|
Kleindeutsche Lösung
The "German question" was a debate in the 19th century, especially during the Revolutions of 1848, over the best way to achieve a unification of all or most lands inhabited by Germans. From 1815 to 1866, about 37 independent German-speaking states existed within the German Confederation. The ("Greater German solution") favored unifying all German-speaking peoples under one state, and was promoted by the Austrian Empire and its supporters. The ("Little German solution") sought only to unify the northern German states and did not include any part of Austria (either its German-inhabited areas or its areas dominated by other ethnic groups); this proposal was favored by the Kingdom of Prussia. The solutions are also referred to by the names of the states they proposed to create, and ("Little Germany" and "Greater Germany"). Both movements were part of a growing German nationalism. They also drew upon similar contemporary efforts to create a unified nation state of people who sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
177 Leuchtkugeln Nr 23
Year 177 (Roman numerals, CLXXVII) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Commodus and Plautius (or, less frequently, year 930 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 177 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Commodus, Lucius Aurelius Commodus Caesar (age 15) and Marcus Peducaeus Plautius Quintillus become Roman Consuls. * Commodus is given the title ''Augustus (honorific), Augustus'', and is made co-emperor, with the same status as his father, Marcus Aurelius. * A systematic persecution of Christianity, Christians begins in Rome; the followers take refuge in the catacombs of Rome, catacombs. * The churches in southern Gaul are destroyed after a crowd accuses the local Christians of practicing cannibalism. * For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Estate
An Imperial State or Imperial Estate ( la, Status Imperii; german: Reichsstand, plural: ') was a part of the Holy Roman Empire with representation and the right to vote in the Imperial Diet ('). Rulers of these Estates were able to exercise significant rights and privileges and were " immediate", meaning that the only authority above them was the Holy Roman Emperor. They were thus able to rule their territories with a considerable degree of autonomy. The system of imperial states replaced the more regular division of Germany into stem duchies in the early medieval period. The old Carolingian stem duchies were retained as the major divisions of Germany under the Salian dynasty, but they became increasingly obsolete during the early high medieval period under the Hohenstaufen, and they were finally abolished in 1180 by Frederick Barbarossa in favour of more numerous territorial divisions. From 1489, the imperial Estates represented in the Diet were divided into three chambers, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis II, Holy Roman Emperor
Francis II (german: Franz II.; 12 February 1768 – 2 March 1835) was the last Holy Roman Emperor (from 1792 to 1806) and the founder and Emperor of the Austrian Empire, from 1804 to 1835. He assumed the title of Emperor of Austria in response to the coronation of Napoleon as Emperor of the French. Soon after Napoleon created the Confederation of the Rhine, Francis abdicated as Holy Roman Emperor. He was King of Hungary, Croatia and Bohemia. He also served as the first president of the German Confederation following its establishment in 1815. Francis II continued his leading role as an opponent of Napoleonic France in the Napoleonic Wars, and suffered several more defeats after the Battle of Austerlitz. The marriage of his daughter Marie Louise of Austria to Napoleon on 10 March 1810 was arguably his severest personal defeat. After the abdication of Napoleon following the War of the Sixth Coalition, Austria participated as a leading member of the Holy Alliance at the