|
List Of Camouflage Methods
Camouflage is the concealment of animals or objects of military interest by any combination of methods that helps them to remain unnoticed. This includes the use of high-contrast disruptive patterns as used on military uniforms, but anything that delays recognition can be used as camouflage. Camouflage involves deception, whether by looking like the background or by resembling something else, which may be plainly visible to observers.Cott, 1940. Chapter 1: General Colour Resemblance. pp. 5–19.Forbes, 2009. p. 51. This article lists methods used by animals and the military to escape notice. Conventions used Different camouflage methods employed by terrestrial, aerial, and aquatic animals, and in military usage, are compared in the table. Several methods are often combined, so for example the Bushbuck is both countershaded over its whole body, and disruptively coloured with small pale spots. Until the discovery of countershading in the 1890s, protective coloration was considered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camouflage
Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the battledress of a modern soldier, and the leaf-mimic katydid's wings. A third approach, motion dazzle, confuses the observer with a conspicuous pattern, making the object visible but momentarily harder to locate, as well as making general aiming easier. The majority of camouflage methods aim for crypsis, often through a general resemblance to the background, high contrast disruptive coloration, eliminating shadow, and countershading. In the open ocean, where there is no background, the principal methods of camouflage are transparency, silvering, and countershading, while the ability to produce light is among other things used for counter-illumination on the undersides of cephalopods such as squid. Some animals, such as chameleons and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
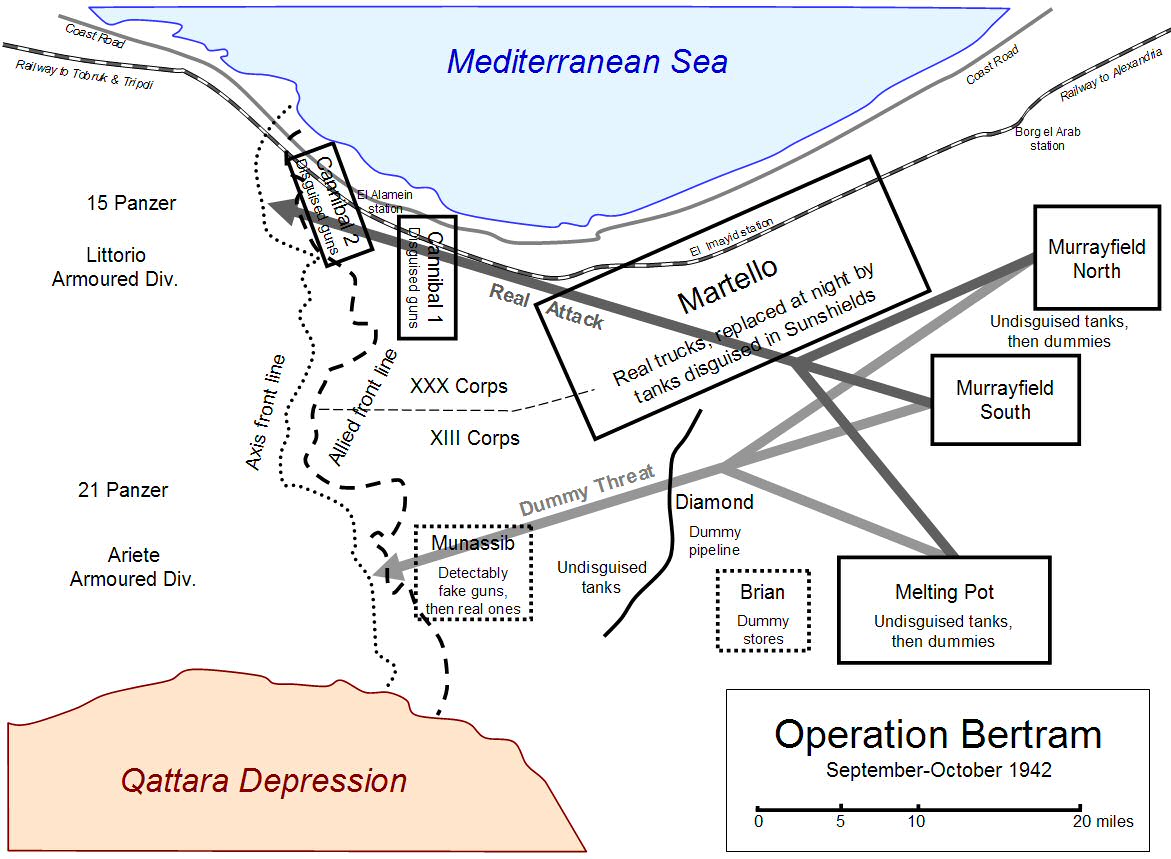
Operation Bertram
Operation Bertram was a Second World War deception operation practised by the Allied forces in Egypt led by Bernard Montgomery, in the months before the Second Battle of El Alamein in 1942. Bertram was devised by Dudley Clarke to deceive Erwin Rommel about the timing and location of the Allied attack. The operation consisted of physical deceptions using dummies and camouflage, designed and made by the British Middle East Command Camouflage Directorate led by Geoffrey Barkas. These were accompanied by electromagnetic deceptions codenamed Operation Canwell, using false radio traffic. All of these were planned to make the Axis believe that the attack would take place to the south, far from the coast road and railway, about two days later than the real attack. Bertram consisted of the creation of the appearance of army units where none existed and in concealing armour, artillery and '' matériel''. Dummy tanks and guns were made mainly of local materials including calico and palm-fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disruptive Coloration
Disruptive coloration (also known as disruptive camouflage or disruptive patterning) is a form of camouflage that works by breaking up the outlines of an animal, soldier or military vehicle with a strongly contrasting pattern. It is often combined with other methods of crypsis including background colour matching and countershading; special cases are coincident disruptive coloration and the disruptive eye mask seen in some fishes, amphibians, and reptiles. It appears paradoxical as a way of not being seen, since disruption of outlines depends on high contrast, so the patches of colour are themselves conspicuous. The importance of high-contrast patterns for successful disruption was predicted in general terms by the artist Abbott Thayer in 1909 and explicitly by the zoologist Hugh Cott in 1940. Later experimental research has started to confirm these predictions. Disruptive patterns work best when all their components match the background. While background matching works best ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Artillery, 1910
Greek may refer to: Greece Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe: *Greeks, an ethnic group. *Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family. **Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all known varieties of Greek. **Mycenaean Greek, most ancient attested form of the language (16th to 11th centuries BC). **Ancient Greek, forms of the language used c. 1000–330 BC. **Koine Greek, common form of Greek spoken and written during Classical antiquity. **Medieval Greek or Byzantine Language, language used between the Middle Ages and the Ottoman conquest of Constantinople. **Modern Greek, varieties spoken in the modern era (from 1453 AD). *Greek alphabet, script used to write the Greek language. *Greek Orthodox Church, several Churches of the Eastern Orthodox Church. *Ancient Greece, the ancient civilization before the end of Antiquity. *Old Greek, the language as spoken from Late Antiquity to around 1500 AD. Other uses * '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khaki
The color khaki (, ) is a light shade of tan with a slight yellowish tinge. Khaki has been used by many armies around the world for uniforms and equipment, particularly in arid or desert regions, where it provides camouflage relative to sandy or dusty terrain. It has been used as a color name in English since 1848 when it was first introduced as a military uniform. In Western fashion, it is a standard color for smart casual dress trousers for civilians, which are also often called ''khakis''. In British English and some other Commonwealth usage, ''khaki'' may also refer to a shade of green known in the US as olive drab. Etymology ''Khaki'' is a loanword from Urdu خاکی 'soil-colored', which in turn comes from Persian خاک ''khâk'' 'soil' + ی (adjectival ending); it came into English via the British Indian Army. Origin Khaki was first worn as a uniform in the Corps of Guides that was raised in December 1846 by Henry Lawrence (1806–1857), agent to the Governor-Gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salmo Trutta
The brown trout (''Salmo trutta'') is a European species of salmonid fish that has been widely introduced into suitable environments globally. It includes purely freshwater populations, referred to as the riverine ecotype, ''Salmo trutta'' morpha ''fario'', a lacustrine ecotype, ''S. trutta'' morpha ''lacustris'', also called the lake trout, and anadromous forms known as the sea trout, ''S. trutta'' morpha ''trutta''. The latter migrates to the oceans for much of its life and returns to fresh water only to spawn. Sea trout in Ireland and Britain have many regional names: sewin in Wales, finnock in Scotland, peal in the West Country, mort in North West England, and white trout in Ireland. The lacustrine morph of brown trout is most usually potamodromous, migrating from lakes into rivers or streams to spawn, although evidence indicates some stocks spawn on wind-swept shorelines of lakes. ''S. trutta'' morpha ''fario'' forms stream-resident populations, typically in alpine stream ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyla Arborea
The European tree frog (''Hyla arborea'') is a small tree frog. As traditionally defined, it was found throughout much of Europe, Asia and northern Africa,Frost, Darrel R. ''Amphibian Species of the World''. Allen Press, Inc., 1985, p. 126. but based on molecular genetic and other data several populations formerly included in it are now recognized as separate species (for example, '' H. intermedia'' of Italy and nearby, '' H. molleri'' of the Iberian Peninsula, '' H. meridionalis'' of parts of southwestern Europe and northern Africa, and '' H. orientalis'' of parts of Eastern Europe, Turkey and the Black Sea and Caspian Sea regions), limiting the true European tree frog to Europe from France to Poland and Greece.Duellman, William E. (2003). ''Grzimek's Animal Encyclopedia''. 2nd Ed., Vol. 2. Gale, p. 235.Stöck M., Dufresnes C., Litvinchuk S.N., Lymberakis P., Biollay S., Berroneau M., Borzée A., Ghali K., Ogielska M., and Perrin N. (2012). Cryptic diversity among Western Palearct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoplophrys Oatesii (Soft Coral Spider Crab)
''Hoplophrys'' is a monotypic genus of crab in the family Epialtidae. It contains the single species Hoplophrys oatesi, also known as the candy crab, Oates's soft coral crab, commensal soft coral crab and ''Dendronephthya'' crab. Description ''Hoplophrys oatesi'' is a very colourful crab that grows from 1.5 to 2 cm. It lives on various species of soft coral in the genus ''Dendronephthya ''Dendronephthya'' is a genus of soft corals in the family Nephtheidae. There are over 250 described species In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversi ...''. It camouflages itself by mimicking the colours of the polyps among which it hides. It adds further camouflage by attaching polyps to its carapace. Colours vary depending on the colour of the coral, and may be white, pink, yellow or red. The first pair of legs of this species has small claws. The body has pointed spines with a red and whit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoplophrys Oatesi
''Hoplophrys'' is a monotypic genus of crab in the Family (biology), family Epialtidae. It contains the single species Hoplophrys oatesi, also known as the candy crab, Oates's soft coral crab, commensal soft coral crab and ''Dendronephthya'' crab. Description ''Hoplophrys oatesi'' is a very colourful crab that grows from 1.5 to 2 cm. It lives on various species of soft coral in the genus ''Dendronephthya''. It camouflages itself by mimicking the colours of the polyps among which it hides. It adds further camouflage by attaching polyps to its carapace. Colours vary depending on the colour of the coral, and may be white, pink, yellow or red. The first pair of legs of this species has small claws. The body has pointed spines with a red and white pattern, similar in appearance to the host coral.http://www.lembehresort.com/candy_crab_hoplophrys_oatesii_c14.html Distribution This crab is widespread in the Indo-Pacific. Diet ''Hoplophrys oatesi'' feeds on plankton. References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kallima Inachus Qtl1
''Kallima'', known as the oakleaf or oak leaf butterflies, is a genus of butterflies of the subfamily Nymphalinae in the family Nymphalidae. They are found in east, south and southeast Asia. Their common name is a reference to the lower surface of their wings, which is various shades of brown like a dead leaf. When the wings are held closed, this results in a remarkable masquerade of a dead leaf, further emphasized by their wing shape. Taxonomy This genus has traditionally also included a number of African species, but they are now usually placed in ''Kallimoides'', ''Junonia'' (alternatively in ''Kamilla'') and ''Mallika''. The following species are currently members of the genus ''Kallima'':"''Kallima'' Doubleday, [1849]"at Markku Savela's ''Lepidoptera and Some Other Life Forms'' *''Kallima albofasciata'' Moore, 1877 – Andaman oakleaf *''Kallima alompra'' Moore, 1879 – scarce blue oak leaf *''Kallima buxtoni'' Moore, 1879 *''Kallima horsfieldii'' (Kollar, 1844) – S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)