Knee Hyperextension on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Genu recurvatum is a deformity in the
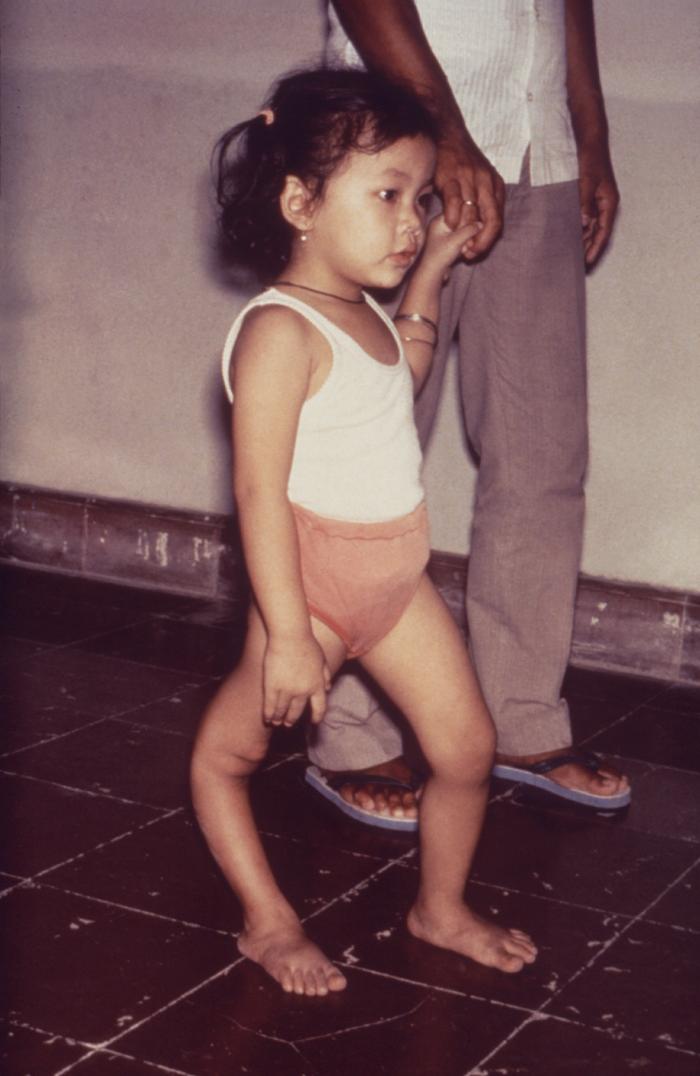 The following factors may be involved in causing this deformity:
* Inherent laxity of the knee ligaments
* Weakness of biceps femoris muscle
* Instability of the knee joint due to ligaments and joint capsule injuries
* Inappropriate alignment of the tibia and femur
* Malunion of the bones around the knee
* Weakness in the hip extensor muscles
* Gastrocnemius muscle weakness (in standing position)
* Upper motor neuron lesion (for example,
The following factors may be involved in causing this deformity:
* Inherent laxity of the knee ligaments
* Weakness of biceps femoris muscle
* Instability of the knee joint due to ligaments and joint capsule injuries
* Inappropriate alignment of the tibia and femur
* Malunion of the bones around the knee
* Weakness in the hip extensor muscles
* Gastrocnemius muscle weakness (in standing position)
* Upper motor neuron lesion (for example,
The American Academy of Orthotists and Prosthetists
The differential diagnosis of children with joint hypermobility: a review of the literature
The American Academy of Orthotists and Prosthetists
{{Congenital malformations and deformations of musculoskeletal system Musculoskeletal disorders Rheumatology Orthopedic problems Knee injuries and disorders Rare diseases
knee joint
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia (tibiofemoral joint), and one between the femur and patella (patellofemoral joint). It is the largest joint in the hu ...
, so that the knee bends backwards. In this deformity, excessive extension occurs in the tibiofemoral joint
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia (tibiofemoral joint), and one between the femur and patella (patellofemoral joint). It is the largest joint in the hu ...
. Genu recurvatum is also called knee hyperextension and back knee. This deformity is more common in women and people with familial ligamentous laxity. Hyperextension of the knee may be mild, moderate or severe.
The normal range of motion (ROM) of the knee joint is from 0 to 135 degrees in an adult. Full knee extension should be no more than 10 degrees. In genu recurvatum, normal extension is increased. The development of genu recurvatum may lead to knee pain and knee osteoarthritis.
Causes
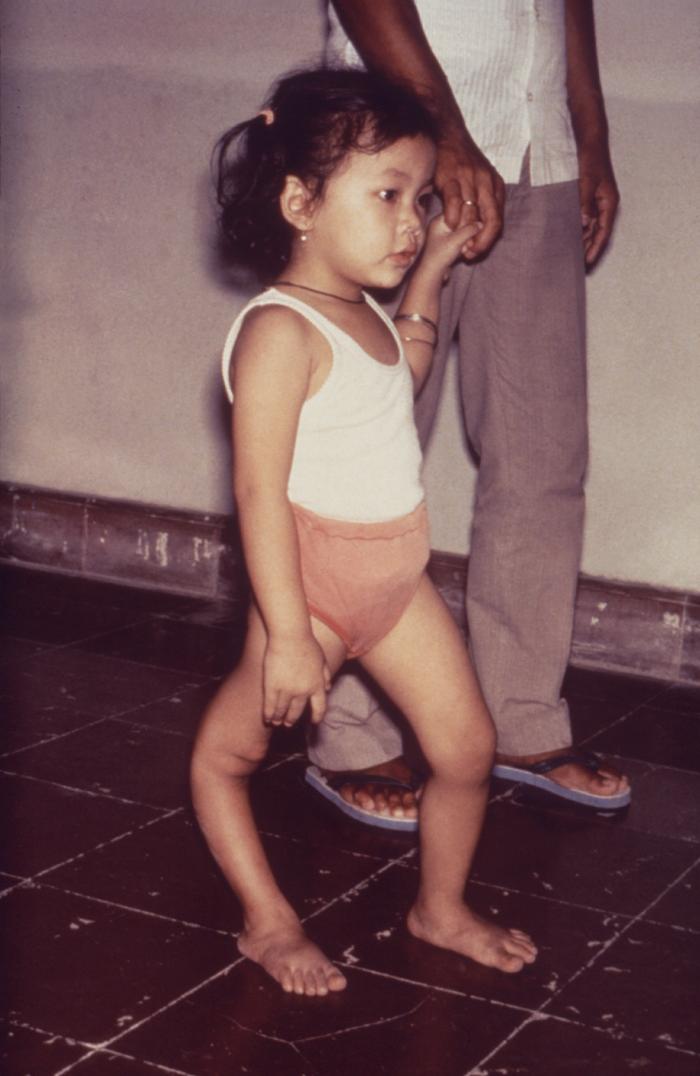 The following factors may be involved in causing this deformity:
* Inherent laxity of the knee ligaments
* Weakness of biceps femoris muscle
* Instability of the knee joint due to ligaments and joint capsule injuries
* Inappropriate alignment of the tibia and femur
* Malunion of the bones around the knee
* Weakness in the hip extensor muscles
* Gastrocnemius muscle weakness (in standing position)
* Upper motor neuron lesion (for example,
The following factors may be involved in causing this deformity:
* Inherent laxity of the knee ligaments
* Weakness of biceps femoris muscle
* Instability of the knee joint due to ligaments and joint capsule injuries
* Inappropriate alignment of the tibia and femur
* Malunion of the bones around the knee
* Weakness in the hip extensor muscles
* Gastrocnemius muscle weakness (in standing position)
* Upper motor neuron lesion (for example, hemiplegia
Hemiparesis, or unilateral paresis, is weakness of one entire side of the body ('' hemi-'' means "half"). Hemiplegia is, in its most severe form, complete paralysis of half of the body. Hemiparesis and hemiplegia can be caused by different medic ...
as the result of a cerebrovascular accident)
* Lower motor neuron lesion (for example, in post-polio syndrome)
* Deficit in joint proprioception
* Lower limb length discrepancy
* Congenital genu recurvatum
* Cerebral palsy
* Muscular dystrophy
Muscular dystrophies (MD) are a genetically and clinically heterogeneous group of rare neuromuscular diseases that cause progressive weakness and breakdown of skeletal muscles over time. The disorders differ as to which muscles are primarily affe ...
* Limited dorsiflexion ( plantar flexion contracture)
* Popliteus muscle weakness
* Connective tissue disorders. In these disorders, there are excessive joint mobility (joint hypermobility) problems. These disorders include:
** Marfan syndrome
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a multi-systemic genetic disorder that affects the connective tissue. Those with the condition tend to be tall and thin, with long arms, legs, fingers, and toes. They also typically have exceptionally flexible joints a ...
** Loeys–Dietz syndrome
Loeys–Dietz syndrome (LDS) is an autosomal dominant genetic connective tissue disorder. It has features similar to Marfan syndrome and Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. The disorder is marked by aneurysms in the aorta, often in children, and the aort ...
** Ehlers–Danlos syndrome
** Benign hypermobile joint syndrome
** Osteogenesis imperfecta disease
Pathophysiology
The most important factors of knee stability include: * Ligaments of the knee: The knee joint is stabilized by four main ligaments: ** Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). The ACL has an important role in stabilization of knee extension movement by preventing the knee from hyperextending. ** Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) ** Medial collateral ligament (MCL) ** Lateral collateral ligament (LCL) * Joint capsule or articular capsule (especially posterior knee capsule) * Quadriceps femoris muscle * Appropriate alignment of the femur and tibia (especially in knee extension position )Incidence
This condition is considered to be rare, with about 1 in 100,000 births being affected by the congenital form of genu recurvatum, although it's a common feature in some disorders, such as in joint hypermobility, which affects 1 in 30 people.Treatment
Treatment generally includes the following: * Sometimes pharmacologic therapy for initial disease treatment *Physical therapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is one of the allied health professions. It is provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through physical examination, diagnosis, management, prognosis, patient ...
: physiotherapy will be beneficial in patient with complaint of pain, discomfort.
* Occupational therapy
Occupational therapy (OT) is a global healthcare profession. It involves the use of assessment and intervention to develop, recover, or maintain the meaningful activities, or ''occupations'', of individuals, groups, or communities. The field of ...
* Use of appropriate assistive devices such as orthoses
* Surgery
See also
* Genu varum * Genu valgum * HypermobilityReferences
External links
The American Academy of Orthotists and Prosthetists
The differential diagnosis of children with joint hypermobility: a review of the literature
The American Academy of Orthotists and Prosthetists
{{Congenital malformations and deformations of musculoskeletal system Musculoskeletal disorders Rheumatology Orthopedic problems Knee injuries and disorders Rare diseases