|
Logical Cube
In the system of Term logic, Aristotelian logic, the logical cube is a Diagram, diagram representing the different ways in which each of the eight propositions of the Formal system, system is logically related ('opposed') to each of the others. The system is also useful in the analysis of Term logic, syllogistic logic, serving to identify the allowed logical conversions from one type to another.Paul Dekker, 2015, "Not Only Barbara", Journal of Logic, Language and Information 24(2), pp. 95-129. See also *Lambda cube *Logical hexagon *Square of opposition *Triangle of opposition References Conceptual models Term logic {{logic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Term Logic
In logic and formal semantics, term logic, also known as traditional logic, syllogistic logic or Aristotelian logic, is a loose name for an approach to formal logic that began with Aristotle and was developed further in ancient history mostly by his followers, the Peripatetics. It was revived after the third century CE by Porphyry's Isagoge. Term logic revived in medieval times, first in Islamic logic by Alpharabius in the tenth century, and later in Christian Europe in the twelfth century with the advent of new logic, remaining dominant until the advent of predicate logic in the late nineteenth century. However, even if eclipsed by newer logical systems, term logic still plays a significant role in the study of logic. Rather than radically breaking with term logic, modern logics typically expand it. Aristotle's system Aristotle's logical work is collected in the six texts that are collectively known as the '' Organon''. Two of these texts in particular, namely th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagram
A diagram is a symbolic Depiction, representation of information using Visualization (graphics), visualization techniques. Diagrams have been used since prehistoric times on Cave painting, walls of caves, but became more prevalent during the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment. Sometimes, the technique uses a Three-dimensional space, three-dimensional visualization which is then graphical projection, projected onto a two-dimensional surface. The word ''graphics, graph'' is sometimes used as a synonym for diagram. Overview The term "diagram" in its commonly used sense can have a general or specific meaning: * ''visual information device'' : Like the term "illustration", "diagram" is used as a collective term standing for the whole class of technical genres, including graphics, graphs, technical drawings and tables. * ''specific kind of visual display'' : This is the genre that shows qualitative data with shapes that are connected by lines, arrows, or other visual links. In scie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proposition
A proposition is a statement that can be either true or false. It is a central concept in the philosophy of language, semantics, logic, and related fields. Propositions are the object s denoted by declarative sentences; for example, "The sky is blue" expresses the proposition that the sky is blue. Unlike sentences, propositions are not linguistic expressions, so the English sentence "Snow is white" and the German "Schnee ist weiß" denote the same proposition. Propositions also serve as the objects of belief and other propositional attitudes, such as when someone believes that the sky is blue. Formally, propositions are often modeled as functions which map a possible world to a truth value. For instance, the proposition that the sky is blue can be modeled as a function which would return the truth value T if given the actual world as input, but would return F if given some alternate world where the sky is green. However, a number of alternative formalizations have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formal System
A formal system is an abstract structure and formalization of an axiomatic system used for deducing, using rules of inference, theorems from axioms. In 1921, David Hilbert proposed to use formal systems as the foundation of knowledge in mathematics. The term ''formalism'' is sometimes a rough synonym for ''formal system'', but it also refers to a given style of notation, for example, Paul Dirac's bra–ket notation. Concepts A formal system has the following: * Formal language, which is a set of well-formed formulas, which are strings of symbols from an alphabet, formed by a formal grammar (consisting of production rules or formation rules). * Deductive system, deductive apparatus, or proof system, which has rules of inference that take axioms and infers theorems, both of which are part of the formal language. A formal system is said to be recursive (i.e. effective) or recursively enumerable if the set of axioms and the set of inference rules are decidable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambda Cube
In mathematical logic and type theory, the λ-cube (also written lambda cube) is a framework introduced by Henk Barendregt to investigate the different dimensions in which the calculus of constructions is a generalization of the simply typed λ-calculus. Each dimension of the cube corresponds to a new kind of dependency between terms and types. Here, "dependency" refers to the capacity of a term or type to Free variables and bound variables, bind a term or type. The respective dimensions of the λ-cube correspond to: * x-axis (\rightarrow): types that can depend on terms, corresponding to dependent types. * y-axis (\uparrow): terms that can depend on types, corresponding to Parametric polymorphism, polymorphism. * z-axis (\nearrow): types that can depend on other types, corresponding to (binding) type operators. The different ways to combine these three dimensions yield the 8 vertices of the cube, each corresponding to a different kind of typed system. The λ-cube can be generali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
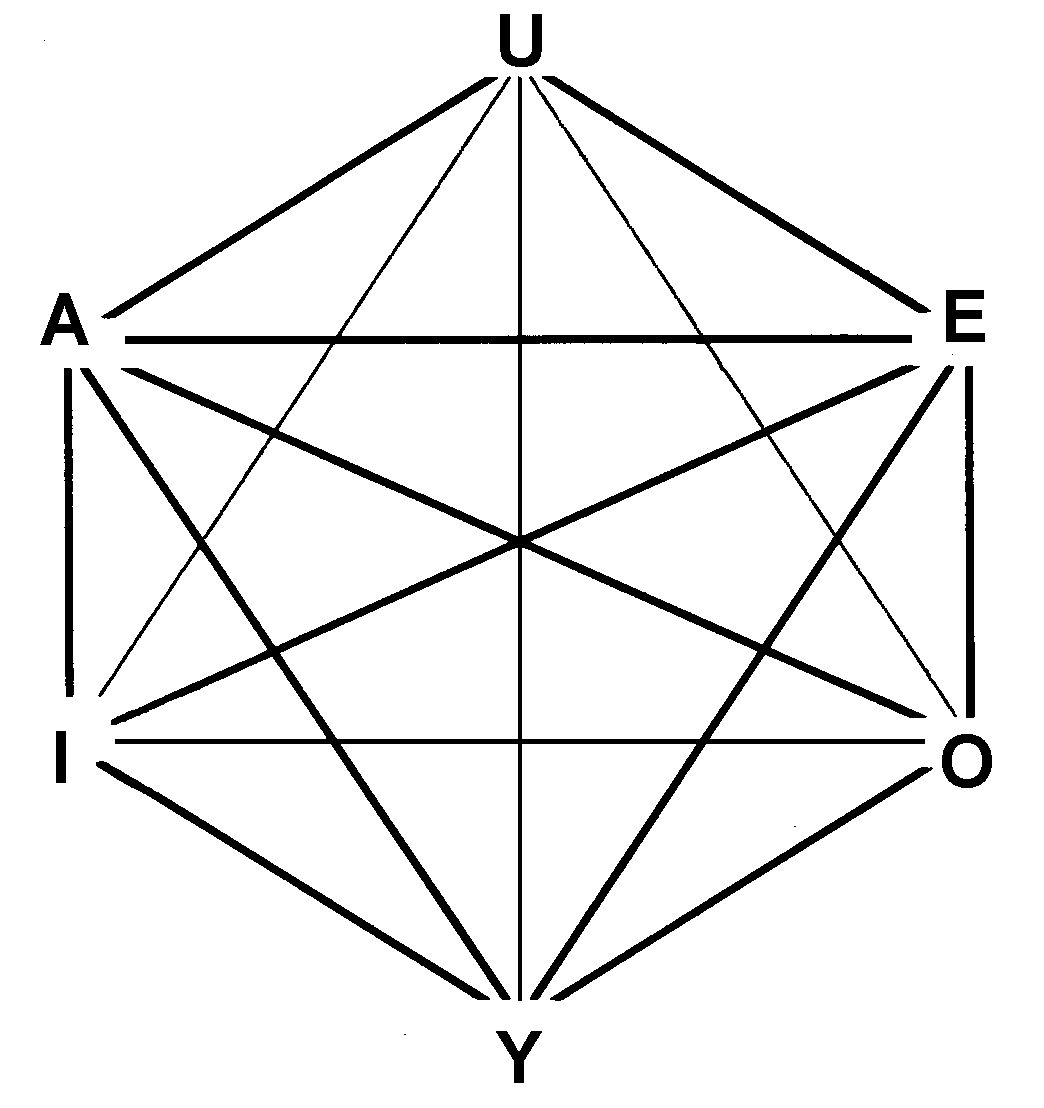
Logical Hexagon
In philosophical logic, the logical hexagon (also called the hexagon of opposition) is a conceptual model of the relationships between the truth values of six statements. It is an extension of Aristotle's square of opposition. It was discovered independently by both Augustin Sesmat and Robert Blanché. This extension consists in introducing two statements U and Y. Whereas U is the disjunction of A and E, Y is the conjunction of the two traditional particulars I and O. Summary of relationships The traditional square of opposition demonstrates two sets of contradictories A and O, and E and I (i.e. they cannot both be true and cannot both be false), two contraries A and E (i.e. they can both be false, but cannot both be true), and two subcontraries I and O (i.e. they can both be true, but cannot both be false) according to Aristotle’s definitions. However, the logical hexagon provides that U and Y are also contradictory. Interpretations The logical hexagon may be interpr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square Of Opposition
In term logic (a branch of philosophical logic), the square of opposition is a diagram representing the relations between the four basic categorical propositions. The origin of the square can be traced back to Aristotle's tractate '' On Interpretation'' and its distinction between two oppositions: contradiction and contrariety. However, Aristotle did not draw any diagram; this was done several centuries later by Boethius. Summary In traditional logic, a proposition (Latin: ''propositio'') is a spoken assertion (''oratio enunciativa''), not the meaning of an assertion, as in modern philosophy of language and logic. A ''categorical proposition'' is a simple proposition containing two terms, subject () and predicate (), in which the predicate is either asserted or denied of the subject. Every categorical proposition can be reduced to one of four logical forms, named , , , and based on the Latin ' (I affirm), for the affirmative propositions and , and ' (I deny), for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangle Of Opposition
In the system of Aristotelian logic, the triangle of opposition is a diagram representing the different ways in which each of the three propositions of the system is logically related ('opposed') to each of the others. The system is also useful in the analysis of syllogistic logic, serving to identify the allowed logical conversions from one type to another. In the 19th and 20th centuries, other triangles were proposed, including Nicolai A. Vasiliev's triangle, the Jespersenian Triangle, Ginzberg’s triangle of contraries and Sir William Hamilton’s subcontraries. See also * Lambda cube * Logical cube * Logical hexagon * Square of opposition In term logic (a branch of philosophical logic), the square of opposition is a diagram representing the relations between the four basic categorical propositions. The origin of the square can be traced back to Aristotle's tractate '' On Int ... References External links [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conceptual Models
Conceptual may refer to: Philosophy and Humanities *Concept *Conceptualism *Philosophical analysis (Conceptual analysis) *Theoretical definition (Conceptual definition) *Thinking about Consciousness (Conceptual dualism) *Pragmatism (Conceptual pragmatism) * Paradigm (Conceptual scheme) * Abstract and concrete (Conceptual object) * Conceptual attrition, an idea of Beverley Skeggs *Conceptual proliferation *Conceptual history *Conceptual necessity Linguistics and Semantics *Conceptual schema *Conceptual metaphor *Conceptual model *Conceptual blending *Conceptual semantics *Conceptual dictionary * Conceptual change *Conceptual dependency theory *Conceptual domain in Frame semantics (linguistics) *Inferential role semantics (Conceptual role semantics) Psychology *Priming (psychology) (Conceptual priming) *Spatial–temporal reasoning (Visuo-conceptual) *Conceptual act model of emotion *Conceptual space Science *Conceptual physics *Conceptual economy *Conceptual model (computer scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |