|
Magnetic Field Imaging
Magnetic Field Imaging (MFI) is a non-invasive and side-effect-free cardiac diagnostic method. In more recent technology, magnetocardiography (MCG) has become the clinically predominant application for recording the heart's magnetic signals. that detects and records the electromagnetic signals that are associated with the heartbeat using a multi-channel magnetic sensor array. The electric signals are known from the ECG. In the 1990s and beyond, more recent technology has supplanted the MFI, particularly MCG (xref. Cardiomag Imaging, Inc.). Through clinical research in Europe, Asia, and the U.S. (see publications in footnotes), MCG has been proven to have practical application for diagnosis of cardiac disease, and has become the clinically predominant application for recording the heart's magnetic signals. In comparison to MCG, MFI, among others, records the whole relevant area above the chest of the person. Background The general principal of MFI is based on two facts: *Cell ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiology
Cardiology () is a branch of medicine that deals with disorders of the heart and the cardiovascular system. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease and electrophysiology. Physicians who specialize in this field of medicine are called cardiologists, a specialty of internal medicine. Pediatric cardiologists are pediatricians who specialize in cardiology. Physicians who specialize in cardiac surgery are called cardiothoracic surgeons or cardiac surgeons, a specialty of general surgery. Specializations All cardiologists study the disorders of the heart, but the study of adult and child heart disorders each require different training pathways. Therefore, an adult cardiologist (often simply called "cardiologist") is inadequately trained to take care of children, and pediatric cardiologists are not trained to treat adult heart disease. Surgical aspects are not included in cardiology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetocardiography
Magnetocardiography (MCG) is a technique to measure the magnetic fields produced by electrical currents in the heart using extremely sensitive devices such as the superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID). If the magnetic field is measured using a multichannel device, a map of the magnetic field is obtained over the chest; from such a map, using mathematical algorithms that take into account the conductivity structure of the torso, it is possible to locate the source of the activity. For example, sources of abnormal rhythms or arrhythmia may be located using MCG. History The first MCG measurements were made by Baule and McFee using two large coils placed over the chest, connected in opposition to cancel out the relatively large magnetic background. Heart signals were indeed seen, but were very noisy. The next development was by David Cohen, who used a magnetically shielded room to reduce the background, and a smaller coil with better electronics; the heart signals we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Sensor
A magnetometer is a device that measures magnetic field or magnetic dipole moment. Different types of magnetometers measure the direction, strength, or relative change of a magnetic field at a particular location. A compass is one such device, one that measures the direction of an ambient magnetic field, in this case, the Earth's magnetic field. Other magnetometers measure the magnetic dipole moment of a magnetic material such as a ferromagnet, for example by recording the effect of this magnetic dipole on the induced current in a coil. The first magnetometer capable of measuring the absolute magnetic intensity at a point in space was invented by Carl Friedrich Gauss in 1833 and notable developments in the 19th century included the Hall effect, which is still widely used. Magnetometers are widely used for measuring the Earth's magnetic field, in geophysical surveys, to detect magnetic anomalies of various types, and to determine the dipole moment of magnetic materials. In an airc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galvani
Luigi Galvani (, also ; ; la, Aloysius Galvanus; 9 September 1737 – 4 December 1798) was an Italian physician, physicist, biologist and philosopher, who studied animal electricity. In 1780, he discovered that the muscles of dead frogs' legs twitched when struck by an electrical spark. This was an early study of bioelectricity, following experiments by John Walsh and Hugh Williamson. Early life Luigi Galvani was born to Domenico Galvani and Barbara Caterina Foschi, in Bologna, then part of the Papal States. Domenico was a goldsmith. Galvani then began taking an interest in the field of "medical electricity". This field emerged in the middle of the 18th century, following electrical researches and the discovery of the effects of electricity on the human body by scientists including Bertrand Bajon and Ramón M. Termeyer in the 1760s, and by John Walsh and Hugh Williamson in the 1770s. Galvani vs. Volta Alessandro Volta, a professor of experimental physics in the Univ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Christian Ørsted
Hans Christian Ørsted ( , ; often rendered Oersted in English; 14 August 17779 March 1851) was a Danish physicist and chemist who discovered that electric currents create magnetic fields, which was the first connection found between electricity and magnetism. Oersted's law and the oersted unit (Oe) are named after him. A leader of the Danish Golden Age, Ørsted was a close friend of Hans Christian Andersen and the brother of politician and jurist Anders Sandøe Ørsted, who served as Prime Minister of Denmark from 1853 to 1854. Early life and studies Ørsted was born in Rudkøbing in 1777. As a young boy he developed an interest in science while working for his father, who owned the local pharmacy. He and his brother Anders received most of their early education through self-study at home, going to Copenhagen in 1793 to take entrance exams for the University of Copenhagen, where both brothers excelled academically. By 1796, Ørsted had been awarded honors for his papers in bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Wikswo
John Peter Wikswo, Jr. (born October 6, 1949) is a biological physicist at Vanderbilt University. He was born in Lynchburg, Virginia, United States. Wikswo is noted for his work on biomagnetism and cardiac electrophysiology. Graduate school In the 1970s, Wikswo was a graduate student at Stanford University, where he worked under physicist William M. Fairbank, studying magnetocardiography. Biomagnetism In 1977 he became an assistant professor in the Department of Physics and Astronomy at Vanderbilt University, where he set up a laboratory to study living state physics. In 1980, he made the first measurement of the magnetic field of an isolated nerve, by threading the a frog sciatic nerve through a wire-wound, ferrite-core toroid and detecting the induced current using a SQUID magnetometer. At the same time, Wikswo and Ken Swinney calculated the magnetic field of a nerve axon. This work was followed a few years later by the first detailed comparison of the measured a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SQUID
True squid are molluscs with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fitting these criteria. Like all other cephalopods, squid have a distinct head, bilateral symmetry, and a mantle. They are mainly soft-bodied, like octopuses, but have a small internal skeleton in the form of a rod-like gladius (cephalopod), gladius or pen, made of chitin. Squid diverged from other cephalopods during the Jurassic and occupy a similar role to teleost fish as open water predators of similar size and behaviour. They play an important role in the open water food web. The two long tentacles are used to grab prey and the eight arms to hold and control it. The beak then cuts the food into suitable size chunks for swallowing. Squid are rapid swimmers, moving by Aquatic locomotion#Jet propulsion, jet propulsion, and largely locate their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
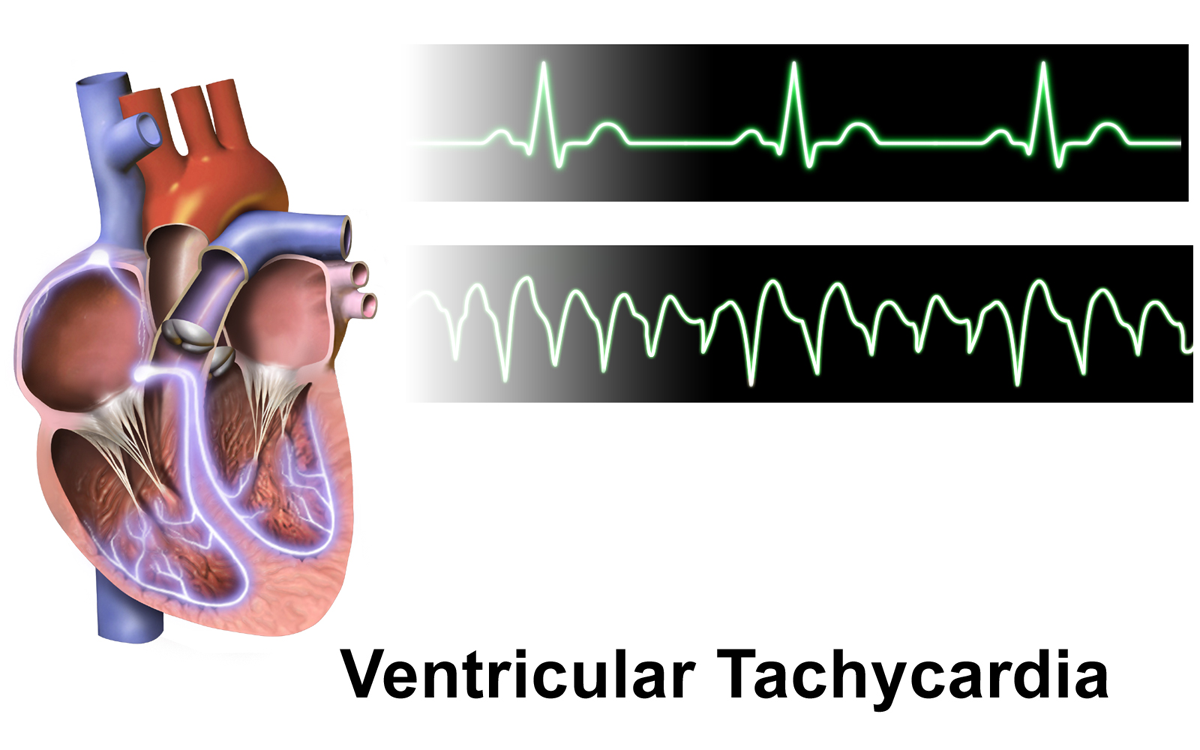
Ventricular Tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia (V-tach or VT) is a fast heart rate arising from the lower chambers of the heart. Although a few seconds of VT may not result in permanent problems, longer periods are dangerous; and multiple episodes over a short period of time are referred to as an electrical storm. Short periods may occur without symptoms, or present with lightheadedness, palpitations, or chest pain. Ventricular tachycardia may result in ventricular fibrillation (VF) and turn into cardiac arrest. This conversion of the VT into VF is called the degeneration of the VT. It is found initially in about 7% of people in cardiac arrest. Ventricular tachycardia can occur due to coronary heart disease, aortic stenosis, cardiomyopathy, electrolyte problems, or a heart attack. Diagnosis is by an electrocardiogram (ECG) showing a rate of greater than 120 beats per minute and at least three wide QRS complexes in a row. It is classified as non-sustained versus sustained based on whether it lasts le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrhythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, heart arrhythmias, or dysrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults – is called tachycardia, and a resting heart rate that is too slow – below 60 beats per minute – is called bradycardia. Some types of arrhythmias have no symptoms. Symptoms, when present, may include palpitations or feeling a pause between heartbeats. In more serious cases, there may be lightheadedness, passing out, shortness of breath or chest pain. While most cases of arrhythmia are not serious, some predispose a person to complications such as stroke or heart failure. Others may result in sudden death. Arrhythmias are often categorized into four groups: extra beats, supraventricular tachycardias, ventricular arrhythmias and bradyarrhythmias. Extra beats include premature atrial contractions, premature ventricular contract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ischemia
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems with blood vessels, with resultant damage to or dysfunction of tissue i.e. hypoxia and microvascular dysfunction. It also implies local hypoxia in a part of a body resulting from constriction (such as vasoconstriction, thrombosis, or embolism). Ischemia causes not only insufficiency of oxygen, but also reduced availability of nutrients and inadequate removal of metabolic wastes. Ischemia can be partial (poor perfusion) or total blockage. The inadequate delivery of oxygenated blood to the organs must be resolved either by treating the cause of the inadequate delivery or reducing the oxygen demand of the system that needs it. For example, patients with myocardial ischemia have a decreased blood flow to the heart and are prescribed with medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angina Pectoris
Angina, also known as angina pectoris, is chest pain or pressure, usually caused by insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardium). It is most commonly a symptom of coronary artery disease. Angina is typically the result of obstruction or spasm of the arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle. The main mechanism of coronary artery obstruction is atherosclerosis as part of coronary artery disease. Other causes of angina include abnormal heart rhythms, heart failure and, less commonly, anemia. The term derives from the Latin ''angere'' ("to strangle") and ''pectus'' ("chest"), and can therefore be translated as "a strangling feeling in the chest". There is a weak relationship between severity of angina and degree of oxygen deprivation in the heart muscle, however, the severity of angina does not always match the degree of oxygen deprivation to the heart or the risk of a myocardial infarction (heart attack). Some people may experience severe pain even though the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
.png)

