|
Masculinization
Virilization or masculinization is the biological development of adult male characteristics in young males or females. Most of the changes of virilization are produced by androgens. Virilization is most commonly used in three medical and biology of sex contexts: prenatal biological sexual differentiation, the postnatal changes of typical chromosomal male (46, XY) puberty, and excessive androgen effects in typical chromosomal females (46, XX). It is also the intended result of androgen replacement therapy in males with delayed puberty and low testosterone. Prenatal virilization In the prenatal period, virilization refers to closure of the perineum, thinning and wrinkling (rugation) of the scrotum, growth of the penis, and closure of the urethral groove to the tip of the penis. In this context, ''masculinization'' is synonymous with ''virilization.'' Prenatal virilization of genetic females and undervirilization of genetic males are common causes of ambiguous genitalia and inters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progestin-induced Virilisation
Maternal use of androgens or high doses of certain weakly androgenic synthetic progestogens (progestins) structurally related to testosterone can masculinize (virilize) the external genitalia of a female fetus during susceptible times in pregnancy. Some degree of fusion of the labioscrotal folds and urogenital folds and clitoral enlargement can occur if exposure occurs from the 8th through the 12th week of gestation, but only clitoral enlargement can occur if exposure occurs after the 12th week. This can in some cases result in ambiguous genitalia. Fetal masculinization of female external genitalia is usually due to enzyme abnormalities involved in adrenal steroid biosynthesis, resulting in congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH); fetal masculinization of female external genitalia is much less frequently due to maternal use of androgenic steroids. Fetal masculinization of female external genitalia due to maternal use of androgenic steroids is generally less advanced than that due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome
Androgen insensitivity syndrome (AIS) is a difference in sex development involving hormonal resistance due to androgen receptor dysfunction. It affects 1 in 20,000 to 64,000 XY (karyotype, karyotypically male) births. The condition results in the partial or complete inability of Animal cell, cells to respond to androgens. This unresponsiveness can impair or prevent the Development of the reproductive system, development of male genitals, as well as impairing or preventing the development of male Secondary sex characteristics, secondary sexual characteristics at puberty. It does not significantly impair female genital or sexual development. The insensitivity to androgens is therefore clinically significant only when it occurs in genetic males, (i.e. individuals with a Y chromosome, Y-chromosome, or more specifically, an SRY, SRY gene). Clinical phenotypes in these individuals range from a typical body shape, male habitus with mild spermatogenesis, spermatogenic defect or reduced sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clitoris
The clitoris ( or ) is a female sex organ present in mammals, ostriches and a limited number of other animals. In humans, the visible portion – the glans – is at the front junction of the labia minora (inner lips), above the opening of the urethra. Unlike the penis, the male homologue (equivalent) to the clitoris, it usually does not contain the distal portion (or opening) of the urethra and is therefore not used for urination. In most species, the clitoris lacks any reproductive function. While few animals urinate through the clitoris or use it reproductively, the spotted hyena, which has an especially large clitoris, urinates, mates, and gives birth via the organ. Some other mammals, such as lemurs and spider monkeys, also have a large clitoris. The clitoris is the human female's most sensitive erogenous zone and generally the primary anatomical source of human female sexual pleasure. In humans and other mammals, it develops from an outgrowth in the em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perineum
The perineum in humans is the space between the anus and scrotum in the male, or between the anus and the vulva in the female. The perineum is the region of the body between the pubic symphysis (pubic arch) and the coccyx (tail bone), including the perineal body and surrounding structures. There is some variability in how the boundaries are defined. The perineal raphe is visible and pronounced to varying degrees. The perineum is an erogenous zone. The word perineum entered English from late Latin via Greek περίναιος ~ περίνεος ''perinaios, perineos'', itself from περίνεος, περίνεοι 'male genitals' and earlier περίς ''perís'' 'penis' through influence from πηρίς ''pērís'' 'scrotum'. The term was originally understood as a purely male body-part with the perineal raphe seen as a continuation of the scrotal septum since masculinization causes the development of a large anogenital distance in men, in comparison to the correspond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning "man") is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This includes the embryological development of the primary male sex organs, and the development of male secondary sex characteristics at puberty. Androgens are synthesized in the testes, the ovaries, and the adrenal glands. Androgens increase in both males and females during puberty. The major androgen in males is testosterone. Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and androstenedione are of equal importance in male development. DHT ''in utero'' causes differentiation of the penis, scrotum and prostate. In adulthood, DHT contributes to balding, prostate growth, and sebaceous gland activity. Although androgens are commonly thought of only as male sex hormones, females also have them, but at lower levels: they function in libido and sexual arousal. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voice Change
' A voice change or voice mutation, sometimes referred to as a voice break or voice crack, commonly refers to the deepening of the voice of men as they reach puberty. Before puberty, both sexes have roughly similar vocal pitch, but during puberty the male voice typically deepens an octave, while the female voice usually deepens only by a few tones. A similar effect is a "voice crack", during which a person's voice suddenly and unintentionally enters a higher register (usually falsetto) for a brief period of time. This may be caused by singing or talking at a pitch outside the person's natural vocal range, stress, fatigue, emotional tension, or the physical changes associated with puberty. An instance of a voice crack (when associated with puberty) lasts for only a moment and generally occurs less frequently as a person grows into maturity. Anatomical changes Most of the voice change begins around puberty. Adult pitch is reached 2–3 years later but the voice does not stabiliz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
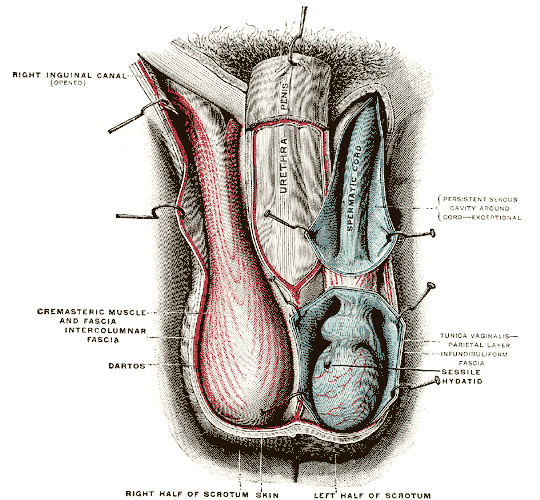
Scrotum
The scrotum or scrotal sac is an anatomical male reproductive structure located at the base of the penis that consists of a suspended dual-chambered sac of skin and smooth muscle. It is present in most terrestrial male mammals. The scrotum contains the external spermatic fascia, testes, epididymis, and ductus deferens. It is a distention of the perineum and carries some abdominal tissues into its cavity including the testicular artery, testicular vein, and pampiniform plexus. The perineal raphe is a small, vertical, slightly raised ridge of scrotal skin under which is found the scrotal septum. It appears as a thin longitudinal line that runs front to back over the entire scrotum. In humans and some other mammals the scrotum becomes covered with pubic hair at puberty. The scrotum will usually tighten during penile erection and when exposed to cold temperatures. One testis is typically lower than the other to avoid compression in the event of an impact. The scrotum is bio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambiguous Genitalia
Intersex people are individuals born with any of several sex characteristics including chromosome patterns, gonads, or genitals that, according to the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights, "do not fit typical binary notions of male or female bodies". Sex assignment at birth usually aligns with a child's anatomical sex and phenotype. The number of births with ambiguous genitals is in the range of 1:2000–1:4500 (0.022%–0.05%). Other conditions involve atypical chromosomes, gonads, or hormones. Some persons may be assigned and raised as a girl or boy but then identify with another gender later in life, while most continue to identify with their assigned sex. The number of births where the baby is intersex has been reported differently depending on who reports and which definition of intersex is used. Anne Fausto-Sterling and her co-authors suggest that the prevalence of "nondimorphic sexual development" might be as high as 1.7%. A study publishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intersex
Intersex people are individuals born with any of several sex characteristics including chromosome patterns, gonads, or genitals that, according to the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights, "do not fit typical binary notions of male or female bodies". Sex assignment at birth usually aligns with a child's anatomical sex and phenotype. The number of births with ambiguous genitals is in the range of 1:2000–1:4500 (0.022%–0.05%). Other conditions involve atypical chromosomes, gonads, or hormones. Some persons may be assigned and raised as a girl or boy but then identify with another gender later in life, while most continue to identify with their assigned sex. The number of births where the baby is intersex has been reported differently depending on who reports and which definition of intersex is used. Anne Fausto-Sterling and her co-authors suggest that the prevalence of "nondimorphic sexual development" might be as high as 1.7%. A study publi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Testosterone
Hypogonadism means diminished functional activity of the gonads—the testes or the ovaries—that may result in diminished production of sex hormones. Low androgen (e.g., testosterone) levels are referred to as hypoandrogenism and low estrogen (e.g., estradiol) as hypoestrogenism. These are responsible for the observed signs and symptoms in both males and females. Hypogonadism, commonly referred to by the symptom "low testosterone" or "Low T", can also decrease other hormones secreted by the gonads including progesterone, DHEA, anti-Müllerian hormone, activin, and inhibin. Sperm development (spermatogenesis) and release of the egg from the ovaries (ovulation) may be impaired by hypogonadism, which, depending on the degree of severity, may result in partial or complete infertility. In January 2020, the American College of Physicians issued clinical guidelines for testosterone treatment in adult men with age-related low levels of testosterone. The guidelines are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Sexual Differentiation
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary information encoded in genes, which can be transmitted to future generations. Another major theme is evolution, which explains the unity and diversity of life. Energy processing is also important to life as it allows organisms to move, grow, and reproduce. Finally, all organisms are able to regulate their own internal environments. Biologists are able to study life at multiple levels of organization, from the molecular biology of a cell to the anatomy and physiology of plants and animals, and evolution of populations.Based on definition from: Hence, there are multiple subdisciplines within biology, each defined by the nature of their research questions and the tools that they use. Like other scientists, biologists use the scientific met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)