|
Choana
The choanae (: choana), posterior nasal apertures or internal nostrils are two openings found at the back of the nasal passage between the nasal cavity and the pharynx, in humans and other mammals (as well as crocodilians and most skinks). They are considered one of the most important synapomorphies of tetrapodomorphs, that allowed the passage from water to land. In animals with secondary palates, they allow breathing when the mouth is closed. Janvier, Philippe (2004) "Wandering nostrils". ''Nature'', 432 (7013): 23–24. In tetrapods without secondary palates their function relates primarily to olfaction (sense of smell). The choanae are separated in two by the vomer. Boundaries A choana is the opening between the nasal cavity and the nasopharynx. It is therefore not a structure but a space bounded as follows: * anteriorly and inferiorly by the horizontal plate of palatine bone, * superiorly and posteriorly by the sphenoid bone * laterally by the medial pterygoid pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
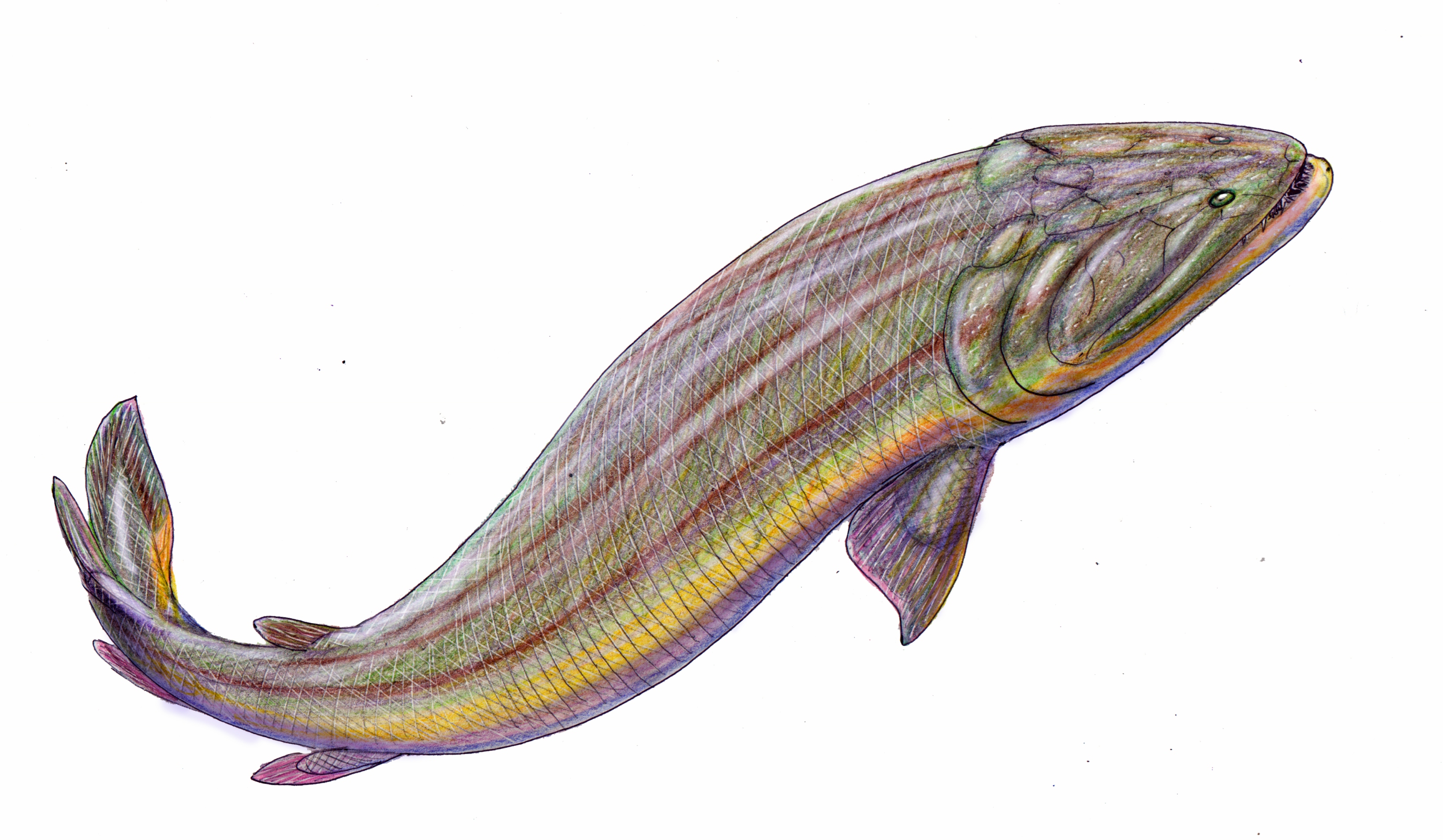
Kenichthys
''Kenichthys'' is a genus of sarcopterygian fish from the Devonian period, and a member of the clade Tetrapodomorpha. The only known species of the genus is ''Kenichthys campbelli'' (named for the Australian palaeontologist Ken Campbell), the first remains of which were found in China in 1993.Chang, M. and Zhu, M. (1993) A new Middle Devonian osteolepidid from Qujing, Yunnan. ''Mem. Assoc. Australas. Palaeontol.'' 15 183-198 The genus is important to the study of the evolution of tetrapods due to the unique nature of its nostrils, which provide vital evidence regarding the evolutionary transition of fish-like nostrils to the tetrapod choanae.Zhu, M. and Ahlberg, P. (2004) The origin of the internal nostril of tetrapods. ''Nature'' 432 94-97 Description ''Kenichthys'' was a small tetrapodomorph, with a skull about long. While only areas of the front of the body are known, it seems likely that ''Kenichthys'' would have been similar in general body form to other basal sarcopte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vomer
The vomer (; ) is one of the unpaired facial bones of the skull. It is located in the midsagittal line, and articulates with the sphenoid, the ethmoid, the left and right palatine bones, and the left and right maxillary bones. The vomer forms the inferior part of the nasal septum in humans, with the superior part formed by the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone. The name is derived from the Latin word for a ploughshare and the shape of the bone. In humans The vomer is situated in the median plane, but its anterior portion is frequently bent to one side. It is thin, somewhat quadrilateral in shape, and forms the hinder and lower part of the nasal septum; it has two surfaces and four borders. The surfaces are marked by small furrows for blood vessels, and on each is the nasopalatine groove, which runs obliquely downward and forward, and lodges the nasopalatine nerve and vessels. Borders The ''superior border'', the thickest, presents a deep furrow, bounded on eith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vomer And Choane
The vomer (; ) is one of the unpaired facial bones of the skull. It is located in the midsagittal line, and articulates with the sphenoid, the ethmoid, the left and right palatine bones, and the left and right maxillary bones. The vomer forms the inferior part of the nasal septum in humans, with the superior part formed by the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone. The name is derived from the Latin word for a ploughshare and the shape of the bone. In humans The vomer is situated in the median plane, but its anterior portion is frequently bent to one side. It is thin, somewhat quadrilateral in shape, and forms the hinder and lower part of the nasal septum; it has two surfaces and four borders. The surfaces are marked by small furrows for blood vessels, and on each is the nasopalatine groove, which runs obliquely downward and forward, and lodges the nasopalatine nerve and vessels. Borders The ''superior border'', the thickest, presents a deep furrow, bounded on either s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
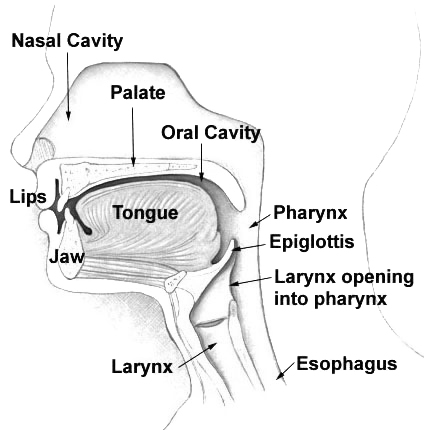
Nasal Cavity
The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nasal cavity is the uppermost part of the respiratory system and provides the nasal passage for inhaled air from the nostrils to the nasopharynx and rest of the respiratory tract. The paranasal sinuses surround and drain into the nasal cavity. Structure The term "nasal cavity" can refer to each of the two cavities of the nose, or to the two sides combined. The lateral wall of each nasal cavity mainly consists of the maxilla. However, there is a deficiency that is compensated for by the perpendicular plate of the palatine bone, the medial pterygoid plate, the labyrinth of ethmoid and the inferior concha. The paranasal sinuses are connected to the nasal cavity through small orifices called ostia. Most of these ostia communicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the human mouth, mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species. The pharynx carries food to the esophagus and air to the larynx. The flap of cartilage called the epiglottis stops food from entering the larynx. In humans, the pharynx is part of the Digestion, digestive system and the conducting zone of the respiratory system. (The conducting zone—which also includes the nostrils of the Human nose, nose, the larynx, trachea, bronchus, bronchi, and bronchioles—filters, warms, and moistens air and conducts it into the lungs). The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections: the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx (hypopharynx). In humans, two sets of pharyngeal muscles form the pharynx and determine the shape of its lumen (anatomy), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapodomorpha
Tetrapodomorpha (also known as Choanata) is a clade of vertebrates consisting of tetrapods (four-limbed vertebrates) and their closest sarcopterygian relatives that are more closely related to living tetrapods than to living lungfish. Advanced forms transitional between fish and the early labyrinthodonts, such as '' Tiktaalik'', have been referred to as "fishapods" by their discoverers, being half-fish, half-tetrapods, in appearance and limb morphology. The Tetrapodomorpha contains the crown group tetrapods (the last common ancestor of living tetrapods and all of its descendants) and several groups of early stem tetrapods, which includes several groups of related lobe-finned fishes, collectively known as the osteolepiforms. The Tetrapodomorpha minus the crown group Tetrapoda are the stem Tetrapoda, a paraphyletic unit encompassing the fish to tetrapod transition. Characteristics Among the characteristics defining tetrapodomorphs are modifications to the fins, notably a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasopharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species. The pharynx carries food to the esophagus and air to the larynx. The flap of cartilage called the epiglottis stops food from entering the larynx. In humans, the pharynx is part of the digestive system and the conducting zone of the respiratory system. (The conducting zone—which also includes the nostrils of the nose, the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles—filters, warms, and moistens air and conducts it into the lungs). The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections: the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx (hypopharynx). In humans, two sets of pharyngeal muscles form the pharynx and determine the shape of its lumen. They are arranged as an inner layer of longitudina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapodomorphs
Tetrapodomorpha (also known as Choanata) is a clade of vertebrates consisting of tetrapods (four-limbed vertebrates) and their closest sarcopterygian relatives that are more closely related to living tetrapods than to living lungfish. Advanced forms transitional between fish and the early labyrinthodonts, such as ''Tiktaalik'', have been referred to as "fishapods" by their discoverers, being half-fish, half-tetrapods, in appearance and limb morphology. The Tetrapodomorpha contains the crown group tetrapods (the last common ancestor of living tetrapods and all of its descendants) and several groups of early stem tetrapods, which includes several groups of related lobe-finned fishes, collectively known as the osteolepiforms. The Tetrapodomorpha minus the crown group Tetrapoda are the stem Tetrapoda, a paraphyletic unit encompassing the fish to tetrapod transition. Characteristics Among the characteristics defining tetrapodomorphs are modifications to the fins, notably a humerus wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Pterygoid Plate
The pterygoid processes of the sphenoid (from Greek ''pteryx'', ''pterygos'', "wing"), one on either side, descend perpendicularly from the regions where the body and the greater wings of the sphenoid bone unite. Each process consists of a medial pterygoid plate and a lateral pterygoid plate, the latter of which serve as the origins of the medial and lateral pterygoid muscles. The medial pterygoid, along with the masseter allows the jaw to move in a vertical direction as it contracts and relaxes. The lateral pterygoid allows the jaw to move in a horizontal direction during mastication (chewing). Fracture of either plate are used in clinical medicine to distinguish the Le Fort fracture classification for high impact injuries to the sphenoid and maxillary bones. The superior portion of the pterygoid processes are fused anteriorly; a vertical groove, the pterygopalatine fossa, descends on the front of the line of fusion. The plates are separated below by an angular cleft, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabolepis
''Diabolepis'' is an extinct genus of very primitive marine lungfish which lived during the Early Devonian period. It contains a single species, ''D. speratus'' of Yunnan, China, from the mid-late Lochkovian of the Xitun Formation. It is one of the oldest known lungfish genera. It is the only member of the family Diabolepididae and the order Diabolepidiformes, although neither of these parent taxa have been officially described, despite their names being in scientific usage. Taxonomy ''Diabolepis'' was originally described as ''Diabolichthys'', but this name was found to be preoccupied by a now-outdated genus name given to the manta ray in the 19th century, thus necessitating a new genus name. It is generally considered the most basal known dipnoan, although some other studies instead find '' Youngolepis'' to be more basal. In addition, some studies do not find it to be a lungfish, but rather a more basal dipnotetrapodomorph. However, other studies have continued to recove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nostril
A nostril (or naris , : nares ) is either of the two orifices of the nose. They enable the entry and exit of air and other gasses through the nasal cavities. In birds and mammals, they contain branched bones or cartilages called turbinates, whose function is to warm air on inhalation and remove moisture on exhalation. Fish do not breathe through noses, but they do have two small holes used for smelling, which can also be referred to as nostrils (with the exception of Cyclostomi, which have just one nostril). In humans, the nasal cycle is the normal ultradian cycle of each nostril's blood vessels becoming engorged in swelling, then shrinking. The nostrils are separated by the septum. The septum can sometimes be deviated, causing one nostril to appear larger than the other. With extreme damage to the septum and columella, the two nostrils are no longer separated and form a single larger external opening. Like other tetrapod A tetrapod (; from Ancient Greek :wikti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |