|
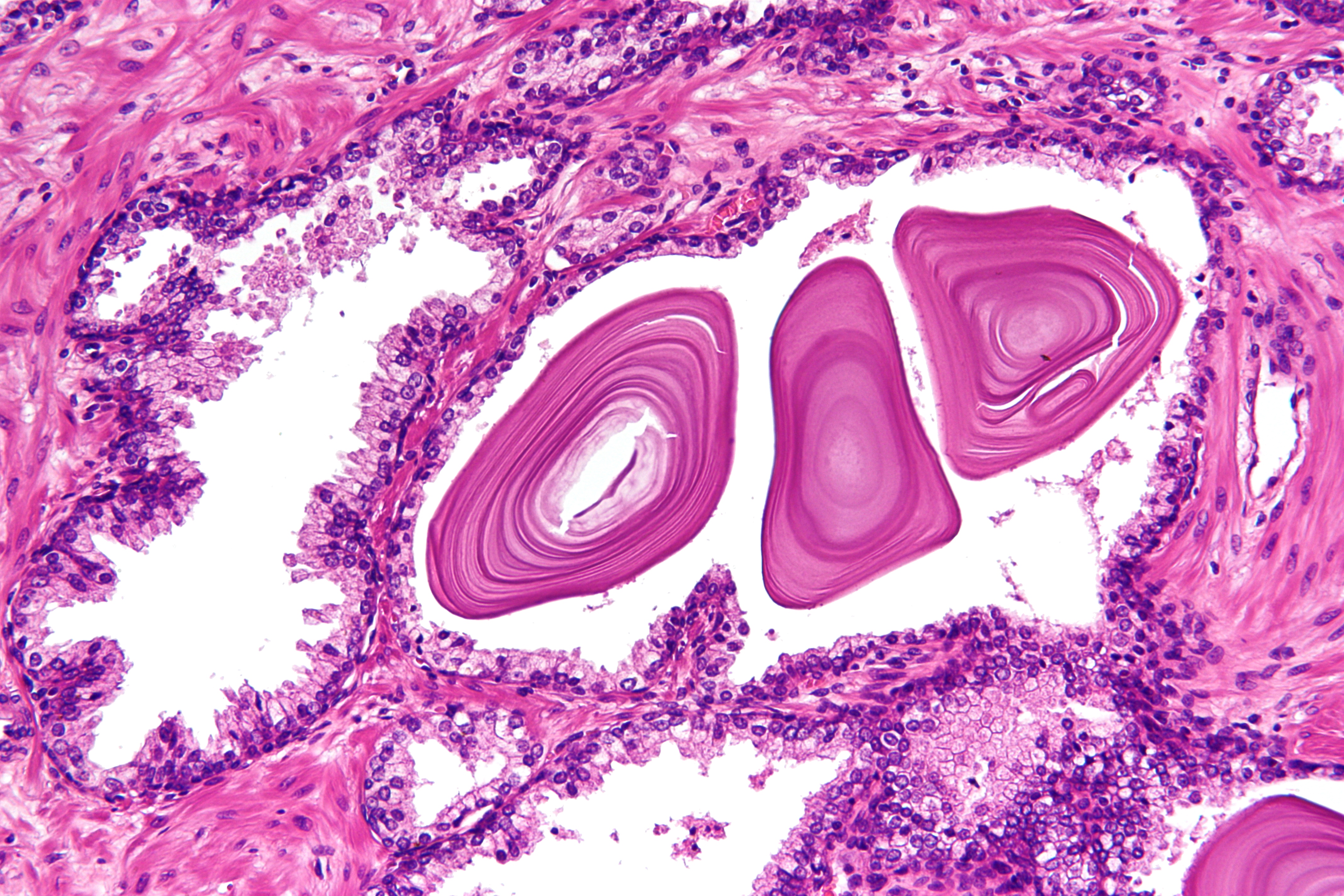
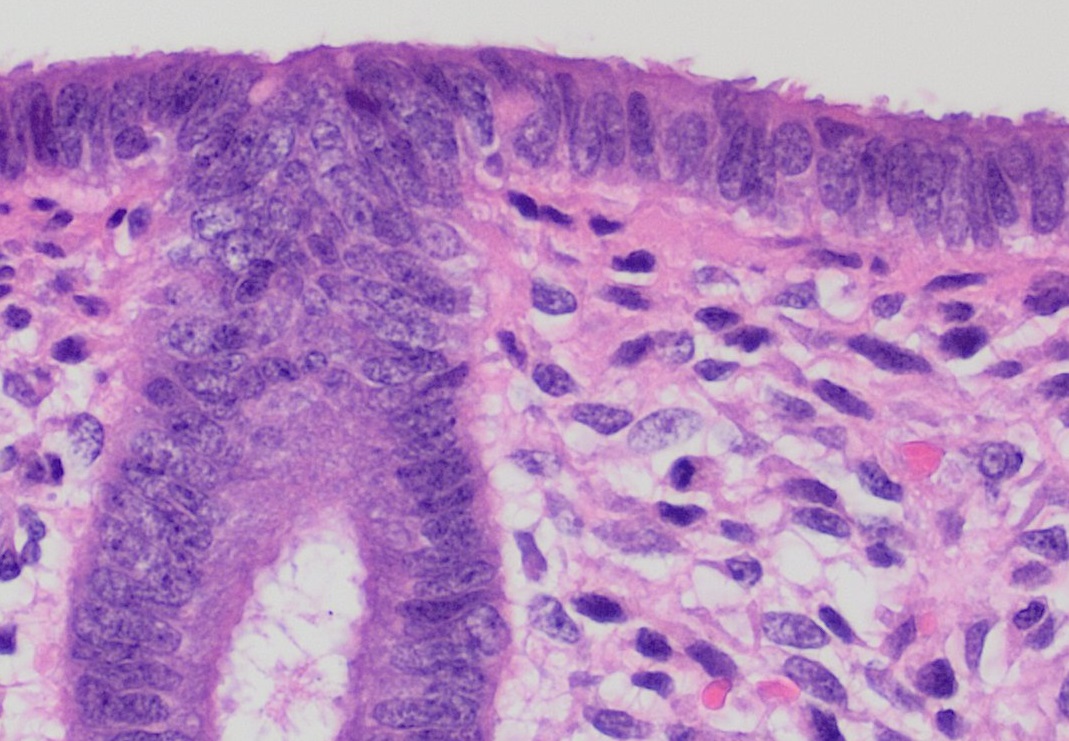
Lymphoepithelioma
Lymphoepithelioma is a type of poorly differentiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma characterized by prominent infiltration of lymphocytes in the area involved by tumor. Lymphoepithelioma is also known as "class III nasopharyngeal carcinoma" in the WHO classification system. It has a high tendency to metastasize and is responsive to radiotherapy. Most cases are associated with Epstein–Barr virus infection. Lymphoepithelioma-like carcinomas are carcinomas that arise outside of the nasopharynx, but resemble a lymphoepithelioma histologically. Lymphoepithelioma-like carcinomas may be found in almost any epithelial organ, including the lung, thymus, breast, colon, endometrium, prostate, and skin, as well as urinary bladder, trachea, esophagus, stomach, salivary glands, vulva.Juan Rosai. Rosai and Ackerman's Surgical Pathology. 9th edition History Lymphoepithelioma may also be referred to as Schmincke–Regaud tumor, after the German pathologist Alexander Schminke and French radiolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphoepithelioma-like Carcinoma
Lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma (LELC) is a medical term referring to a histological variant of malignant tumor arising from the uncontrolled mitosis of transformed cells originating in epithelial tissue (or in cells that display epithelial characteristics) that bear microscopic resemblance to lymphoepithelioma (nasopharyngeal carcinoma). There is considerable variation in the classification of LELC—while it is perhaps most commonly considered a subtype of squamous cell carcinoma, it can also be classified as a form of large cell carcinoma (i.e. when occurring in the lung), and can be considered as a separate, unique entity. In most anatomical sites, many cases are associated with the Epstein–Barr virus. In the breast, the macroscopic, microscopic, epidemiologic, and prognostic features of LELC are very similar to ''medullary carcinoma''; EBV status is one differentiator. See also *Nasopharyngeal carcinoma *Lymphoepithelioma Lymphoepithelioma is a type of poorly different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), or nasopharynx cancer, is the most common cancer originating in the nasopharynx, most commonly in the postero-lateral nasopharynx or pharyngeal recess ( fossa of Rosenmüller), accounting for 50% of cases. NPC occurs in children and adults. NPC differs significantly from other cancers of the head and neck in its occurrence, causes, clinical behavior, and treatment. It is vastly more common in certain regions of East Asia and Africa than elsewhere, with viral, dietary and genetic factors implicated in its causation. It is most common in males. It is a squamous cell carcinoma of an undifferentiated type. Squamous epithelial cells are a flat type of cell found in the skin and the membranes that line some body cavities. ''Undifferentiated cells'' are cells that do not have their mature features or functions. Signs and symptoms NPC may present as a lump or a mass on both sides towards the back of the neck. These lumps usually are not tender or pain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oncology
Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with the study, treatment, diagnosis and prevention of cancer. A medical professional who practices oncology is an ''oncologist''. The name's etymological origin is the Greek word ὄγκος (''ónkos''), meaning "tumor", "volume" or "mass". Oncology is concerned with: * The diagnosis of any cancer in a person (pathology) * Therapy (e.g. surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy and other modalities) * Follow-up of cancer patients after successful treatment * Palliative care of patients with terminal malignancies * Ethical questions surrounding cancer care * Screening efforts: ** of populations, or ** of the relatives of patients (in types of cancer that are thought to have a hereditary basis, such as breast cancer) Diagnosis Medical histories remain an important screening tool: the character of the complaints and nonspecific symptoms (such as fatigue, weight loss, unexplained anemia, fever of unknown origin, paraneoplastic phenome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colon (anatomy)
The large intestine, also known as the large bowel, is the last part of the gastrointestinal tract and of the digestive system in tetrapods. Water is absorbed here and the remaining waste material is stored in the rectum as feces before being removed by defecation. The colon is the longest portion of the large intestine, and the terms are often used interchangeably but most sources define the large intestine as the combination of the cecum, colon, rectum, and anal canal. Some other sources exclude the anal canal. In humans, the large intestine begins in the right iliac region of the pelvis, just at or below the waist, where it is joined to the end of the small intestine at the cecum, via the ileocecal valve. It then continues as the colon ascending the abdomen, across the width of the abdominal cavity as the transverse colon, and then descending to the rectum and its endpoint at the anal canal. Overall, in humans, the large intestine is about long, which is about one-fifth o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinoma
Carcinoma is a malignancy that develops from epithelial cells. Specifically, a carcinoma is a cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body, and that arises from cells originating in the endodermal, mesodermal or ectodermal germ layer during embryogenesis. Carcinomas occur when the DNA of a cell is damaged or altered and the cell begins to grow uncontrollably and become malignant. It is from the el, καρκίνωμα, translit=karkinoma, lit=sore, ulcer, cancer (itself derived from meaning ''crab''). Classification As of 2004, no simple and comprehensive classification system has been devised and accepted within the scientific community. Traditionally, however, malignancies have generally been classified into various types using a combination of criteria, including: The cell type from which they start; specifically: * Epithelial cells ⇨ carcinoma * Non-hematopoietic mesenchymal cells ⇨ sarcoma * Hematopoietic cells **Bone marrow-de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claude Regaud , a form of brainstem stroke syndrome
{{disambig, geo ...
Claude may refer to: __NOTOC__ People and fictional characters * Claude (given name), a list of people and fictional characters * Claude (surname), a list of people * Claude Lorrain (c. 1600–1682), French landscape painter, draughtsman and etcher traditionally called just "Claude" in English * Madame Claude, French brothel keeper Fernande Grudet (1923–2015) Places * Claude, Texas, a city * Claude, West Virginia, an unincorporated community Other uses * Allied reporting name of the Mitsubishi A5M Japanese carrier-based fighter aircraft * Claude (alligator), an albino alligator at the California Academy of Sciences See also * Claude's syndrome Claude's syndrome is a form of brainstem stroke syndrome characterized by the presence of an ipsilateral oculomotor nerve palsy, contralateral hemiparesis, contralateral ataxia, and contralateral hemiplegia of the lower face, tongue, and shoulder. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Schminke
Alexander is a male given name. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history. Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Aleksander and Aleksandr. Related names and diminutives include Iskandar, Alec, Alek, Alex, Alexandre, Aleks, Aleksa and Sander; feminine forms include Alexandra, Alexandria, and Sasha. Etymology The name ''Alexander'' originates from the (; 'defending men' or 'protector of men'). It is a compound of the verb (; 'to ward off, avert, defend') and the noun (, genitive: , ; meaning 'man'). It is an example of the widespread motif of Greek names expressing "battle-prowess", in this case the ability to withstand or push back an enemy battle line. The earliest attested form of the name, is the Mycenaean Greek feminine anthroponym , , (/Alexandra/), written in the Linear B syllabic script. Alaksandu, alternatively called ''Alakasandu'' or ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation. Other cuticle, animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different cellular differentiation, developmental origin, structure and chemical composition. The adjective cutaneous means "of the skin" (from Latin ''cutis'' 'skin'). In mammals, the skin is an organ (anatomy), organ of the integumentary system made up of multiple layers of ectodermal tissue (biology), tissue and guards the underlying muscles, bones, ligaments, and internal organs. Skin of a different nature exists in amphibians, reptiles, and birds. Skin (including cutaneous and subcutaneous tissues) plays crucial roles in formation, structure, and function of extraskeletal apparatus such as horns of bovids (e.g., cattle) and rhinos, cervids' antlers, giraffids' ossicones, armadillos' osteoderm, and os penis/os clitoris. All mammals have som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostate
The prostate is both an Male accessory gland, accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found only in some mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemically, and physiologically. Anatomically, the prostate is found below the Urinary bladder, bladder, with the urethra passing through it. It is described in gross anatomy as consisting of lobes and in microanatomy by zone. It is surrounded by an elastic, fibromuscular capsule and contains glandular tissue as well as connective tissue. The prostate glands produce and contain fluid that forms part of semen, the substance emitted during ejaculation as part of the male Human sexual response cycle, sexual response. This prostatic fluid is slightly alkaline, milky or white in appearance. The alkalinity of semen helps neutralize the acidity of the vagina, vaginal tract, prolonging the lifespan of sperm. The prostatic fluid is expelled in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endometrium
The endometrium is the inner epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The functional layer thickens and then is shed during menstruation in humans and some other mammals, including apes, Old World monkeys, some species of bat, the elephant shrew and the Cairo spiny mouse. In most other mammals, the endometrium is reabsorbed in the estrous cycle. During pregnancy, the glands and blood vessels in the endometrium further increase in size and number. Vascular spaces fuse and become interconnected, forming the placenta, which supplies oxygen and nutrition to the embryo and fetus.Blue Histology - Female Reproductive System . School ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thymus
The thymus is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, thymus cell lymphocytes or ''T cells'' mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. The thymus is located in the upper front part of the chest, in the anterior superior mediastinum, behind the sternum, and in front of the heart. It is made up of two lobes, each consisting of a central medulla and an outer cortex, surrounded by a capsule. The thymus is made up of immature T cells called thymocytes, as well as lining cells called epithelial cells which help the thymocytes develop. T cells that successfully develop react appropriately with MHC immune receptors of the body (called ''positive selection'') and not against proteins of the body (called ''negative selection''). The thymus is largest and most active during the neonatal and pre-adolescent periods. By the early teens, the thymus begins to decrease in size and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast
The breast is one of two prominences located on the upper ventral region of a primate's torso. Both females and males develop breasts from the same embryological tissues. In females, it serves as the mammary gland, which produces and secretes milk to feed infants. Subcutaneous fat covers and envelops a network of ducts that converge on the nipple, and these tissues give the breast its size and shape. At the ends of the ducts are lobules, or clusters of alveoli, where milk is produced and stored in response to hormonal signals. During pregnancy, the breast responds to a complex interaction of hormones, including estrogens, progesterone, and prolactin, that mediate the completion of its development, namely lobuloalveolar maturation, in preparation of lactation and breastfeeding. Humans are the only animals with permanent breasts. At puberty, estrogens, in conjunction with growth hormone, cause permanent breast growth in female humans. This happens only to a much lesser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |