|
Keratoacanthoma
Keratoacanthoma (KA) is a common low-grade (unlikely to metastasize or invade) rapidly-growing skin tumour that is believed to originate from the hair follicle (pilosebaceous unit) and can resemble squamous cell carcinoma. The defining characteristic of a keratoacanthoma is that it is dome-shaped, symmetrical, surrounded by a smooth wall of inflamed skin, and capped with keratin scales and debris. It grows rapidly, reaching a large size within days or weeks, and if untreated for months will almost always starve itself of nourishment, necrose (die), slough, and heal with scarring. Keratoacanthoma is commonly found on sun-exposed skin, often face, forearms and hands. It is rarely found at a mucocutaneous junction or on mucous membranes. Keratoacanthoma may be difficult to distinguish visually from a skin cancer. Under the microscope, keratoacanthoma very closely resembles squamous cell carcinoma. In order to differentiate between the two, almost the entire structure needs to be re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohs Surgery
Mohs surgery, developed in 1938 by a general surgeon, Frederic E. Mohs, is microscopically controlled surgery used to treat both common and rare types of skin cancer. During the surgery, after each removal of tissue and while the patient waits, the tissue is examined for cancer cells. That examination dictates the decision for additional tissue removal. Mohs surgery is the gold standard method for obtaining complete margin control during removal of a skin cancer (complete circumferential peripheral and deep margin assessment - CCPDMA) using frozen section histology. CCPDMA or Mohs surgery allows for the removal of a skin cancer with very narrow surgical margin and a high cure rate. The cure rate with Mohs surgery cited by most studies is between 97% and 99.8% for primary basal-cell carcinoma, the most common type of skin cancer. Mohs procedure is also used for squamous cell carcinoma, but with a lower cure rate. Recurrent basal-cell cancer has a lower cure rate with Mohs surgery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous-cell carcinomas (SCCs), also known as epidermoid carcinomas, comprise a number of different types of cancer that begin in squamous cells. These cells form on the surface of the skin, on the lining of hollow organs in the body, and on the lining of the respiratory and digestive tracts. Common types include: * Squamous-cell skin cancer: A type of skin cancer * Squamous-cell carcinoma of the lung: A type of lung cancer * Squamous-cell thyroid carcinoma: A type of thyroid cancer * Esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma: A type of esophageal cancer * Squamous-cell carcinoma of the vagina: A type of vaginal cancer Despite sharing the name "squamous-cell carcinoma", the SCCs of different body sites can show differences in their presented symptoms, natural history, prognosis, and response to treatment. By body location Human papillomavirus infection has been associated with SCCs of the oropharynx, lung, fingers, and anogenital region. Head and neck cancer About 90% of cases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatology
Dermatology is the branch of medicine dealing with the skin.''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary.'' Random House, Inc. 2001. Page 537. . It is a speciality with both medical and surgical aspects. A dermatologist is a specialist medical doctor who manages diseases related to skin, hair, nails, and some cosmetic problems. Etymology Attested in English in 1819, the word "dermatology" derives from the Greek δέρματος (''dermatos''), genitive of δέρμα (''derma''), "skin" (itself from δέρω ''dero'', "to flay") and -λογία '' -logia''. Neo-Latin ''dermatologia'' was coined in 1630, an anatomical term with various French and German uses attested from the 1730s. History In 1708, the first great school of dermatology became a reality at the famous Hôpital Saint-Louis in Paris, and the first textbooks (Willan's, 1798–1808) and atlases ( Alibert's, 1806–1816) appeared in print around the same time.Freedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorouracil
Fluorouracil (5-FU), sold under the brand name Adrucil among others, is a cytotoxic chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. By intravenous injection it is used for treatment of colorectal cancer, oesophageal cancer, stomach cancer, pancreatic cancer, breast cancer, and cervical cancer. As a cream it is used for actinic keratosis, basal cell carcinoma, and skin warts. Side effects of use by injection are common. They may include inflammation of the mouth, loss of appetite, low blood cell counts, hair loss, and inflammation of the skin. When used as a cream, irritation at the site of application usually occurs. Use of either form in pregnancy may harm the baby. Fluorouracil is in the antimetabolite and pyrimidine analog families of medications. How it works is not entirely clear, but it is believed to involve blocking the action of thymidylate synthase and thus stopping the production of DNA. Fluorouracil was patented in 1956 and came into medical use in 1962. It is on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curettage
Curettage ( or ), in medical procedures, is the use of a curette (French, meaning scoopMosby's Medical, Nursing & Allied Health Dictionary, Fourth Edition, Mosby-Year Book 1994, p. 422) to remove tissue by scraping or scooping. Curettages are also a declining method of abortion. It has been replaced by vacuum aspiration over the last decade. Curettage has been used to treat teeth affected by periodontitis. Curettage is also a major method used for removing osteoid osteoma and osteoblastoma. Curettage with subsequent culture is more accurate than ulcer base swan culture or aspiration and culture for diabetic foot ulcers. Curettage is also used when excising a chalazion of the eyelid. See also * Dilation and curettage Dilation (or dilatation) and curettage (D&C) refers to the dilation (widening/opening) of the cervix and surgical removal of part of the lining of the uterus and/or contents of the uterus by scraping and scooping (curettage). It is a gynecolog ... Refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrodesiccation
Cauterization (or cauterisation, or cautery) is a medical practice or technique of burning a part of a body to remove or close off a part of it. It destroys some tissue in an attempt to mitigate bleeding and damage, remove an undesired growth, or minimize other potential medical harm, such as infections when antibiotics are unavailable. The practice was once widespread for treatment of wounds. Its utility before the advent of antibiotics was said to be effective at more than one level: *To prevent exsanguination *To close amputations Cautery was historically believed to prevent infection, but current research shows that cautery actually increases the risk for infection by causing more tissue damage and providing a more hospitable environment for bacterial growth. Actual cautery refers to the metal device, generally heated to a dull red glow, that a physician applies to produce blisters, to stop bleeding of a blood vessel, and for other similar purposes., page 16. The main forms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin Keratoacanthoma Whole Slide
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation. Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different developmental origin, structure and chemical composition. The adjective cutaneous means "of the skin" (from Latin ''cutis'' 'skin'). In mammals, the skin is an organ of the integumentary system made up of multiple layers of ectodermal tissue and guards the underlying muscles, bones, ligaments, and internal organs. Skin of a different nature exists in amphibians, reptiles, and birds. Skin (including cutaneous and subcutaneous tissues) plays crucial roles in formation, structure, and function of extraskeletal apparatus such as horns of bovids (e.g., cattle) and rhinos, cervids' antlers, giraffids' ossicones, armadillos' osteoderm, and os penis/os clitoris. All mammals have some hair on their skin, even marine mammals like whales, dolphins, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dabrafenib
Dabrafenib, sold under the brand name Tafinlar & Rafinlar ( both by Novartis) among others, is a medication for the treatment of cancers associated with a mutated version of the gene BRAF. Dabrafenib acts as an inhibitor of the associated enzyme B-Raf, which plays a role in the regulation of cell growth. Dabrafenib has clinical activity with a manageable safety profile in clinical trials of phase 1 and 2 in patients with BRAF (V600)-mutated metastatic melanoma. Approvals and indications The US Food and Drug Administration initially approved dabrafenib as a single agent treatment for patients with BRAF V600E mutation-positive advanced melanoma on May 29, 2013. Dabrafenib was approved for use in the European Union in August 2013. Clinical trial data demonstrated that resistance to dabrafenib and other BRAF inhibitors occurs within six to seven months. To overcome this resistance, the BRAF inhibitor dabrafenib was combined with the MEK inhibitor trametinib. On January 8, 2014, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vemurafenib
Vemurafenib (INN, marketed as Zelboraf) is an inhibitor of the B-Raf enzyme developed by Plexxikon (now part of Daiichi-Sankyo) and Genentech for the treatment of late-stage melanoma.; The name "vemurafenib" comes from V600E mutated BRAF inhibition. Approvals Vemurafenib received FDA approval for the treatment of late-stage melanoma on August 17, 2011, making it the first drug designed using fragment-based lead discovery to gain regulatory approval. Vemurafenib later received Health Canada approval on February 15, 2012. On February 20, 2012, the European Commission approved vemurafenib as a monotherapy for the treatment of adult patients with BRAF V600E mutation positive unresectable or metastatic melanoma, the most aggressive form of skin cancer. On November 6, 2017, the FDA approved Vemurafenib for the treatment of some patients with Erdheim–Chester disease (ECD), a rare type of histiocytic neoplasm. Mechanism of action Vemurafenib causes programmed cell death in m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BRAF (gene)
BRAF is a human gene that encodes a protein called B-Raf. The gene is also referred to as proto-oncogene B-Raf and v-Raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B, while the protein is more formally known as serine/threonine-protein kinase B-Raf. The B-Raf protein is involved in sending signals inside cells which are involved in directing cell growth. In 2002, it was shown to be mutated in some human cancers. Certain other inherited ''BRAF'' mutations cause birth defects. Drugs that treat cancers driven by ''BRAF'' mutations have been developed. Two of these drugs, vemurafenib Vemurafenib (INN, marketed as Zelboraf) is an inhibitor of the B-Raf enzyme developed by Plexxikon (now part of Daiichi-Sankyo) and Genentech for the treatment of late-stage melanoma.; The name "vemurafenib" comes from V600E mutated BRAF in ... and dabrafenib are approved by FDA for treatment of late-stage melanoma. Vemurafenib was the first approved drug to come out of fragment-based drug discovery. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
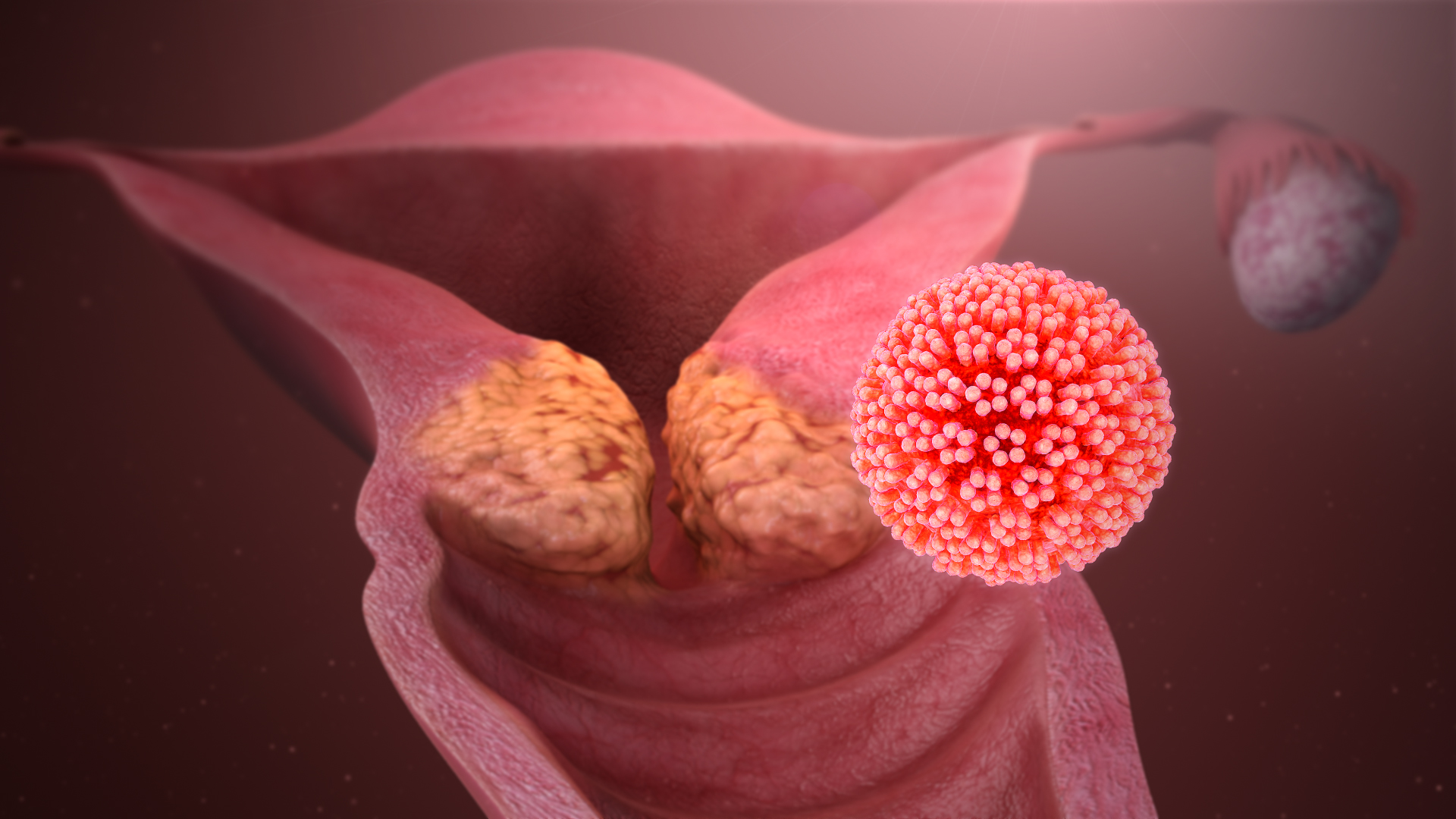
Human Papilloma Virus
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the ''Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and results in either warts or precancerous lesions. These lesions, depending on the site affected, increase the risk of cancer of the cervix, vulva, vagina, penis, anus, mouth, tonsils, or throat. Nearly all cervical cancer is due to HPV and two strains – HPV16 and HPV18 – account for 70% of cases. HPV16 is responsible for almost 90% of HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers. Between 60% and 90% of the other cancers listed above are also linked to HPV. HPV6 and HPV11 are common causes of genital warts and laryngeal papillomatosis. An HPV infection is caused by ''human papillomavirus'', a DNA virus from the papillomavirus family. Over 170 types have been described. An individual can become infected with more than one type of HPV, and the dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Predisposition
A genetic predisposition is a genetic characteristic which influences the possible phenotypic development of an individual organism within a species or population under the influence of environmental conditions. In medicine, genetic susceptibility to a disease refers to a genetic predisposition to a health problem, which may eventually be triggered by particular environmental or lifestyle factors, such as tobacco smoking or diet. Genetic testing is able to identify individuals who are genetically predisposed to certain diseases. Behavior Predisposition is the capacity humans are born with to learn things such as language and concept of self. Negative environmental influences may block the predisposition (ability) one has to do some things. Behaviors displayed by animals can be influenced by genetic predispositions. Genetic predisposition towards certain human behaviors is scientifically investigated by attempts to identify patterns of human behavior that seem to be invariant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |