|
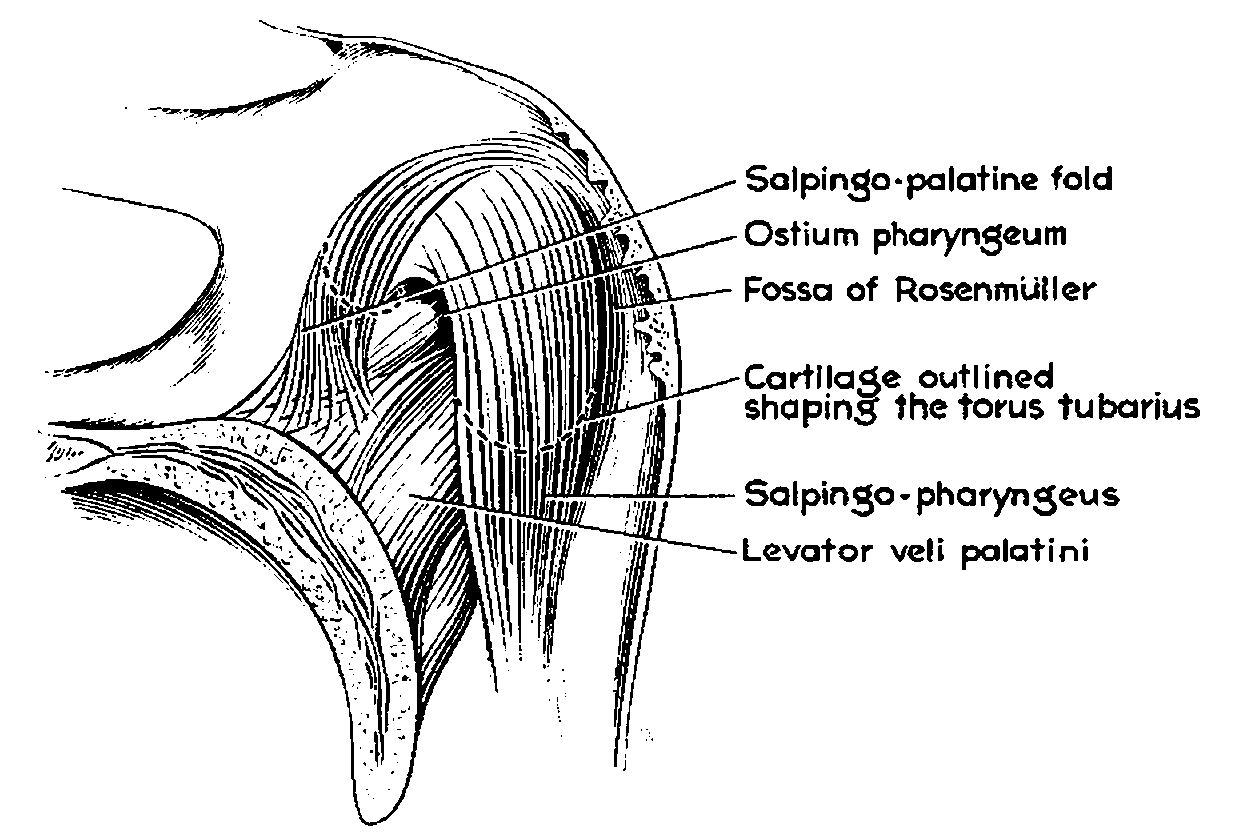
Levator Veli Palatini Muscle
The levator veli palatini () is the elevator muscle of the soft palate in the human body. It is supplied via the pharyngeal plexus. During swallowing, it contracts, elevating the soft palate to help prevent food from entering the nasopharynx. Structure The levator veli palatini muscle is found in the soft palate of the mouth. It arises from the under surface of the apex of the petrous part of the temporal bone, and from the surface inferolateral to the medial lamina of the cartilage of the Eustachian tube. It does not connect with the medial lamina. It passes above the upper concave margin of the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle. It spreads out in the palatine velum, its fibers extending obliquely downward and medially to the middle line, where they blend with those of the opposite side. It lies lateral to the choana. Nerve supply The levator veli palatini muscle is supplied by the pharyngeal plexus, which is supplied by the vagus nerve (CN X). Function The levator ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporal Bone
The temporal bones are situated at the sides and base of the skull, and lateral to the temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex. The temporal bones are overlaid by the sides of the head known as the temples, and house the structures of the ears. The lower seven cranial nerves and the major vessels to and from the brain traverse the temporal bone. Structure The temporal bone consists of four parts— the squamous, mastoid, petrous and tympanic parts. The squamous part is the largest and most superiorly positioned relative to the rest of the bone. The zygomatic process is a long, arched process projecting from the lower region of the squamous part and it articulates with the zygomatic bone. Posteroinferior to the squamous is the mastoid part. Fused with the squamous and mastoid parts and between the sphenoid and occipital bones lies the petrous part, which is shaped like a pyramid. The tympanic part is relatively small and lies inferior to the squamous part, anterior to the mast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mouth
In animal anatomy, the mouth, also known as the oral cavity, or in Latin cavum oris, is the opening through which many animals take in food and issue vocal sounds. It is also the cavity lying at the upper end of the alimentary canal, bounded on the outside by the lips and inside by the pharynx. In tetrapods, it contains the tongue and, except for some like birds, teeth. This cavity is also known as the buccal cavity, from the Latin ''bucca'' ("cheek"). Some animal phyla, including arthropods, molluscs and chordates, have a complete digestive system, with a mouth at one end and an anus at the other. Which end forms first in ontogeny is a criterion used to classify bilaterian animals into protostomes and deuterostomes. Development In the first multicellular animals, there was probably no mouth or gut and food particles were engulfed by the cells on the exterior surface by a process known as endocytosis. The particles became enclosed in vacuoles into which enzymes were secr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tensor Veli Palatini Muscle
The tensor veli palatini muscle (tensor palati or tensor muscle of the velum palatinum) is a broad, thin, ribbon-like muscle in the head that tenses the soft palate. Structure The tensor veli palatini is found anterior-lateral to the levator veli palatini muscle. It arises by a flat lamella from the scaphoid fossa at the base of the medial pterygoid plate, from the spina angularis of the sphenoid and from the lateral wall of the cartilage of the auditory tube. Descending vertically between the medial pterygoid plate and the medial pterygoid muscle, it ends in a tendon which winds around the pterygoid hamulus, being retained in this situation by some of the fibers of origin of the medial pterygoid muscle. Between the tendon and the hamulus is a small bursa. The tendon then passes medially and is inserted into the palatine aponeurosis and into the surface behind the transverse ridge on the horizontal part of the palatine bone. Nerve supply The tensor veli palatini muscle is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species. The pharynx carries food and air to the esophagus and larynx respectively. The flap of cartilage called the epiglottis stops food from entering the larynx. In humans, the pharynx is part of the digestive system and the conducting zone of the respiratory system. (The conducting zone—which also includes the nostrils of the nose, the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles—filters, warms and moistens air and conducts it into the lungs). The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections: the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx. It is also important in vocalization. In humans, two sets of pharyngeal muscles form the pharynx and determine the shape of its lumen. They are arranged as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swallowing
Swallowing, sometimes called deglutition in scientific contexts, is the process in the human or animal body that allows for a substance to pass from the mouth, to the pharynx, and into the esophagus, while shutting the epiglottis. Swallowing is an important part of eating and drinking. If the process fails and the material (such as food, drink, or medicine) goes through the trachea, then choking or pulmonary aspiration can occur. In the human body the automatic temporary closing of the epiglottis is controlled by the swallowing reflex. The portion of food, drink, or other material that will move through the neck in one swallow is called a bolus. In colloquial English, the term "swallowing" is also used to describe the action of taking in a large mouthful of food without any biting, where the word gulping is more adequate. In humans Swallowing comes so easily to most people that the process rarely prompts much thought. However, from the viewpoints of physiology, of speech� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagus Nerve
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, cranial nerve X, or simply CN X, is a cranial nerve that interfaces with the parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. It comprises two nerves—the left and right vagus nerves—but they are typically referred to collectively as a single subsystem. The vagus is the longest nerve of the autonomic nervous system in the human body and comprises both sensory and motor fibers. The sensory fibers originate from neurons of the nodose ganglion, whereas the motor fibers come from neurons of the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus and the nucleus ambiguus. The vagus was also historically called the pneumogastric nerve. Structure Upon leaving the medulla oblongata between the olive and the inferior cerebellar peduncle, the vagus nerve extends through the jugular foramen, then passes into the carotid sheath between the internal carotid artery and the internal jugular vein down to the neck, chest, and abdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choana
The choanae (singular choana), posterior nasal apertures or internal nostrils are two openings found at the back of the nasal passage between the nasal cavity and the throat in tetrapods, including humans and other mammals (as well as crocodilians and most skinks). They are considered one of the most important synapomorphies of tetrapodomorphs, that allowed the passage from water to land. In animals with secondary palates, they allow breathing when the mouth is closed. Janvier, Philippe (2004) "Wandering nostrils". ''Nature'', 432 (7013): 23–24. In tetrapods without secondary palates their function relates primarily to olfaction (sense of smell). The choanae are separated in two by the vomer. Boundaries A choana is the opening between the nasal cavity and the nasopharynx. It is therefore not a structure but a space bounded as follows: * anteriorly and inferiorly by the horizontal plate of palatine bone, * superiorly and posteriorly by the sphenoid bone * laterally by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatine Velum
The soft palate (also known as the velum, palatal velum, or muscular palate) is, in mammals, the soft tissue constituting the back of the roof of the mouth. The soft palate is part of the palate of the mouth; the other part is the hard palate. The soft palate is distinguished from the hard palate at the front of the mouth in that it does not contain bone. Structure Muscles The five muscles of the soft palate play important roles in swallowing and breathing. The muscles are: # Tensor veli palatini, which is involved in swallowing # Palatoglossus, involved in swallowing # Palatopharyngeus, involved in breathing # Levator veli palatini, involved in swallowing # Musculus uvulae, which moves the uvula These muscles are innervated by the pharyngeal plexus via the vagus nerve, with the exception of the tensor veli palatini. The tensor veli palatini is innervated by the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (V3). Function The soft palate is moveable, consisting of muscle fib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Pharyngeal Constrictor Muscle
The superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle is a muscle in the pharynx. It is the highest located muscle of the three pharyngeal constrictors. The muscle is a quadrilateral muscle, thinner and paler than the inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle and middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle. The muscle is divided into four parts: A pterygopharyngeal, buccopharyngeal, mylopharyngeal and a glossopharyngeal part. Origin and insertion The four parts of this muscle arise from: - the lower third of the posterior margin of the medial pterygoid plate and its hamulus (Pterygopharyngeal part) - from the pterygomandibular raphe (Buccopharyngeal part) - from the alveolar process of the mandible above the posterior end of the mylohyoid line (Mylopharyngeal part) - and by a few fibers from the side of the tongue (Glossopharyngeal part) The fibers curve backward to be inserted into the median raphe, being also prolonged by means of an aponeurosis to the pharyngeal spine on the basilar part of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasopharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species. The pharynx carries food and air to the esophagus and larynx respectively. The flap of cartilage called the epiglottis stops food from entering the larynx. In humans, the pharynx is part of the digestive system and the conducting zone of the respiratory system. (The conducting zone—which also includes the nostrils of the nose, the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles—filters, warms and moistens air and conducts it into the lungs). The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections: the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx. It is also important in vocalization. In humans, two sets of pharyngeal muscles form the pharynx and determine the shape of its lumen. They are arranged as an in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eustachian Tube
In anatomy, the Eustachian tube, also known as the auditory tube or pharyngotympanic tube, is a tube that links the nasopharynx to the middle ear, of which it is also a part. In adult humans, the Eustachian tube is approximately long and in diameter. It is named after the sixteenth-century Italian anatomist Bartolomeo Eustachi. In humans and other tetrapods, both the middle ear and the ear canal are normally filled with air. Unlike the air of the ear canal, however, the air of the middle ear is not in direct contact with the atmosphere outside the body; thus, a pressure difference can develop between the atmospheric pressure of the ear canal and the middle ear. Normally, the Eustachian tube is collapsed, but it gapes open with swallowing and with positive pressure, allowing the middle ear's pressure to adjust to the atmospheric pressure. When taking off in an aircraft, the ambient air pressure goes from higher (on the ground) to lower (in the sky). The air in the middle ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharyngeal Plexus Of Vagus Nerve
The pharyngeal plexus is a network of nerve fibers innervating most of the palate and pharynx. (The larynx, which is innervated by the superior and recurrent laryngeal nerves from vagus nerve (CN X), is not included.) It is located on the surface of the middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle. Sources Although the ''Terminologia Anatomica'' name of the plexus has "vagus nerve" in the title, other nerves make contributions to the plexus. It has the following sources: * CN IX – pharyngeal branches of glossopharyngeal nerve – sensory * CN X – pharyngeal branch of vagus nerve – motor * superior cervical ganglion sympathetic fibers – vasomotor Because the cranial part of accessory nerve (CN XI) leaves the jugular foramen as a part of the CN X, it is sometimes considered part of the plexus as well. Innervation Sensory The pharyngeal plexus provides sensory innervation of the oropharynx and laryngopharynx from CN IX and CN X. (The nasopharynx above the pharyngotympanic tube ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |