|
Longitudinal-section Mode
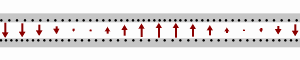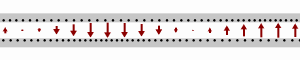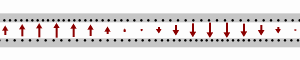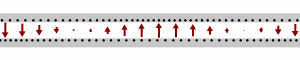
Longitudinal-section modes are a set of a particular kind of electromagnetic transmission modes found in some types of transmission line. They are a subset of hybrid electromagnetic modes (HEM modes). HEM modes are those modes that have both an electric field and a magnetic field component longitudinally in the direction of travel of the propagating wave. Longitudinal-section modes, additionally, have a component of either magnetic or electric field that is zero in one transverse direction. In longitudinal-section electric (LSE) modes this field component is electric. In longitudinal-section magnetic (LSM) modes the zero field component is magnetic. Hybrid modes are to be compared to transverse modes which have, at most, only one component of either electric or magnetic field in the longitudinal direction. Derivation and notation There is an analogy between the way transverse modes (TE and TM modes) are arrived at and the definition of longitudinal section modes (LSE and LS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mode (electromagnetism)
The mode of electromagnetic radiation describes the field pattern of the propagating waves. Electromagnetic modes are analogous to the normal modes of vibration in other systems, such as mechanical systems. Some of the classifications of electromagnetic modes include; * Free space modes ** Plane waves, waves in which the electric and magnetic fields are both orthogonal to the direction of travel of the wave. These are the waves that exist in free space far from any antenna. * Modes in waveguides and transmission lines ** Transverse modes, modes that have at least one of the electric field and magnetic field entirely in a transverse direction. *** Transverse electromagnetic mode (TEM), as with a free space plane wave, both the electric field and magnetic field are entirely transverse. *** Transverse electric (TE) modes, only the electric field is entirely transverse. Also notated as H modes to indicate there is a longitudinal magnetic component. *** Transverse magnetic (TM) modes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmission Line
In electrical engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable or other structure designed to conduct electromagnetic waves in a contained manner. The term applies when the conductors are long enough that the wave nature of the transmission must be taken into account. This applies especially to radio-frequency engineering because the short wavelengths mean that wave phenomena arise over very short distances (this can be as short as millimetres depending on frequency). However, the theory of transmission lines was historically developed to explain phenomena on very long telegraph lines, especially submarine telegraph cables. Transmission lines are used for purposes such as connecting radio transmitters and receivers with their antennas (they are then called feed lines or feeders), distributing cable television signals, trunklines routing calls between telephone switching centres, computer network connections and high speed computer data buses. RF engineers commonly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Field
An electric field (sometimes E-field) is the physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles and exerts force on all other charged particles in the field, either attracting or repelling them. It also refers to the physical field for a system of charged particles. Electric fields originate from electric charges and time-varying electric currents. Electric fields and magnetic fields are both manifestations of the electromagnetic field, one of the four fundamental interactions (also called forces) of nature. Electric fields are important in many areas of physics, and are exploited in electrical technology. In atomic physics and chemistry, for instance, the electric field is the attractive force holding the atomic nucleus and electrons together in atoms. It is also the force responsible for chemical bonding between atoms that result in molecules. The electric field is defined as a vector field that associates to each point in space the electrostatic ( Coulomb) for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field. A permanent magnet's magnetic field pulls on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets. In addition, a nonuniform magnetic field exerts minuscule forces on "nonmagnetic" materials by three other magnetic effects: paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, although these forces are usually so small they can only be detected by laboratory equipment. Magnetic fields surround magnetized materials, and are created by electric currents such as those used in electromagnets, and by electric fields varying in time. Since both strength and direction of a magnetic field may vary with location, it is described mathematically by a function assigning a vector to each point of space, cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transverse Mode
A transverse mode of electromagnetic radiation is a particular electromagnetic field pattern of the radiation in the plane perpendicular (i.e., transverse) to the radiation's propagation direction. Transverse modes occur in radio waves and microwaves confined to a waveguide, and also in light waves in an optical fiber and in a laser's optical resonator. Transverse modes occur because of boundary conditions imposed on the wave by the waveguide. For example, a radio wave in a hollow metal waveguide must have zero tangential electric field amplitude at the walls of the waveguide, so the transverse pattern of the electric field of waves is restricted to those that fit between the walls. For this reason, the modes supported by a waveguide are quantized. The allowed modes can be found by solving Maxwell's equations for the boundary conditions of a given waveguide. Types of modes Unguided electromagnetic waves in free space, or in a bulk isotropic dielectric, can be described as a super ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxwell's Equations
Maxwell's equations, or Maxwell–Heaviside equations, are a set of coupled partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electromagnetism, classical optics, and electric circuits. The equations provide a mathematical model for electric, optical, and radio technologies, such as power generation, electric motors, wireless communication, lenses, radar etc. They describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated by charges, currents, and changes of the fields.''Electric'' and ''magnetic'' fields, according to the theory of relativity, are the components of a single electromagnetic field. The equations are named after the physicist and mathematician James Clerk Maxwell, who, in 1861 and 1862, published an early form of the equations that included the Lorentz force law. Maxwell first used the equations to propose that light is an electromagnetic phenomenon. The modern form of the equations in their most common formul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boundary Condition
In mathematics, in the field of differential equations, a boundary value problem is a differential equation together with a set of additional constraints, called the boundary conditions. A solution to a boundary value problem is a solution to the differential equation which also satisfies the boundary conditions. Boundary value problems arise in several branches of physics as any physical differential equation will have them. Problems involving the wave equation, such as the determination of normal modes, are often stated as boundary value problems. A large class of important boundary value problems are the Sturm–Liouville problems. The analysis of these problems involves the eigenfunctions of a differential operator. To be useful in applications, a boundary value problem should be well posed. This means that given the input to the problem there exists a unique solution, which depends continuously on the input. Much theoretical work in the field of partial differential eq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superposition Principle
The superposition principle, also known as superposition property, states that, for all linear systems, the net response caused by two or more stimuli is the sum of the responses that would have been caused by each stimulus individually. So that if input ''A'' produces response ''X'' and input ''B'' produces response ''Y'' then input (''A'' + ''B'') produces response (''X'' + ''Y''). A function F(x) that satisfies the superposition principle is called a linear function. Superposition can be defined by two simpler properties: additivity F(x_1+x_2)=F(x_1)+F(x_2) \, and homogeneity F(a x)=a F(x) \, for scalar . This principle has many applications in physics and engineering because many physical systems can be modeled as linear systems. For example, a beam can be modeled as a linear system where the input stimulus is the load on the beam and the output response is the deflection of the beam. The importance of linear systems is that they are easier to analyze mathematically; the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planar Transmission Line
Planar transmission lines are transmission lines with conductors, or in some cases dielectric (insulating) strips, that are flat, ribbon-shaped lines. They are used to interconnect components on printed circuits and integrated circuits working at microwave frequencies because the planar type fits in well with the manufacturing methods for these components. Transmission lines are more than simply interconnections. With simple interconnections, the propagation of the electromagnetic wave along the wire is fast enough to be considered instantaneous, and the voltages at each end of the wire can be considered identical. If the wire is longer than a large fraction of a wavelength (one tenth is often used as a rule of thumb), these assumptions are no longer true and transmission line theory must be used instead. With transmission lines, the geometry of the line is precisely controlled (in most cases, the cross-section is kept constant along the length) so that its electrical behav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wave Mechanics
Wave mechanics may refer to: * the mechanics of waves * the ''wave equation'' in quantum physics, see Schrödinger equation See also * Quantum mechanics * Wave equation The (two-way) wave equation is a second-order linear partial differential equation for the description of waves or standing wave fields — as they occur in classical physics — such as mechanical waves (e.g. water waves, sound waves and s ... {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of waves of the electromagnetic field, electromagnetic (EM) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, Light, (visible) light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. All of these waves form part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Classical electromagnetism, Classically, electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves, which are synchronized oscillations of electric field, electric and magnetic fields. Depending on the frequency of oscillation, different wavelengths of electromagnetic spectrum are produced. In a vacuum, electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light, commonly denoted ''c''. In homogeneous, isotropic media, the oscillations of the two fields are perpendicular to each other and perpendicular to the direction of energy and wave propagation, forming a transverse wave. The position of an electromagnetic wave w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |