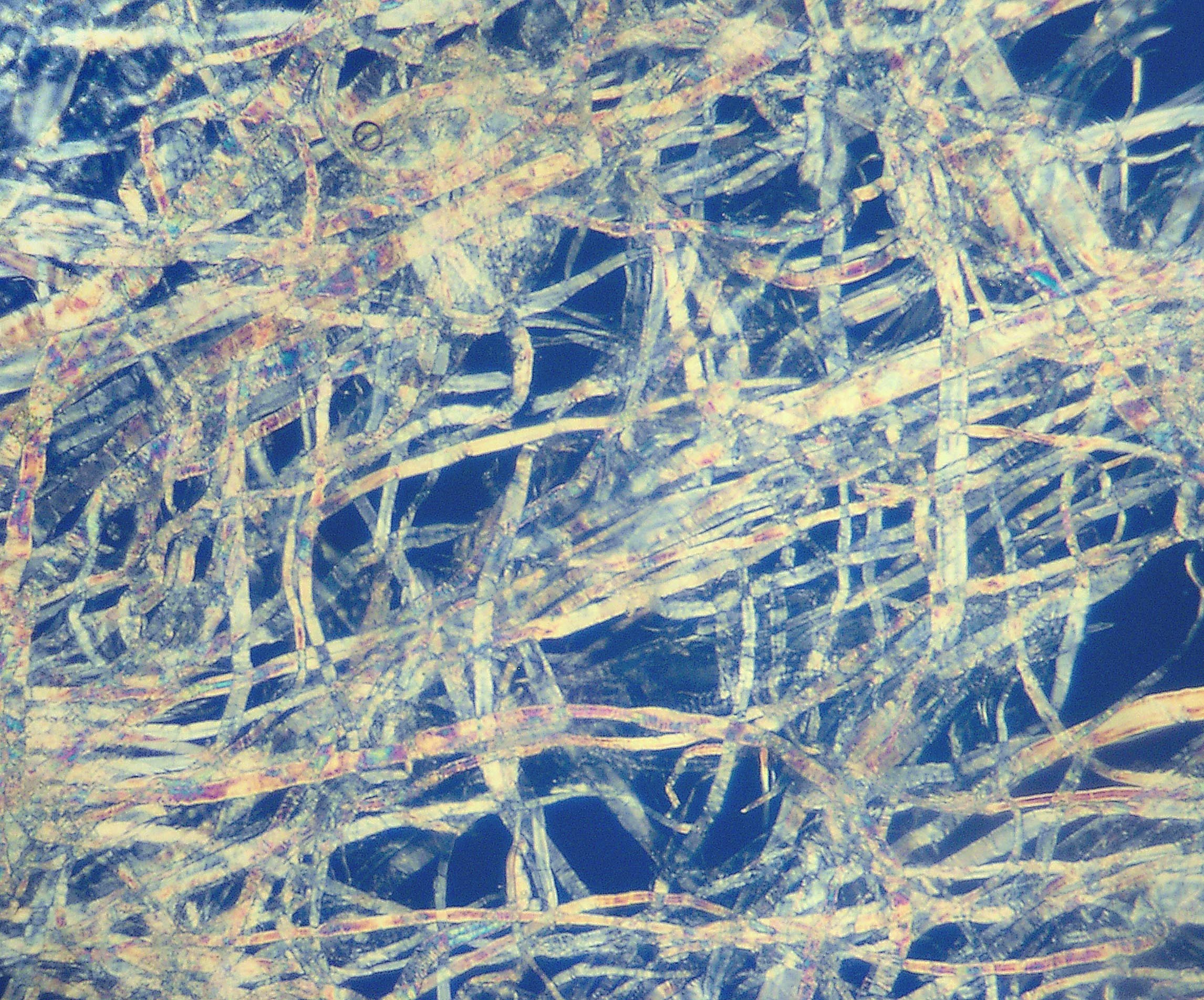
Newton's Rings
Newton's rings is a phenomenon in which an interference pattern is created by the reflection of light between two surfaces, typically a spherical surface and an adjacent touching flat surface. It is named after Isaac Newton, who investigated the effect in 1666. When viewed with monochromatic light, Newton's rings appear as a series of concentric, alternating bright and dark rings centered at the point of contact between the two surfaces. When viewed with white light, it forms a concentric ring pattern of rainbow colors because the different wavelengths of light interfere at different thicknesses of the air layer between the surfaces. History The phenomenon was first described by Robert Hooke in his 1665 book ''Micrographia''. Its name derives from the mathematician and physicist Sir Isaac Newton, who studied the phenomenon in 1666 while sequestered at home in Lincolnshire in the time of the Great Plague that had shut down Trinity College, Cambridge. He recorded his observations in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovak University Of Technology In Bratislava
Slovak University of Technology in Bratislava (STU) ( sk, Slovenská technická univerzita v Bratislave) is the biggest and oldest university of technology in Slovakia. In the 2012 Academic Ranking of World Universities it was ranked in the first 150 in Computer Science, the only university in central Europe in the first 200. However, it lost this position in the two following years. University structure * Faculty of Civil Engineering * Faculty of Mechanical Engineering * Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Information Technology * Faculty of Chemical and Food Technology * Faculty of Architecture and Design * Faculty of Materials Science and Technology (in Trnava) * Faculty of Informatics and Information Technologies * Institute of Management * Institute of Engineering Studies European Alliance for Innovation The Slovak University of Technology in Bratislava signed a Memorandum of Understandinghttp://www.stuba.sk/sk/vyskume/europska-aliancia-pre-inovacie-na-stu.html?pag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |