|
Lettres De Cachet
''Lettres de cachet'' (; ) were letters signed by the king of France, countersigned by one of his ministers, and closed with the royal seal. They contained orders directly from the king, often to enforce arbitrary actions and judgments that could not be appealed. In the case of organized bodies, 'lettres de cachet’ were issued for the purpose of preventing assembly or accomplishing some other definite act. The provincial estates were convoked (called to assembly) in this manner, and it was by a ''lettre de cachet'' (in this case, a ''lettre de jussipri''), or by showing in person in a ''lit de justice'', that the king ordered a ''parlement'' to register a law despite that ''parlement''s refusal to pass it. The best-known ''lettres de cachet'', however, were penal, by which a subject was imprisoned without trial and without an opportunity of defense (after inquiry and due diligence by the ''lieutenant de police'') in a state prison or an ordinary jail, confinement in a conv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Law
Roman law is the legal system of ancient Rome, including the legal developments spanning over a thousand years of jurisprudence, from the Twelve Tables (c. 449 BC), to the '' Corpus Juris Civilis'' (AD 529) ordered by Eastern Roman emperor Justinian I. Roman law forms the basic framework for civil law, the most widely used legal system today, and the terms are sometimes used synonymously. The historical importance of Roman law is reflected by the continued use of Latin legal terminology in many legal systems influenced by it, including common law. After the dissolution of the Western Roman Empire, the Roman law remained in effect in the Eastern Roman Empire. From the 7th century onward, the legal language in the East was Greek. ''Roman law'' also denoted the legal system applied in most of Western Europe until the end of the 18th century. In Germany, Roman law practice remained in place longer under the Holy Roman Empire (963–1806). Roman law thus served as a basis for leg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marquis De Sade
Donatien Alphonse François, Marquis de Sade (; 2 June 1740 – 2 December 1814), was a French nobleman, revolutionary politician, philosopher and writer famous for his literary depictions of a libertine sexuality as well as numerous accusations of sex crimes. His works include novels, short stories, plays, dialogues, and political tracts. In his lifetime some of these were published under his own name while others, which Sade denied having written, appeared anonymously. Sade is best known for his erotic works, which combined philosophical discourse with pornography, depicting sexual fantasies with an emphasis on violence, suffering, anal sex (which he calls sodomy), child rape, crime, and blasphemy against Christianity. Many of the characters in his works are teenagers or adolescents. His work is a depiction of extreme absolute freedom, unrestrained by morality, religion, or law. The words '' sadism'' and ''sadist'' are derived from his name in reference to the works of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forms Of Government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state. In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a means by which organizational policies are enforced, as well as a mechanism for determining policy. In many countries, the government has a kind of constitution, a statement of its governing principles and philosophy. While all types of organizations have governance, the term ''government'' is often used more specifically to refer to the approximately 200 independent national governments and subsidiary organizations. The major types of political systems in the modern era are democracies, monarchies, and authoritarian and totalitarian regimes. Historically prevalent forms of government include monarchy, aristocracy, timocracy, oligarchy, democracy, theocracy, and tyranny. These forms are not always mutually exclusive, and mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chancellor
Chancellor ( la, cancellarius) is a title of various official positions in the governments of many nations. The original chancellors were the of Roman courts of justice—ushers, who sat at the or lattice work screens of a basilica or law court, which separated the judge and counsel from the audience. A chancellor's office is called a chancellery or chancery. The word is now used in the titles of many various officers in various settings (government, education, religion). Nowadays the term is most often used to describe: *The head of the government *A person in charge of foreign affairs *A person with duties related to justice *A person in charge of financial and economic issues *The head of a university Governmental positions Head of government Austria The Chancellor of Austria, denominated ' for males and ' for females, is the title of the head of the Government of Austria. Since 2021, the Chancellor of Austria is Karl Nehammer. Germany The Chancellor of Germany, denomi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Letters Close
__NOTOC__ Letters close ( la, litterae clausae) are a type of obsolete legal document once used by the Pope, the British monarchy and by certain officers of government, which is a sealed letter granting a right, monopoly, title, or status to an individual or to some entity such as a corporation. These letters were personal in nature, and were delivered folded and sealed, so that only the recipient could read their contents. This type of letter contrasts with the better-known letters patent. It was necessary to break the seal to open and read the letter, and so its arrival with the seal intact showed that it had not been intercepted or tampered with. However, once the seal was broken, it could no longer confirm the authenticity of the document. ''Litterae clausae'' of the Pope Another example of letters close is papal letters close. These often had the leaden papal bulla attached to the letter with a hemp cord that was a sign that the letter contains an order or the fine silk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles IX Of France
Charles IX (Charles Maximilien; 27 June 1550 – 30 May 1574) was King of France from 1560 until his death in 1574. He ascended the French throne upon the death of his brother Francis II in 1560, and as such was the penultimate monarch of the House of Valois. Charles' reign saw the culmination of decades of tension between Protestants and Catholics. Civil and religious war broke out between the two parties after the massacre of Vassy in 1562. In 1572, following several unsuccessful attempts at brokering peace, Charles arranged the marriage of his sister Margaret to Henry of Navarre, a major Protestant nobleman in the line of succession to the French throne, in a last desperate bid to reconcile his people. Facing popular hostility against this policy of appeasement and at the instigation of his mother Catherine de' Medici, Charles oversaw the massacre of numerous Huguenot leaders who gathered in Paris for the royal wedding, though his direct involvement is still debated. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, fashion, gastronomy, and science. For its leading role in the arts and sciences, as well as its very early system of street lighting, in the 19th century it became known as "the City of Light". Like London, prior to the Second World War, it was also sometimes called the capital of the world. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France region, or Paris Region, with an estimated population of 12,262,544 in 2019, or about 19% of the population of France, making the region France's primate city. The Paris Region had a GDP of €739 billion ($743 billion) in 2019, which is the highest in Europe. According to the Economis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
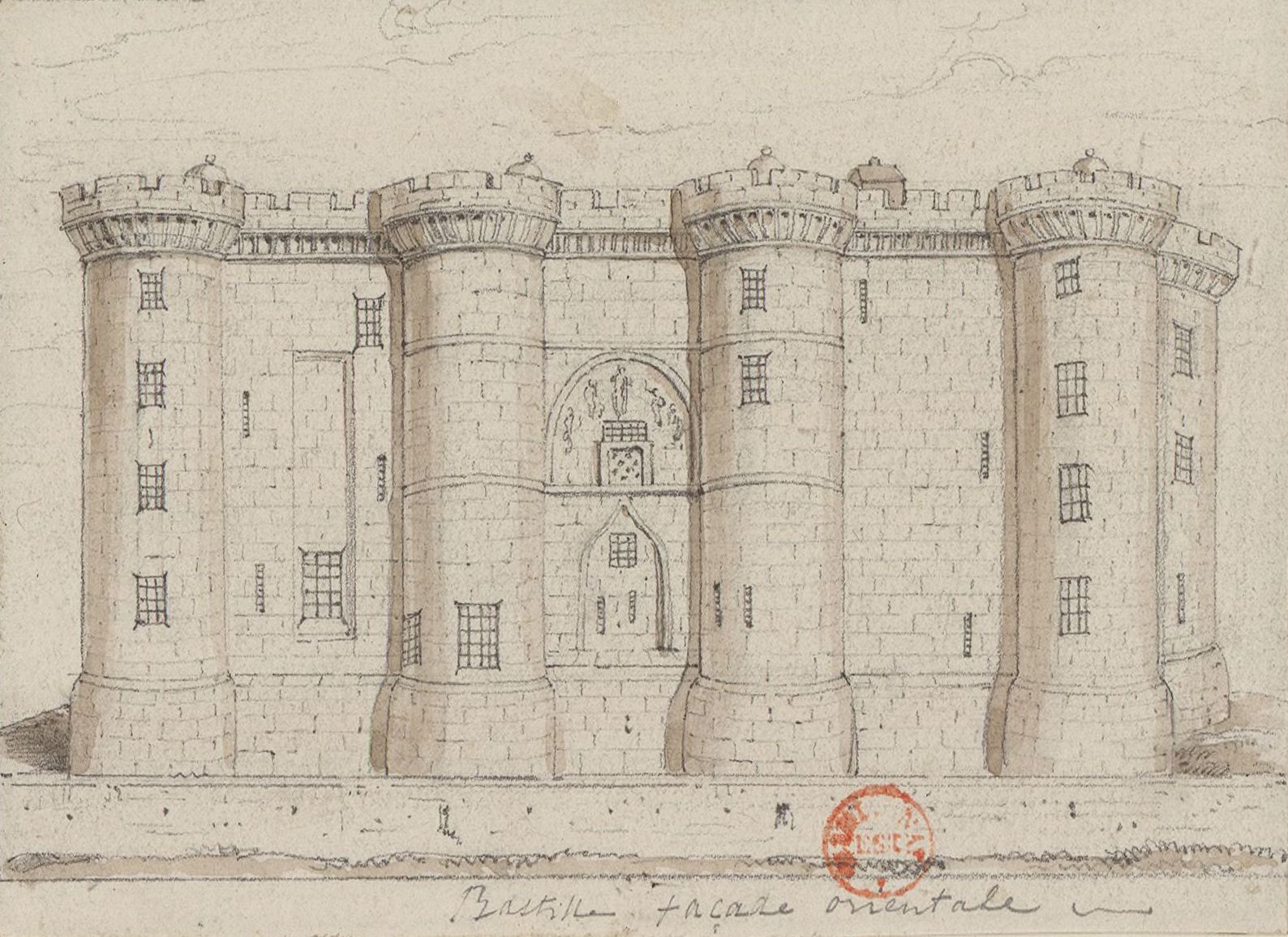
Bastille
The Bastille (, ) was a fortress in Paris, known formally as the Bastille Saint-Antoine. It played an important role in the internal conflicts of France and for most of its history was used as a state prison by the kings of France. It was stormed by a crowd on 14 July 1789, in the French Revolution, becoming an important symbol for the French Republican movement. It was later demolished and replaced by the Place de la Bastille. The castle was built to defend the eastern approach to the city from potential English attacks during the Hundred Years' War. Construction was underway by 1357, but the main construction occurred from 1370 onwards, creating a strong fortress with eight towers that protected the strategic gateway of the Porte Saint-Antoine heading out to the east. The innovative design proved influential in both France and England and was widely copied. The Bastille figured prominently in France's domestic conflicts, including the fighting between the rival factions o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François De Montmorency
François de Montmorency, Duc de Montmorency (17 July 1530 – 6 May 1579) was a French soldier, diplomat and peer who served as governor of Paris. He was Duke of Montmorency, Count of Dammartin, Baron of Châteaubriant and Lord of L'Isle-Adam, Grand Master of France, and Marshal of France. He fought for France in the Hapsburg-Valois wars and for the crown in the early French Wars of Religion before his family's rivalry with the house of Guise pushed him into rebellion in 1574. Restored to favour in 1575 he died several years later. Family François was the eldest son of Anne, constable of France, and Madeleine of Savoy. In 1557 a marriage was arranged for him with Diane de France, natural daughter of Henry II; he resented the arrangement. Italian Wars In 1552 he accompanied the King to the border of Germany in the latest round of fighting with the Hapsburgs, and was present at the capture of Damvillers and of Ivoy. He took part in the defence of the town of Thérouanne aga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Letters Patent
Letters patent ( la, litterae patentes) ( always in the plural) are a type of legal instrument in the form of a published written order issued by a monarch, president or other head of state, generally granting an office, right, monopoly, title or status to a person or corporation. Letters patent can be used for the creation of corporations or government offices, or for granting city status or a coat of arms. Letters patent are issued for the appointment of representatives of the Crown, such as governors and governors-general of Commonwealth realms, as well as appointing a Royal Commission. In the United Kingdom, they are also issued for the creation of peers of the realm. A particular form of letters patent has evolved into the modern intellectual property patent (referred to as a utility patent or design patent in United States patent law) granting exclusive rights in an invention or design. In this case it is essential that the written grant should be in the form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corpus Juris Civilis
The ''Corpus Juris'' (or ''Iuris'') ''Civilis'' ("Body of Civil Law") is the modern name for a collection of fundamental works in jurisprudence, issued from 529 to 534 by order of Justinian I, Byzantine Emperor. It is also sometimes referred to metonymically after one of its parts, the Code of Justinian. The work as planned had three parts: the ''Code'' (''Codex'') is a compilation, by selection and extraction, of imperial enactments to date; the ''Digest'' or ''Pandects'' (the Latin title contains both ''Digesta'' and ''Pandectae'') is an encyclopedia composed of mostly brief extracts from the writings of Roman jurists; and the ''Institutes'' (''Institutiones'') is a student textbook, mainly introducing the ''Code'', although it has important conceptual elements that are less developed in the ''Code'' or the ''Digest''. All three parts, even the textbook, were given force of law. They were intended to be, together, the sole source of law; reference to any other source, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)






.jpg)