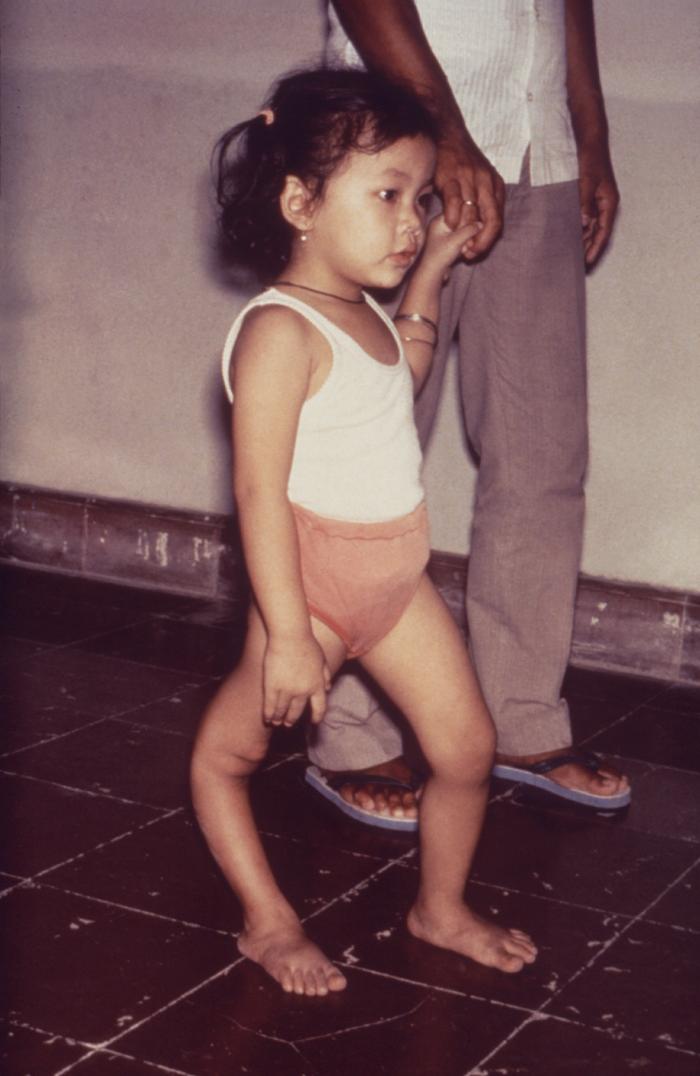|
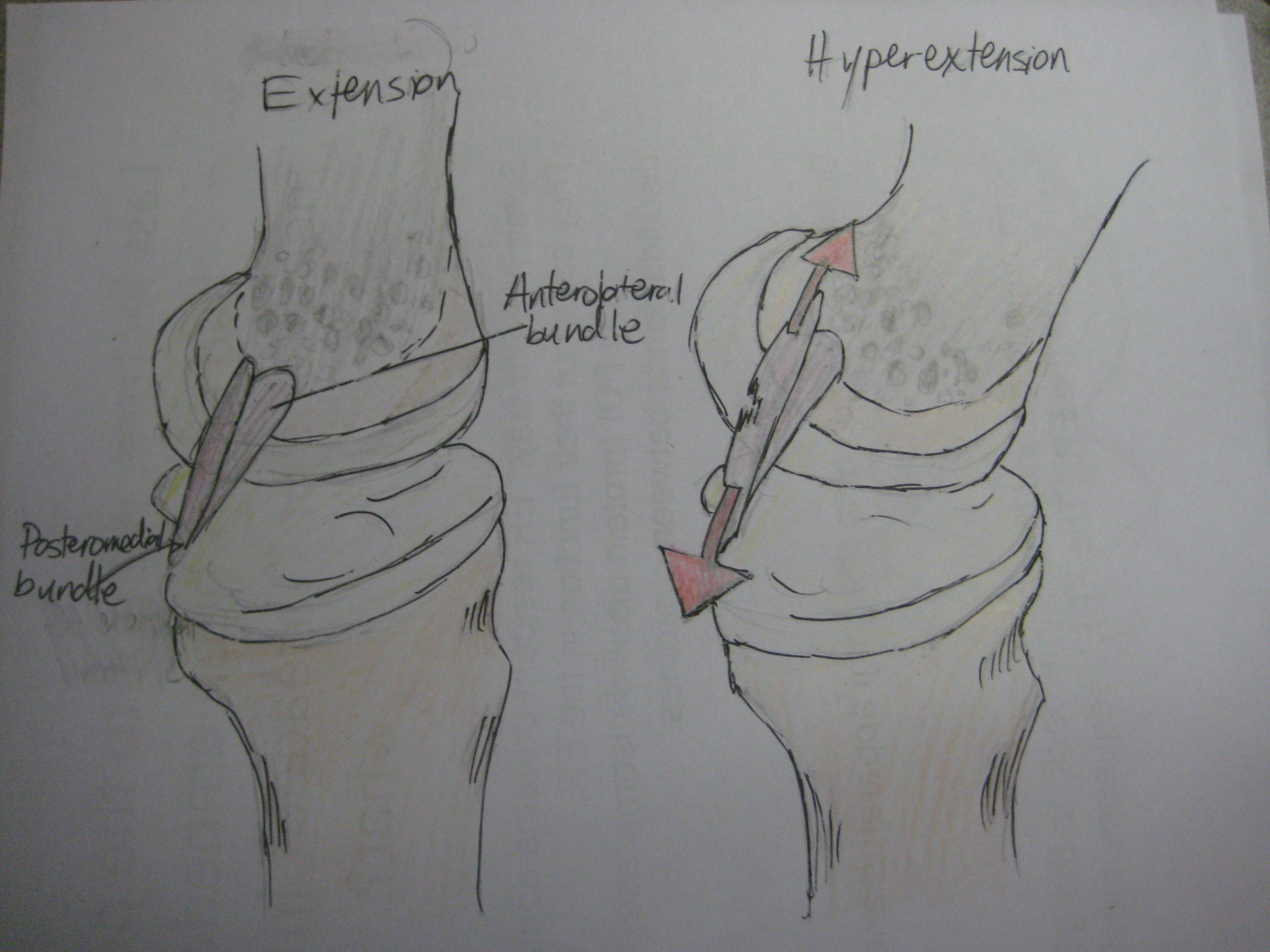
Knee Hyperextension
Genu recurvatum is a deformity in the knee joint, so that the knee bends backwards. In this deformity, excessive extension occurs in the tibiofemoral joint. Genu recurvatum is also called knee hyperextension and back knee. This deformity is more common in women and people with familial ligamentous laxity. Hyperextension of the knee may be mild, moderate or severe. The normal range of motion (ROM) of the knee joint is from 0 to 135 degrees in an adult. Full knee extension should be no more than 10 degrees. In genu recurvatum, normal extension is increased. The development of genu recurvatum may lead to knee pain and knee osteoarthritis. Causes The following factors may be involved in causing this deformity: * Inherent laxity of the knee ligaments * Weakness of biceps femoris muscle * Instability of the knee joint due to ligaments and joint capsule injuries * Inappropriate alignment of the tibia and femur * Malunion of the bones around the knee * Weakness in the hip extensor muscl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ella Harper
Ella Harper (January 5, 1870 – December 19, 1921), known professionally as The Camel Girl, was born with a very rare orthopedic condition that caused her knees to bend backwards, called ''congenital genu recurvatum''. Her preference to walk on all fours resulted in her nickname "Camel Girl". In 1886 she was featured as the star in W. H. Harris's Nickel Plate Circus, appearing in newspapers wherever the circus visited. The back of her pitch card reads: Harper received a $200 per week salary that likely opened new doors for her. She is buried in Nashville, Tennessee Nashville is the capital city of the U.S. state of Tennessee and the county seat, seat of Davidson County, Tennessee, Davidson County. With a population of 689,447 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 U.S. census, Nashville is the List of muni ...'s Spring Hill Cemetery. References External links * 1870 births American people with disabilities 1921 deaths Deaths from colorectal cancer Sideshow p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsiflexion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint Capsule
In anatomy, a joint capsule or articular capsule is an envelope surrounding a synovial joint. Each joint capsule has two parts: an outer fibrous layer or membrane, and an inner synovial layer or membrane. Membranes Each capsule consists of two layers or membranes: * an outer (fibrous membrane, ''fibrous stratum'') composed of avascular white fibrous tissue * an inner ('' synovial membrane'', ''synovial stratum'') which is a secreting layer On the inside of the capsule, articular cartilage covers the end surfaces of the bones that articulate within that joint. The outer layer is hi ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibular Collateral Ligament
The lateral collateral ligament (LCL, long external lateral ligament or fibular collateral ligament) is a ligament located on the lateral (outer) side of the knee, and thus belongs to the extrinsic knee ligaments and posterolateral corner of the knee. Structure Rounded, more narrow and less broad than the medial collateral ligament, the lateral collateral ligament stretches obliquely downward and backward from the lateral epicondyle of the femur above, to the head of the fibula below. In contrast to the medial collateral ligament, it is fused with neither the capsular ligament nor the lateral meniscus. Because of this, the lateral collateral ligament is more flexible than its medial counterpart, and is therefore less susceptible to injury. Both collateral ligaments are taut when the knee joint is in extension. With the knee in flexion, the radius of curvatures of the condyles is decreased and the origin and insertions of the ligaments are brought closer together which make t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Collateral Ligament
The medial collateral ligament (MCL), or tibial collateral ligament (TCL), is one of the four major ligaments of the knee. It is on the medial (inner) side of the knee joint in humans and other primates. Its primary function is to resist outward turning forces on the knee. Structure It is a broad, flat, membranous band, situated slightly posterior on the medial side of the knee joint. It is attached proximally to the medial epicondyle of the femur immediately below the adductor tubercle; below to the medial condyle of the tibia and medial surface of its body. It resists forces that would push the knee medially, which would otherwise produce valgus deformity. The fibers of the posterior part of the ligament are short and incline backward as they descend; they are inserted into the tibia above the groove for the semimembranosus muscle. The anterior part of the ligament is a flattened band, about 10 centimeters long, which inclines forward as it descends. It is inserted into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Cruciate Ligament
The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is a ligament in each knee of humans and various other animals. It works as a counterpart to the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). It connects the posterior intercondylar area of the tibia to the medial condyle of the femur. This configuration allows the PCL to resist forces pushing the tibia posteriorly relative to the femur. The PCL and ACL are intracapsular ligaments because they lie deep within the knee joint. They are both isolated from the fluid-filled synovial cavity, with the synovial membrane wrapped around them. The PCL gets its name by attaching to the posterior portion of the tibia. The PCL, ACL, MCL, and LCL are the four main ligaments of the knee in primates. Structure The PCL is located within the knee joint where it stabilizes the articulating bones, particularly the femur and the tibia, during movement. It originates from the lateral edge of the medial femoral condyle and the roof of the intercondyle notch then stretches ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Cruciate Ligament
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of a pair of cruciate ligaments (the other being the posterior cruciate ligament) in the human knee. The two ligaments are also called "cruciform" ligaments, as they are arranged in a crossed formation. In the quadruped stifle joint (analogous to the knee), based on its anatomical position, it is also referred to as the cranial cruciate ligament. The term cruciate translates to cross. This name is fitting because the ACL crosses the posterior cruciate ligament to form an “X”. It is composed of strong, fibrous material and assists in controlling excessive motion. This is done by limiting mobility of the joint. The anterior cruciate ligament is one of the four main ligaments of the knee, providing 85% of the restraining force to anterior tibial displacement at 30 and 90° of knee flexion. The ACL is the most injured ligament of the four located in the knee. Structure The ACL originates from deep within the notch of the distal fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligaments
A ligament is the fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones. It is also known as ''articular ligament'', ''articular larua'', ''fibrous ligament'', or ''true ligament''. Other ligaments in the body include the: * Peritoneal ligament: a fold of peritoneum or other membranes. * Fetal remnant ligament: the remnants of a fetal tubular structure. * Periodontal ligament: a group of fibers that attach the cementum of teeth to the surrounding alveolar bone. Ligaments are similar to tendons and fasciae as they are all made of connective tissue. The differences among them are in the connections that they make: ligaments connect one bone to another bone, tendons connect muscle to bone, and fasciae connect muscles to other muscles. These are all found in the skeletal system of the human body. Ligaments cannot usually be regenerated naturally; however, there are periodontal ligament stem cells located near the periodontal ligament which are involved in the adult regener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Osteogenesis imperfecta (; OI), colloquially known as brittle bone disease, is a group of genetic disorders that all result in bones that break easily. The range of symptoms—on the skeleton as well as on the body's other organs—may be mild to severe. Symptoms found in various types of OI include whites of the eye (sclerae) that are blue instead, short stature, loose joints, hearing loss, breathing problems and problems with the teeth (dentinogenesis imperfecta). Potentially life-threatening complications, all of which become more common in more severe OI, include: tearing ( dissection) of the major arteries, such as the aorta; pulmonary valve insufficiency secondary to distortion of the ribcage; and basilar invagination. The underlying mechanism is usually a problem with connective tissue due to a lack of, or poorly formed, type I collagen. In more than 90% of cases, OI occurs due to mutations in the ''COL1A1'' or ''COL1A2'' genes. These mutations may be inherited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypermobility (joints)
Hypermobility, also known as double-jointedness, describes joints that stretch farther than normal. For example, some hypermobile people can bend their thumbs backwards to their wrists, bend their knee joints backwards, put their leg behind the head or perform other contortionist "tricks". It can affect one or more joints throughout the body. Hypermobile joints are common and occur in about 10 to 25% of the population, but in a minority of people, pain and other symptoms are present. This may be a sign of what is known as joint hypermobility syndrome (JMS) or, more recently, hypermobility spectrum disorder (HSD). Hypermobile joints are a feature of genetic connective tissue disorders such as hypermobility spectrum disorder (HSD) or Ehlers–Danlos syndromes (EDS). Until new diagnostic criteria were introduced, hypermobility syndrome was sometimes considered identical to hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome (hEDS), formerly called EDS Type 3. As no genetic test can distinguish the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loeys–Dietz Syndrome
Loeys–Dietz syndrome (LDS) is an autosomal dominant genetic connective tissue disorder. It has features similar to Marfan syndrome and Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. The disorder is marked by aneurysms in the aorta, often in children, and the aorta may also undergo sudden dissection in the weakened layers of the wall of the aorta. Aneurysms and dissections also can occur in arteries other than the aorta. Because aneurysms in children tend to rupture early, children are at greater risk for dying if the syndrome is not identified. Surgery to repair aortic aneurysms is essential for treatment. There are five types of the syndrome, labelled types I through V, which are distinguished by their genetic cause. Type 1, Type 2, Type 3, Type 4 and Type 5 are caused by mutations in '' TGFBR1'', ''TGFBR2'', '' SMAD3'', ''TGFB2'', and ''TGFB3'' respectively. These five genes encoding transforming growth factors play a role in cell signaling that promotes growth and development of the body's tissu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |