|
Linear Optics
Linear optics is a sub-field of optics, consisting of linear systems, and is the opposite of nonlinear optics. Linear optics includes most applications of lenses, mirrors, waveplates, diffraction gratings, and many other common optical components and systems. If an optical system is linear, it has the following properties (among others): * If monochromatic light enters an unchanging linear-optical system, the output will be at the same frequency. For example, if red light enters a lens, it will still be red when it exits the lens. * The superposition principle is valid for linear-optical systems. For example, if a mirror transforms light input A into output B, and input C into output D, then an input consisting of A and C simultaneously give an output of B and D simultaneously. * Relatedly, if the input light is made more intense, then the output light is made more intense but otherwise unchanged. These properties are violated in nonlinear optics, which frequently involves high-pow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Because light is an electromagnetic wave, other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties. Most optical phenomena can be accounted for by using the classical electromagnetic description of light. Complete electromagnetic descriptions of light are, however, often difficult to apply in practice. Practical optics is usually done using simplified models. The most common of these, geometric optics, treats light as a collection of rays that travel in straight lines and bend when they pass through or reflect from surfaces. Physical optics is a more comprehensive model of light, which includes wave effects such as diffraction and interference that cannot be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Computing
Quantum computing is a type of computation whose operations can harness the phenomena of quantum mechanics, such as superposition, interference, and entanglement. Devices that perform quantum computations are known as quantum computers. Though current quantum computers may be too small to outperform usual (classical) computers for practical applications, larger realizations are believed to be capable of solving certain computational problems, such as integer factorization (which underlies RSA encryption), substantially faster than classical computers. The study of quantum computing is a subfield of quantum information science. There are several models of quantum computation with the most widely used being quantum circuits. Other models include the quantum Turing machine, quantum annealing, and adiabatic quantum computation. Most models are based on the quantum bit, or "qubit", which is somewhat analogous to the bit in classical computation. A qubit can be in a 1 or 0 quantum s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Physics
Atomic, molecular, and optical physics (AMO) is the study of matter-matter and light-matter interactions; at the scale of one or a few atoms and energy scales around several electron volts. The three areas are closely interrelated. AMO theory includes classical, semi-classical and quantum treatments. Typically, the theory and applications of emission, absorption, scattering of electromagnetic radiation (light) from excited atoms and molecules, analysis of spectroscopy, generation of lasers and masers, and the optical properties of matter in general, fall into these categories. Atomic and molecular physics Atomic physics is the subfield of AMO that studies atoms as an isolated system of electrons and an atomic nucleus, while molecular physics is the study of the physical properties of molecules. The term ''atomic physics'' is often associated with nuclear power and nuclear bombs, due to the synonymous use of ''atomic'' and ''nuclear'' in standard English. However, ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Phase Space
In quantum optics, an optical phase space is a phase space in which all quantum states of an optical system are described. Each point in the optical phase space corresponds to a unique state of an ''optical system''. For any such system, a plot of the ''quadratures'' against each other, possibly as functions of time, is called a phase diagram. If the quadratures are functions of time then the optical phase diagram can show the evolution of a quantum optical system with time. An optical phase diagram can give insight into the properties and behaviors of the system that might otherwise not be obvious. This can allude to qualities of the system that can be of interest to an individual studying an optical system that would be very hard to deduce otherwise. Another use for an optical phase diagram is that it shows the evolution of the state of an optical system. This can be used to determine the state of the optical system at any point in time. Background information When discussing t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Optical Quantum Computing
Linear optical quantum computing or linear optics quantum computation (LOQC) is a paradigm of quantum computation, allowing (under certain conditions, described below) universal quantum computation. LOQC uses photons as information carriers, mainly uses linear optical elements, or optical instruments (including reciprocal mirrors and waveplates) to process quantum information, and uses photon detectors and quantum memories to detect and store quantum information. Overview Although there are many other implementations for quantum information processing (QIP) and quantum computation, optical quantum systems are prominent candidates, since they link quantum computation and quantum communication in the same framework. In optical systems for quantum information processing, the unit of light in a given mode—or photon—is used to represent a qubit. Superpositions of quantum states can be easily represented, encrypted, transmitted and detected using photons. Besides, linear opti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonlinear Optics
Nonlinear optics (NLO) is the branch of optics that describes the behaviour of light in ''nonlinear media'', that is, media in which the polarization density P responds non-linearly to the electric field E of the light. The non-linearity is typically observed only at very high light intensities (when the electric field of the light is >108 V/m and thus comparable to the atomic electric field of ~1011 V/m) such as those provided by lasers. Above the Schwinger limit, the vacuum itself is expected to become nonlinear. In nonlinear optics, the superposition principle no longer holds. History The first nonlinear optical effect to be predicted was two-photon absorption, by Maria Goeppert Mayer for her PhD in 1931, but it remained an unexplored theoretical curiosity until 1961 and the almost simultaneous observation of two-photon absorption at Bell Labs and the discovery of second-harmonic generation by Peter Franken ''et al.'' at University of Michigan, both shortly after the constru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Optics
Quantum optics is a branch of atomic, molecular, and optical physics dealing with how individual quanta of light, known as photons, interact with atoms and molecules. It includes the study of the particle-like properties of photons. Photons have been used to test many of the counter-intuitive predictions of quantum mechanics, such as entanglement and teleportation, and are a useful resource for quantum information processing. History Light propagating in a restricted volume of space has its energy and momentum quantized according to an integer number of particles known as photons. Quantum optics studies the nature and effects of light as quantized photons. The first major development leading to that understanding was the correct modeling of the blackbody radiation spectrum by Max Planck in 1899 under the hypothesis of light being emitted in discrete units of energy. The photoelectric effect was further evidence of this quantization as explained by Albert Einstein in a 1905 paper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Because light is an electromagnetic wave, other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties. Most optical phenomena can be accounted for by using the classical electromagnetic description of light. Complete electromagnetic descriptions of light are, however, often difficult to apply in practice. Practical optics is usually done using simplified models. The most common of these, geometric optics, treats light as a collection of rays that travel in straight lines and bend when they pass through or reflect from surfaces. Physical optics is a more comprehensive model of light, which includes wave effects such as diffraction and interference that cannot be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boson Sampling
Boson sampling is a restricted model of non-universal quantum computation introduced by Scott Aaronson and Alex Arkhipov after the original work of Lidror Troyansky and Naftali Tishby, that explored possible usage of boson scattering to evaluate expectation values of permanents of matrices. The model consists of sampling from the probability distribution of identical bosons scattered by a linear interferometer. Although the problem is well defined for any bosonic particles, its photonic version is currently considered as the most promising platform for a scalable implementation of a boson sampling device, which makes it a non-universal approach to linear optical quantum computing. Moreover, while not universal, the boson sampling scheme is strongly believed to implement computing tasks which are hard to implement with classical computers by using far fewer physical resources than a full linear-optical quantum computing setup. This advantage makes it an ideal candidate for dem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KLM Protocol
The KLM scheme or KLM protocol is an implementation of linear optical quantum computing (LOQC), developed in 2000 by Emanuel Knill, Raymond Laflamme and Gerard J. Milburn. This protocol makes it possible to create universal quantum computers solely with linear optical tools. The KLM protocol uses linear optical elements, single-photon sources and photon detectors as resources to construct a quantum computation scheme involving only ancilla resources, quantum teleportations and error corrections. Overview The KLM scheme induces an effective interaction between photons by making projective measurements with photodetectors, which falls into the category of non-deterministic quantum computation. It is based on a non-linear sign shift between two qubits that uses two ancilla photons and post-selection. It is also based on the demonstrations that the probability of success of the quantum gates can be made close to one by using entangled states prepared non-deterministically and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
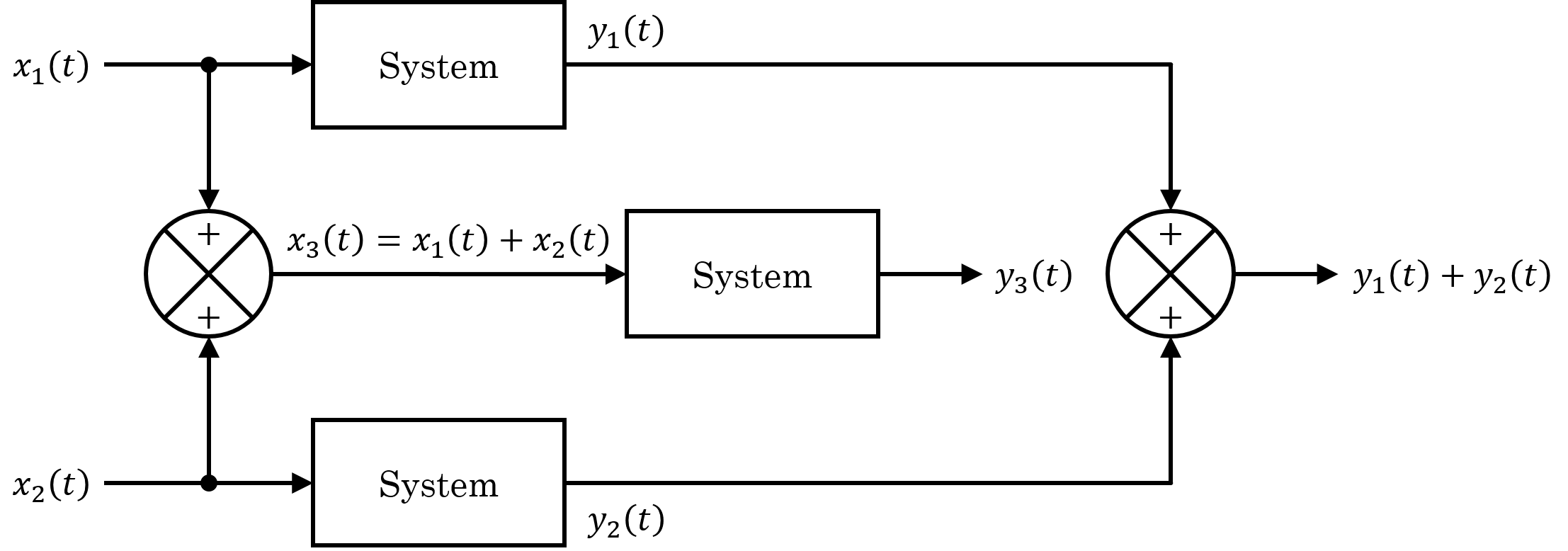
Linear System
In systems theory, a linear system is a mathematical model of a system based on the use of a linear operator. Linear systems typically exhibit features and properties that are much simpler than the nonlinear case. As a mathematical abstraction or idealization, linear systems find important applications in automatic control theory, signal processing, and telecommunications. For example, the propagation medium for wireless communication systems can often be modeled by linear systems. Definition A general deterministic system can be described by an operator, that maps an input, as a function of to an output, a type of black box description. A system is linear if and only if it satisfies the superposition principle, or equivalently both the additivity and homogeneity properties, without restrictions (that is, for all inputs, all scaling constants and all time.) The superposition principle means that a linear combination of inputs to the system produces a linear combination ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Optical Quantum Computing
Linear optical quantum computing or linear optics quantum computation (LOQC) is a paradigm of quantum computation, allowing (under certain conditions, described below) universal quantum computation. LOQC uses photons as information carriers, mainly uses linear optical elements, or optical instruments (including reciprocal mirrors and waveplates) to process quantum information, and uses photon detectors and quantum memories to detect and store quantum information. Overview Although there are many other implementations for quantum information processing (QIP) and quantum computation, optical quantum systems are prominent candidates, since they link quantum computation and quantum communication in the same framework. In optical systems for quantum information processing, the unit of light in a given mode—or photon—is used to represent a qubit. Superpositions of quantum states can be easily represented, encrypted, transmitted and detected using photons. Besides, linear opti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)