Congress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Habsburg, french: Maison des Habsbourg and also known as the House of Austriagerman: link=no, Haus Österreich, ; es, link=no, Casa de Austria; nl, Huis van Oostenrijk, pl, dom Austrii, la, Domus Austriæ, french: Maison d'Autriche; hu, Ausztria Háza; it, Casa d'Austria; pt, Casa da Áustria is one of the most prominent and important dynasties in European history. The house takes its name from Habsburg Castle, a fortress built in the 1020s in present-day Switzerland by Radbot of Klettgau, who named his fortress Habsburg. His grandson Otto II was the first to take the fortress name as his own, adding "Count of Habsburg" to his title. In 1273, Count Radbot's seventh-generation descendant Rudolph of Habsburg was elected King of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led successful campaigns during the Revolutionary Wars. He was the ''de facto'' leader of the French Republic as First Consul from 1799 to 1804, then Emperor of the French from 1804 until 1814 and again in 1815. Napoleon's political and cultural legacy endures to this day, as a highly celebrated and controversial leader. He initiated many liberal reforms that have persisted in society, and is considered one of the greatest military commanders in history. His wars and campaigns are studied by militaries all over the world. Between three and six million civilians and soldiers perished in what became known as the Napoleonic Wars. Napoleon was born on the island of Corsica, not long af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considered fundamental principles of liberal democracy, while phrases like ''liberté, égalité, fraternité'' reappeared in other revolts, such as the 1917 Russian Revolution, and inspired campaigns for the abolition of slavery and universal suffrage. The values and institutions it created dominate French politics to this day. Its causes are generally agreed to be a combination of social, political and economic factors, which the ''Ancien Régime'' proved unable to manage. In May 1789, widespread social distress led to the convocation of the Estates General, which was converted into a National Assembly in June. Continuing unrest culminated in the Storming of the Bastille on 14 July, which led to a series of radical measures by the Assembly, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Austrian Succession
The War of the Austrian Succession () was a European conflict that took place between 1740 and 1748. Fought primarily in Central Europe, the Austrian Netherlands, Italy, the Atlantic and Mediterranean, related conflicts included King George's War in North America, the War of Jenkins' Ear, the First Carnatic War and the First Silesian War, First and Second Silesian Wars. Its pretext was the right of Maria Theresa to succeed her father Emperor Charles VI as ruler of the Habsburg monarchy. Kingdom of France, France, Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia and Electorate of Bavaria, Bavaria saw it as an opportunity to challenge Habsburg power, while Maria Theresa was backed by Kingdom of Great Britain, Britain, the Dutch Republic and Electorate of Hanover, Hanover, collectively known as the Pragmatic Sanction of 1713, Pragmatic Allies. As the conflict widened, it drew in other participants, among them History of Spain (1700–1810), Spain, Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia, Electorate of Saxony, S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
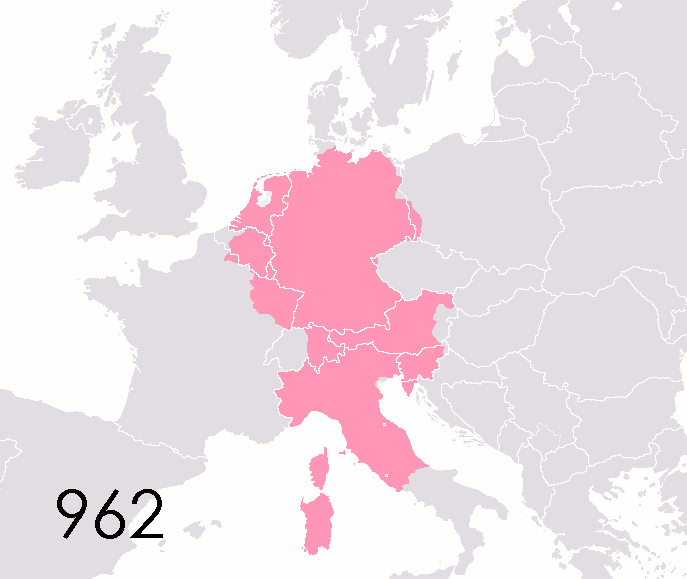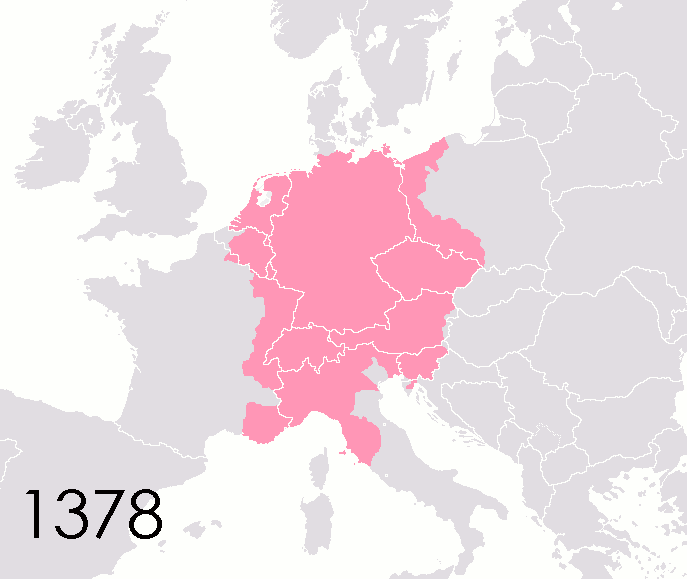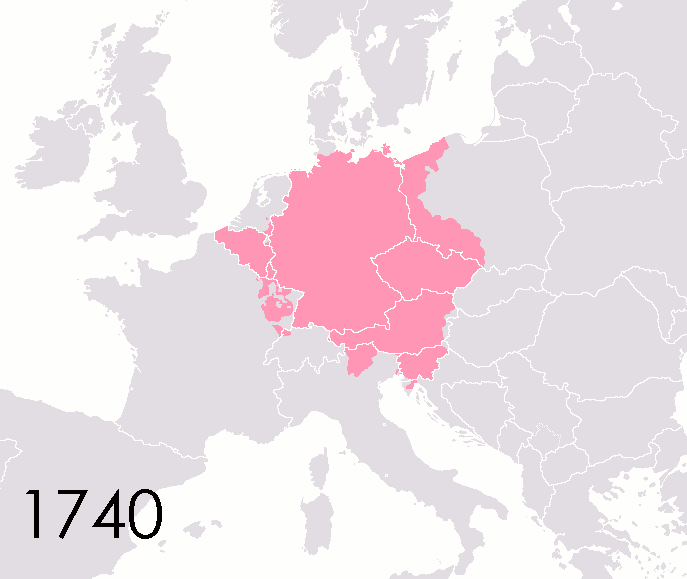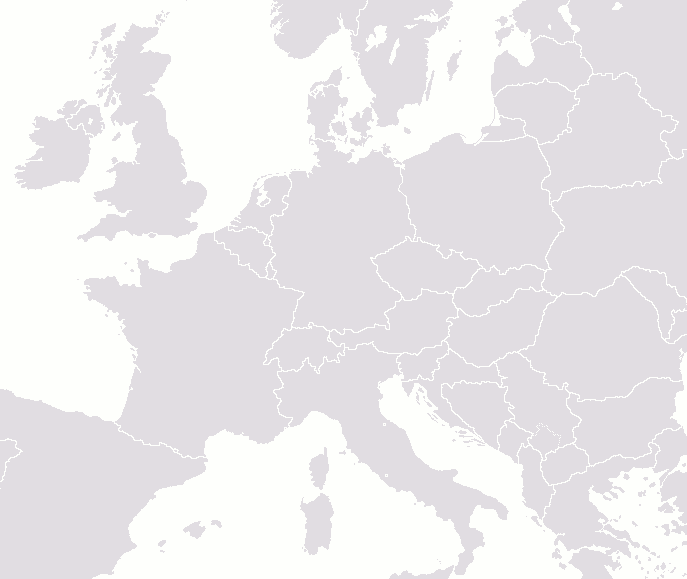
Kleinstaaterei
In the history of Germany, (, ''"small-statewikt:-ery#English, -ery"'') is a German language, German word used, often pejoratively, to denote the territorial fragmentation during the Holy Roman Empire (especially after the end of the Thirty Years' War), and during the German Confederation in the first half of the 19th century. It refers to the large number of nearly sovereign small and medium-sized secular and Hochstift, ecclesiastical principalities and free imperial cities, some of which were little larger than a single town or the surrounding grounds of the monastery of an List of Imperial abbeys, Imperial abbey. Estimates of the total number of List of states in the Holy Roman Empire, German states at any given time during the 18th century vary, ranging from 294 to 348 or more; however, the number of states rapidly decreased with the onset of German mediatisation in the early 19th century. Territorial fragmentation was compounded by the fact that, due to the haphaz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of States In The Holy Roman Empire
This list of states in the Holy Roman Empire includes any territory ruled by an authority that had been granted imperial immediacy, as well as many other feudal entities such as lordships, sous-fiefs and allodial fiefs. The Holy Roman Empire was a complex political entity that existed in central Europe for most of the medieval and early modern periods and was generally ruled by a German-speaking Emperor. The states that composed the Empire, while enjoying a unique form of territorial authority (called '' Landeshoheit'') that granted them many attributes of sovereignty, were never fully sovereign states in the sense that term is understood today. In the 18th century, the Holy Roman Empire consisted of approximately 1,800 such territories, the majority being tiny estates owned by the families of Imperial Knights. This page does not directly contain the list but discusses the format of the various lists and offers some background to understand the complex organisation of the Holy R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absolute Monarchy
Absolute monarchy (or Absolutism as a doctrine) is a form of monarchy in which the monarch rules in their own right or power. In an absolute monarchy, the king or queen is by no means limited and has absolute power, though a limited constitution may exist in some countries. These are often hereditary monarchies. On the other hand, in constitutional monarchies, in which the authority of the head of state is also bound or restricted by the constitution, a legislature, or unwritten customs, the king or queen is not the only one to decide, and their entourage also exercises power, mainly the prime minister. Absolute monarchy in Europe declined substantially following the French Revolution and World War I, both of which led to the popularization of theories of government based on the notion of popular sovereignty. Absolute monarchies include Brunei, Eswatini, Oman, Saudi Arabia, Vatican City, and the individual emirates composing the United Arab Emirates, which itself is a fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brandenburg-Prussia
Brandenburg-Prussia (german: Brandenburg-Preußen; ) is the historiographic denomination for the early modern realm of the Brandenburgian Hohenzollerns between 1618 and 1701. Based in the Electorate of Brandenburg, the main branch of the Hohenzollern intermarried with the branch ruling the Duchy of Prussia, and secured succession upon the latter's extinction in the male line in 1618. Another consequence of the intermarriage was the incorporation of the lower Rhenish principalities of Cleves, Mark and Ravensberg after the Treaty of Xanten in 1614. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) was especially devastating. The Elector changed sides three times, and as a result Protestant and Catholic armies swept the land back and forth, killing, burning, seizing men and taking the food supplies. Upwards of half the population was killed or dislocated. Berlin and the other major cities were in ruins, and recovery took decades. By the Peace of Westphalia, which ended the Thirty Years' War i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)